The document discusses the marketing environment and its influence on marketing management. It can be divided into two parts:
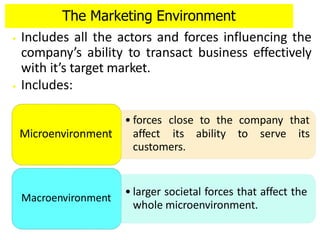
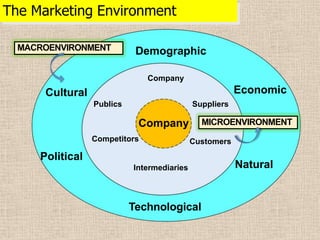
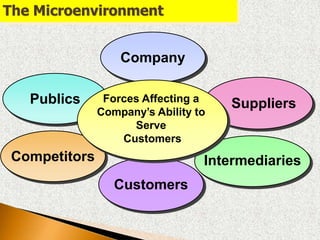
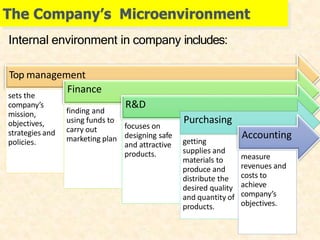
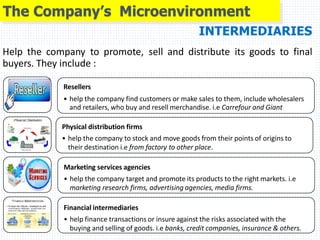
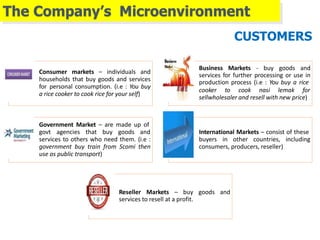
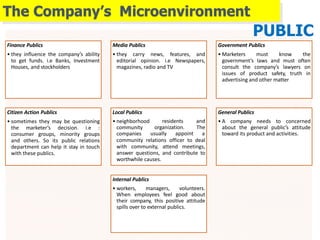
1) The microenvironment includes forces close to the company like customers, competitors, suppliers, marketing intermediaries, and the company itself. It directly affects the company's ability to serve customers.
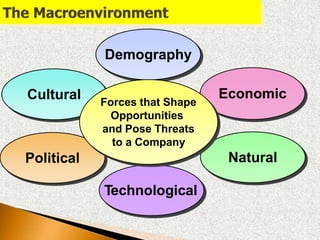
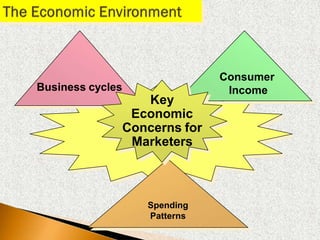
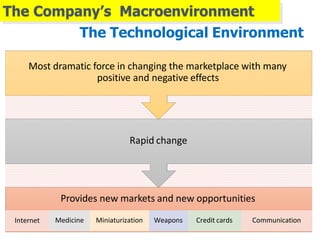
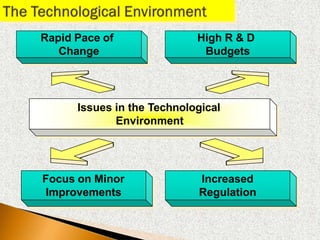
2) The macroenvironment includes larger societal forces like demographic, economic, natural, technological, political, and cultural factors. It creates opportunities and threats for companies. Successful companies constantly monitor and adapt to changes in the dynamic marketing environment.