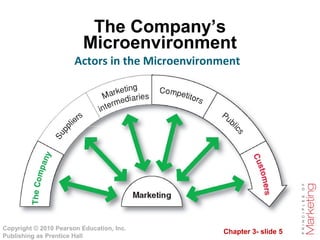
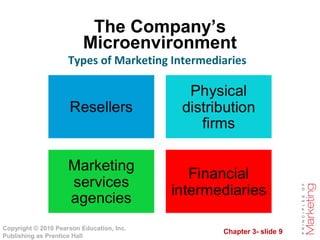
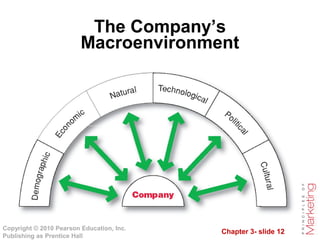
The document outlines the key components of a company's marketing environment, including the microenvironment and macroenvironment. The microenvironment includes factors close to the company like its departments, suppliers, marketing intermediaries, customers, and publics. The macroenvironment comprises broader forces like demographic, economic, natural, technological, political, and cultural factors in the environment. The document discusses how companies must analyze and respond to changes in both the micro and macroenvironments that impact marketing activities.