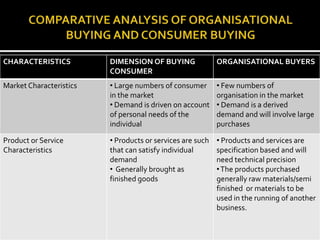
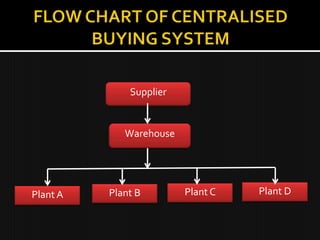
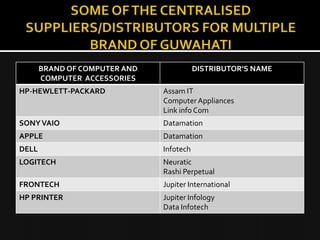
The presentation explores organisational buying behaviour, defining it as the decision-making process by which companies determine their purchasing needs and select suppliers. It highlights the characteristics and differences between organisational and consumer buying, the centralised buying system, and various internal and external factors influencing purchasing decisions. Understanding these elements is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies in various organisational contexts.