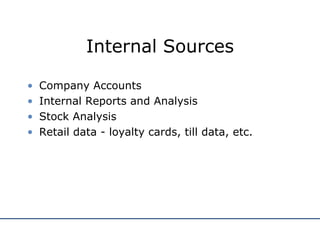
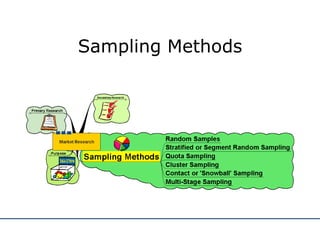
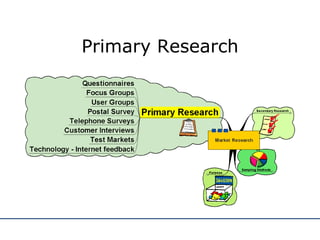
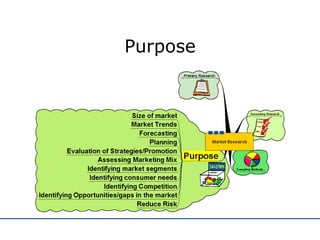
The document discusses various methods for conducting market research, including secondary research using internal company data and external sources, as well as primary research collecting first-hand information. It describes different sampling methods like random sampling, stratified sampling, quota sampling, and cluster sampling. It also distinguishes between quantitative and qualitative research approaches. The purpose of market research is outlined as helping businesses focus on objectives, aid planning, reduce risks, and communicate their image. Both advantages and disadvantages of market research are provided.