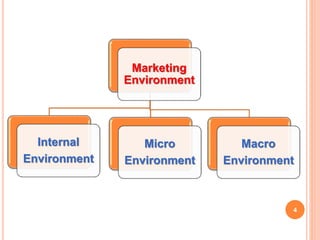
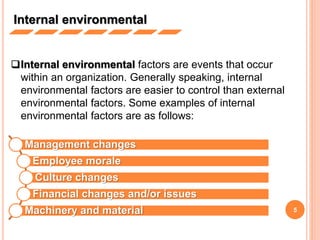
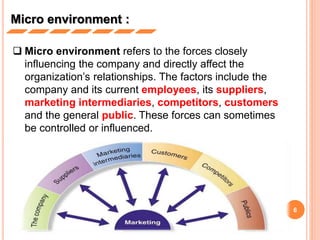
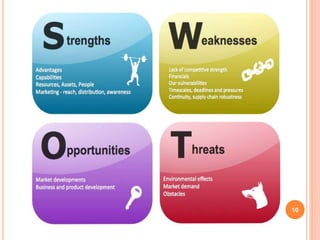
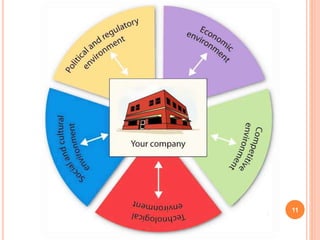
The document discusses analyzing a company's marketing environment. It identifies the internal, micro, and macro environmental factors that affect an organization's relationships with customers. The internal environment includes management changes, employee morale, and financial issues. The micro environment refers to suppliers, competitors, and customers. The macro environment comprises political, economic, technological, and socio-cultural influences. A PEST analysis assesses these uncontrollable macro factors to determine threats and opportunities for the organization.