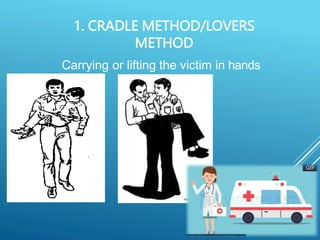
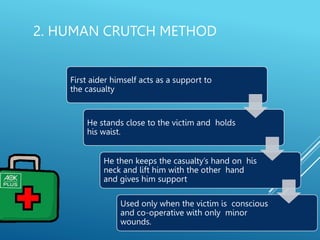
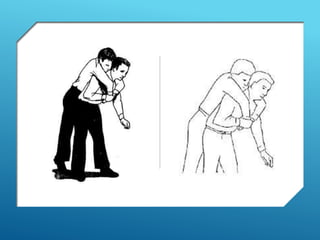
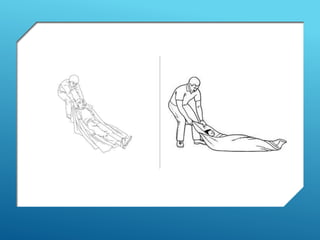
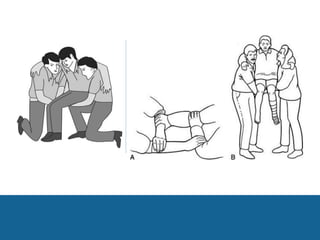
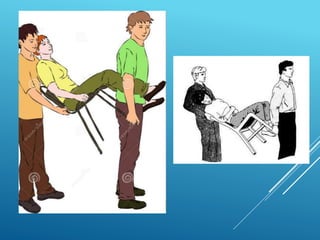
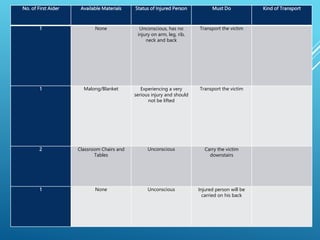
This document provides guidance on safely transporting an injured person. It outlines key factors to consider like the victim's weight, injuries, and environment. When only one first aider is available for minor injuries, methods like the cradle carry, human crutch, or piggyback can be used. For major injuries or with two people, techniques like the four-handed seat, chair carry, or blanket drag are recommended. Proper body mechanics and reassuring the victim are important principles to follow. The document also includes an application section describing a practice activity to demonstrate different carrying techniques in groups.