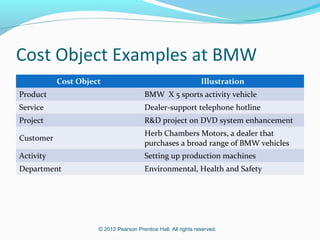
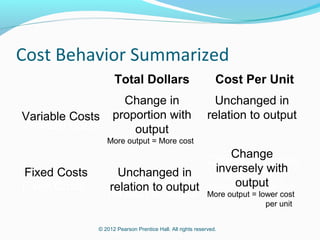
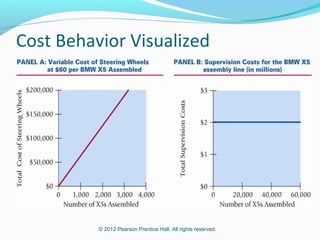
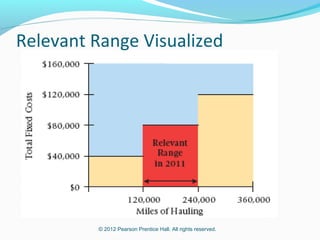
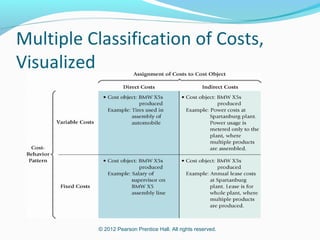
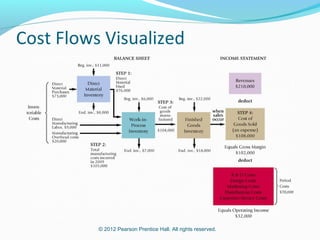
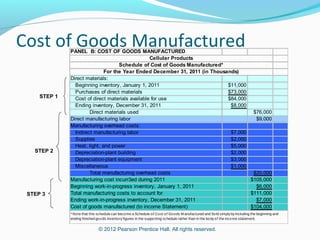
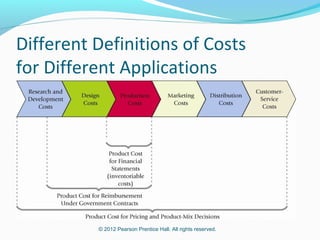
This document provides an introduction to basic cost accounting terminology and concepts. It defines key terms like direct and indirect costs, fixed and variable costs, cost objects and behaviors. It also discusses how costs flow through a manufacturing company, including inventory accounts. Finally, it notes that costs are defined differently depending on the context, like financial reporting versus government contracting.