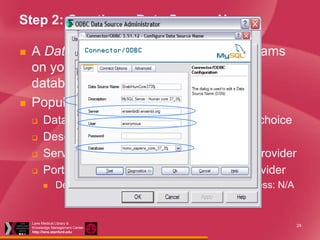
This document provides a summary of a training session on managing experiment data using Excel and related tools. The training covered essential Excel functions like conditional formatting, named ranges, pivot tables, and querying web data or databases. It demonstrated how to use MS Query to directly query databases and retrieve results in Excel. Resources for further learning about Excel, Access, SQL, and related topics were also provided. The goal was to teach practical skills for better organizing and analyzing experimental data using common office tools.