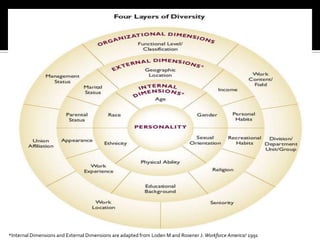
The document discusses the concept of diversity, emphasizing its various dimensions including race, ethnicity, and other personal characteristics. It outlines the importance of managing diversity in the workplace to enhance communication, creativity, and problem-solving, while also highlighting the consequences of ignoring diversity. Each individual has a role in promoting an organizational culture that respects and values diversity, which entails self-awareness and challenging existing biases.