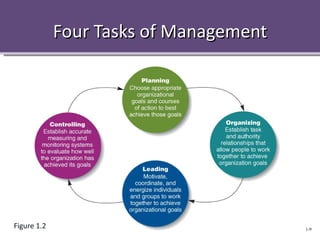
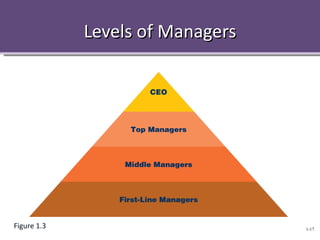
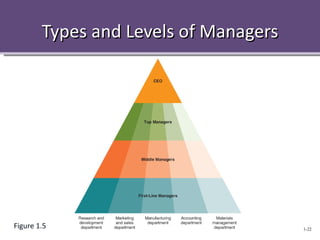
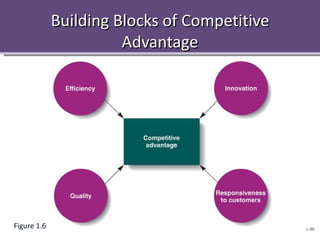
The document provides an overview of management concepts including the definition of management as planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources to achieve goals. It discusses the four main tasks of management as planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. It also describes different management levels, skills, and how management practices are changing with trends like outsourcing, empowerment, and globalization. Building competitive advantage and crisis management in a global environment are highlighted as key challenges for modern management.