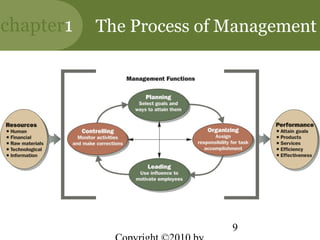
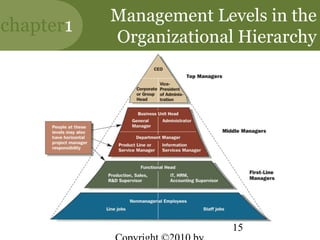
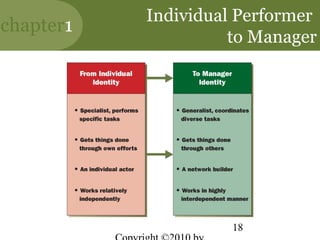
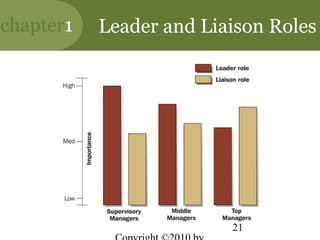
This chapter discusses the key concepts of management. It defines management as attaining organizational goals through planning, organizing, leading and controlling resources. The four management functions are described. Organizational effectiveness and efficiency are important for performance. Managers require conceptual, human and technical skills. Management occurs at different levels and functions within an organization. The roles and challenges of management are outlined. The chapter also discusses the new competencies needed for managing in today's turbulent environment.