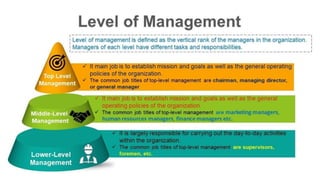
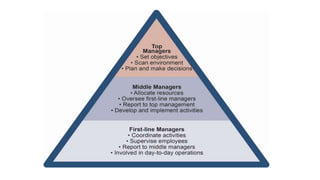
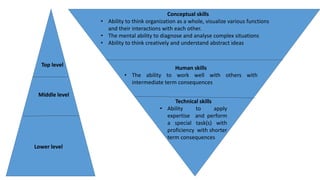
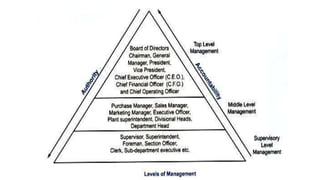
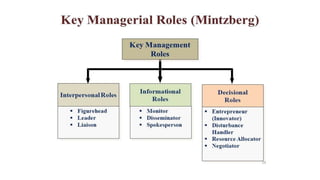
Management is a process aimed at achieving organizational goals through planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources, primarily involving human interaction. It encompasses various functions and roles across different management levels, such as monitoring, disseminating information, and making decisions to address challenges. Effective management requires conceptual, human, and technical skills, ensuring productive relationships and resource utilization within an organization.