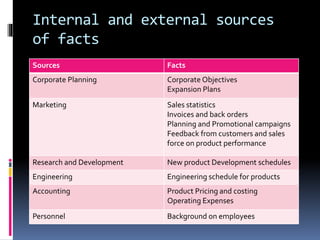
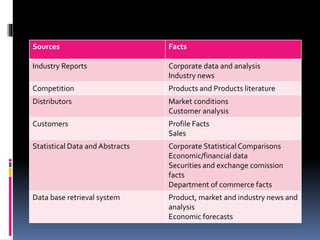
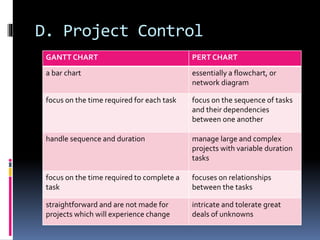
The document outlines the stages of a management consulting engagement: 1) negotiating the engagement between the consultant and client, 2) planning the engagement, 3) conducting the assignment through problem identification, data analysis, solution development, and reporting, 4) evaluating the engagement and providing post-engagement follow-up. Key aspects of each stage are discussed at a high level, including proposal letters, work plans, data collection techniques, and project management.