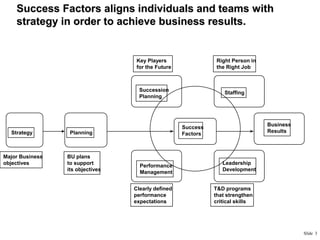
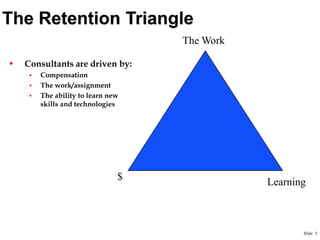
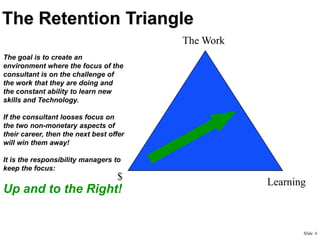
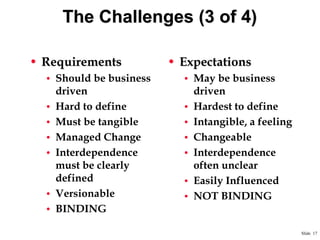
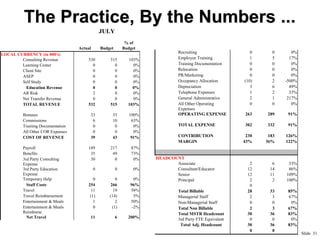
This document provides an overview of building a successful consulting practice, including key success factors, strategies for consultant retention, project management best practices, and metrics for measuring financial performance. Some of the main points covered include focusing on customer satisfaction, communication skills, innovation, leadership development, managing projects effectively through planning, control, and communication, and monitoring key metrics like revenue, expenses, headcount, and contribution margin. The overall aim is to execute projects successfully and profitably while developing consultants and satisfying customers.