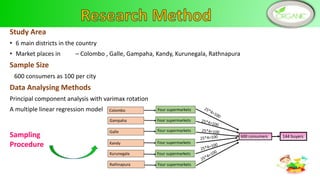
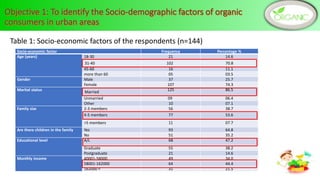
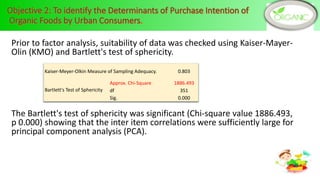
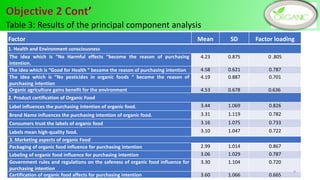
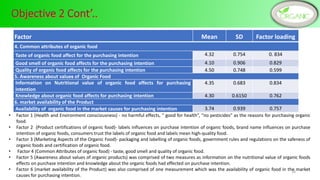
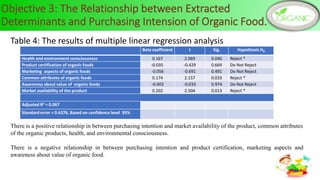
Health and environmental consciousness, common attributes of organic foods, and market availability are key determinants of Sri Lankan consumers' purchase intention of organic foods. A survey of 144 organic food consumers in 6 Sri Lankan cities found that over half were female aged 31-45. While consumers were aware of organic foods' values, lack of availability was a constraint. Improving awareness, accessibility, and certification could help stimulate demand. Policymakers should promote health benefits and support farmers to increase organic production and market conditions.