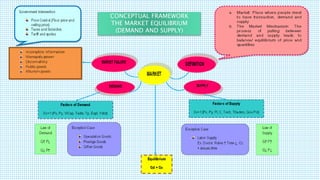
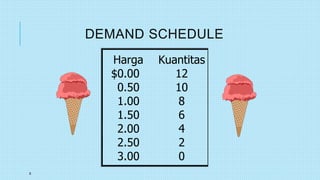
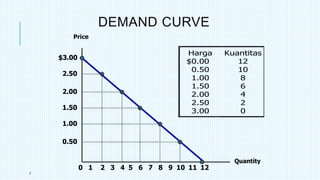
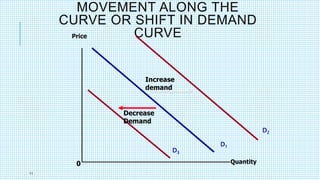
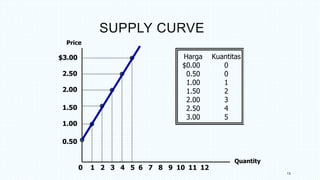
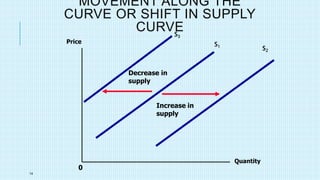
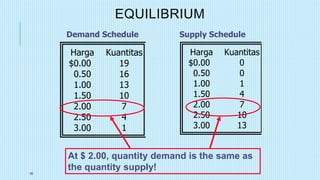
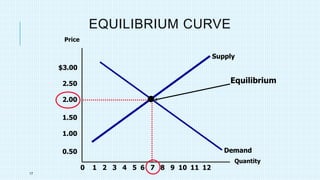
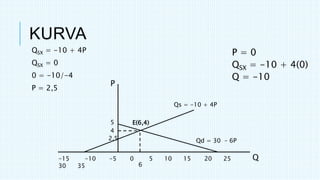
This document discusses market equilibrium between demand and supply. It defines key concepts like market, demand, supply, demand curves, supply curves, and equilibrium. The equilibrium price and quantity occur where the demand and supply curves intersect, and where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. An example equilibrium calculation is shown using algebraic demand and supply functions. The concepts are illustrated with graphs of the demand curve, supply curve, and equilibrium point.