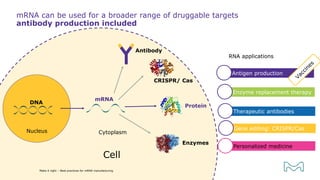
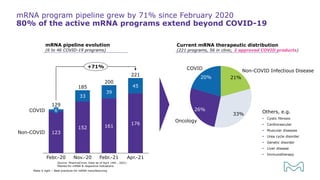
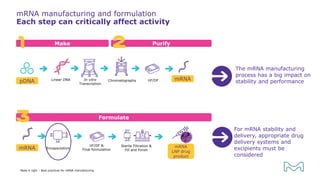
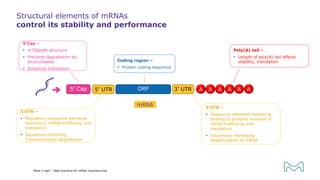
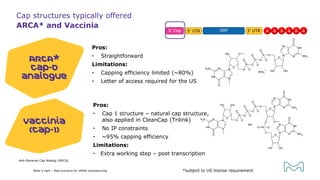
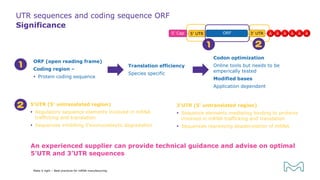
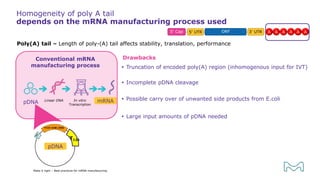
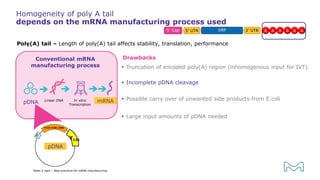
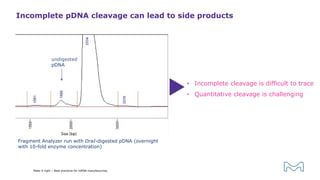
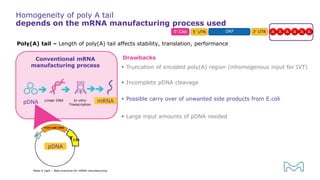
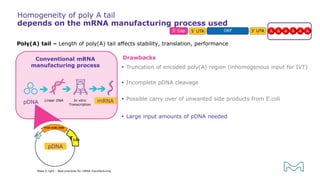
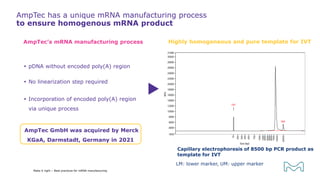
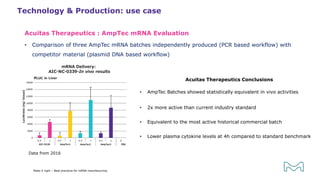
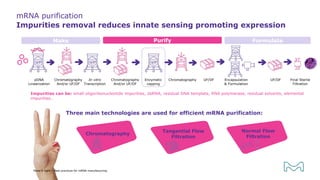
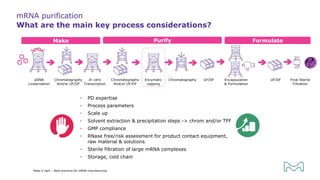
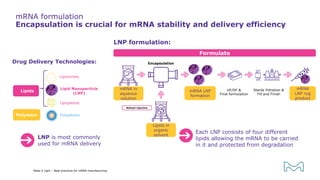
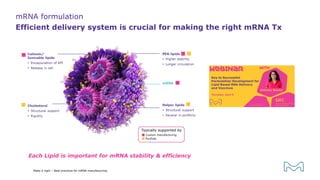
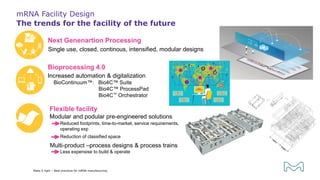
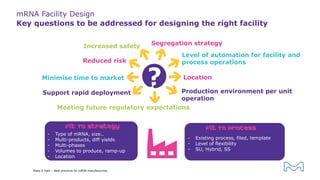
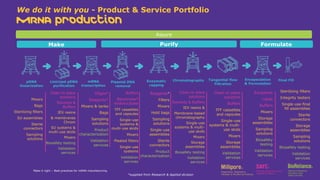
The document outlines best practices for mRNA manufacturing by Merck KGaA, emphasizing the critical factors that influence mRNA performance, including identity, purity, and formulation. It highlights the significant growth in the mRNA program pipeline, driven largely by applications beyond COVID-19, and emphasizes the importance of advanced technologies and flexible manufacturing processes. Key considerations for successful mRNA production include selecting the right partners and facilities to ensure efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards.