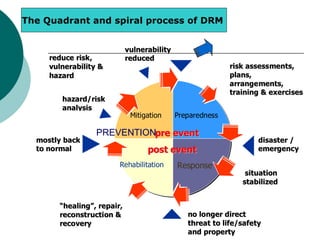
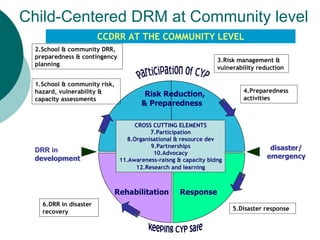
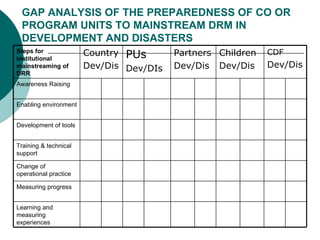
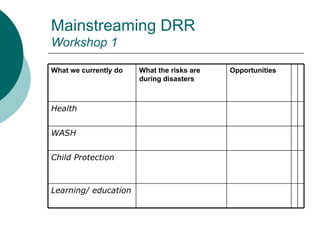
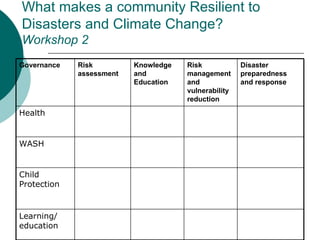
The document discusses mainstreaming disaster risk management (DRM) into development work. It outlines steps to mainstream DRM institutionally, such as raising awareness and developing tools and methodologies. It also discusses the Hyogo Framework for Action's five priority areas: governance, risk assessment, knowledge and education, risk management, and preparedness and response. Finally, it presents workshops and an action plan for mainstreaming DRM at the community, program unit, and country office levels.