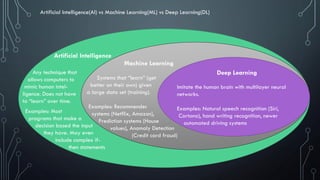
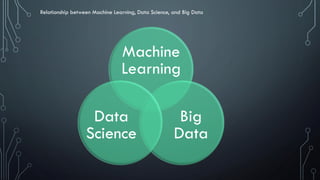
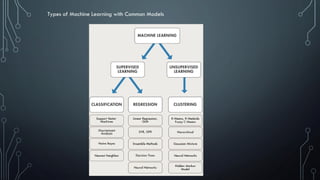
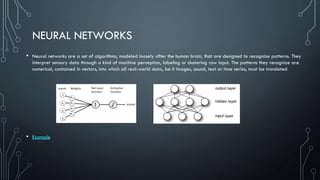
This document provides an introduction to machine learning. It begins by defining machine learning according to several experts as computational steps that can produce the best answer when applied iteratively to large data sets without being explicitly programmed. It distinguishes machine learning, deep learning, artificial intelligence, and discusses their relationships with data science and big data. The document outlines different types of machine learning including supervised, unsupervised, regression, and classification. It also discusses implementing machine learning solutions, neural networks, and provides suggestions for further research.