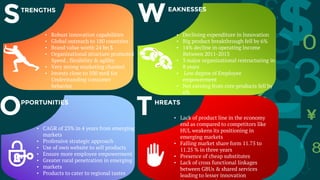
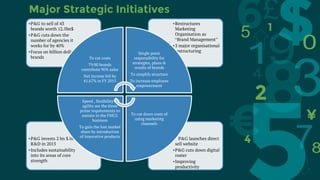
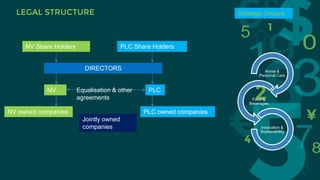
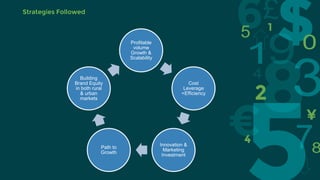
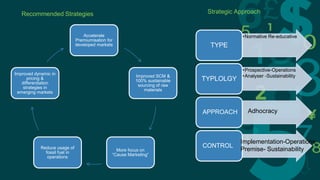
Procter & Gamble and Unilever are two large consumer goods companies that have undergone organizational structure changes over time. P&G originally had a geographic structure but now focuses on industry-based sectors grouped into global business units. Unilever was jointly owned but now focuses on fewer, stronger brands through acquisitions. Both companies face opportunities in emerging markets but also threats from low-cost competitors. Recommendations include decentralizing responsibilities, motivating employees, adapting to new technologies, pursuing economies of scale for R&D, and focusing on emerging markets.