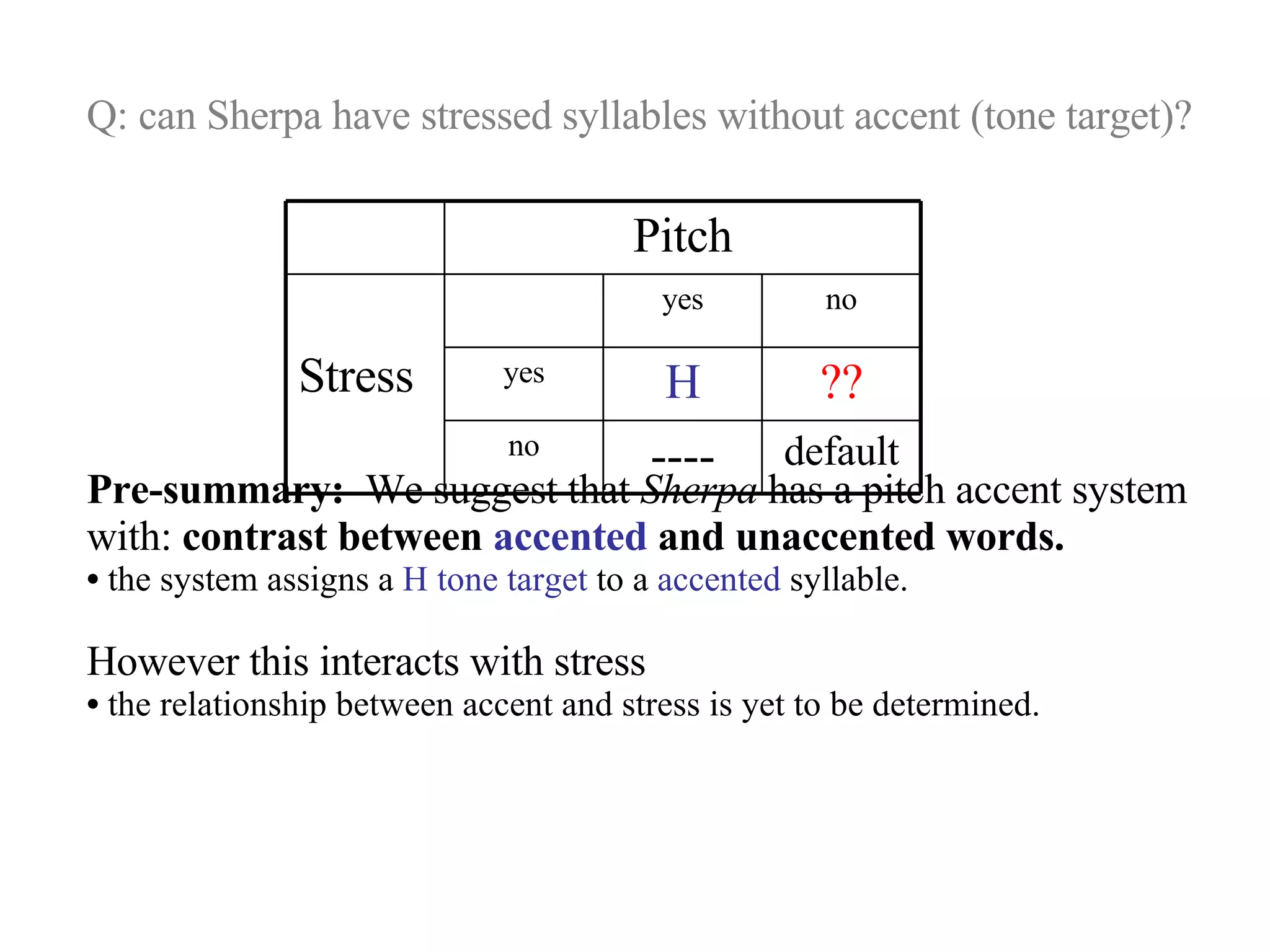
This study examines tonal patterns in Sherpa spoken in Nepal. Previous research claimed Sherpa has two contrastive falling tones, one starting higher than the other. The study finds instrumental evidence supporting this, finding a bimodal pitch distribution in citation forms with a clear contrast between words with a high vs. low starting fall. However, the falls were not present utterance-medially. The study suggests Sherpa has a pitch accent system where stressed syllables can receive a high tone, interacting with intonation patterns. However, more research is needed to clarify the relationship between stress, accent and tone.






![Contrast between H and L toned marked words in citation forms. The forms exhibit the falling contour reported by Kelly (2003): H starts higher than the L toned words. It’s a word level phenomena. Both mono- and bi- syllabic tokens showed the same pitch contours: falling over the course of the word H tone associated to the 1 st syllable L drop at end timing differences between mono- and bi- syllablic tokens indicate a syllable affiliation of tone Note the pitch contour for the 1 st syllable of a L toned word [ lola ] ‘wall’ [ß´rwa] ‘sherpa’ vs ‘blind’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lsa2sherpa06-1225480748333039-9/75/Lsa2-Sherpa-06-7-2048.jpg)
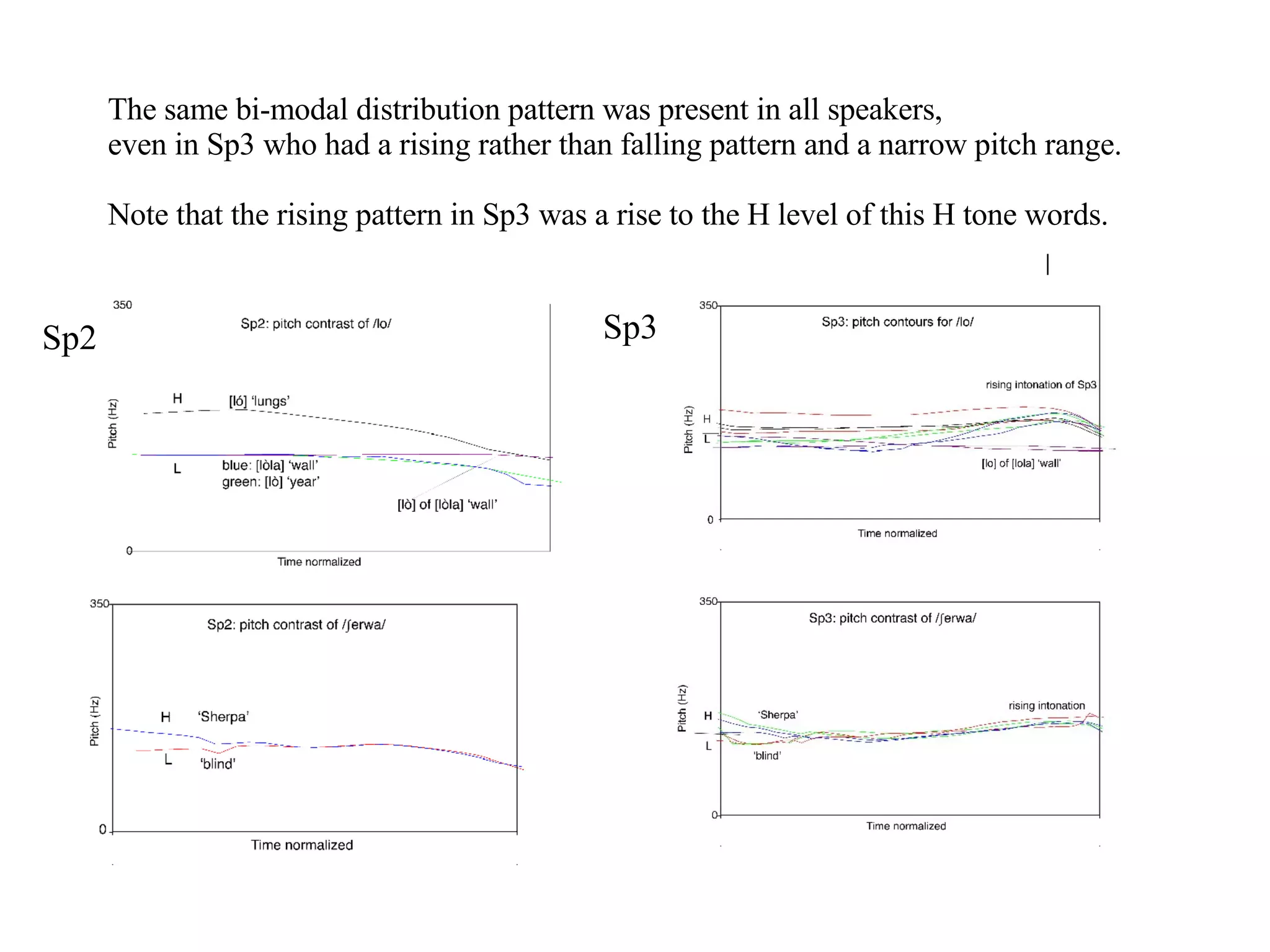
![Sp 4 produced words in citation forms and in short utterances. She had the same bi-model distribution patterns on the accented syllable with a falling contour in citation forms. However, the falling pitch contour was not always present. Sp4 produced H tone forms within sentences. In these forms there was no fall. Sp4 also produced rises, like Sp3. Sp4: pitch contours of [ ß ´rwå]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lsa2sherpa06-1225480748333039-9/75/Lsa2-Sherpa-06-9-2048.jpg)
![The force of the pattern is apparent in these graphs of tokens showing the contrast between a H and L tone marked [ s ´r ]. As before, Sp4 tokens are taken from both isolation and citation forms, the two patterns are present. Sp3 has three tokens, two H tone, one L (blue), in citation forms. Sp4 Sp3 [s ´r] : H vs L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lsa2sherpa06-1225480748333039-9/75/Lsa2-Sherpa-06-10-2048.jpg)
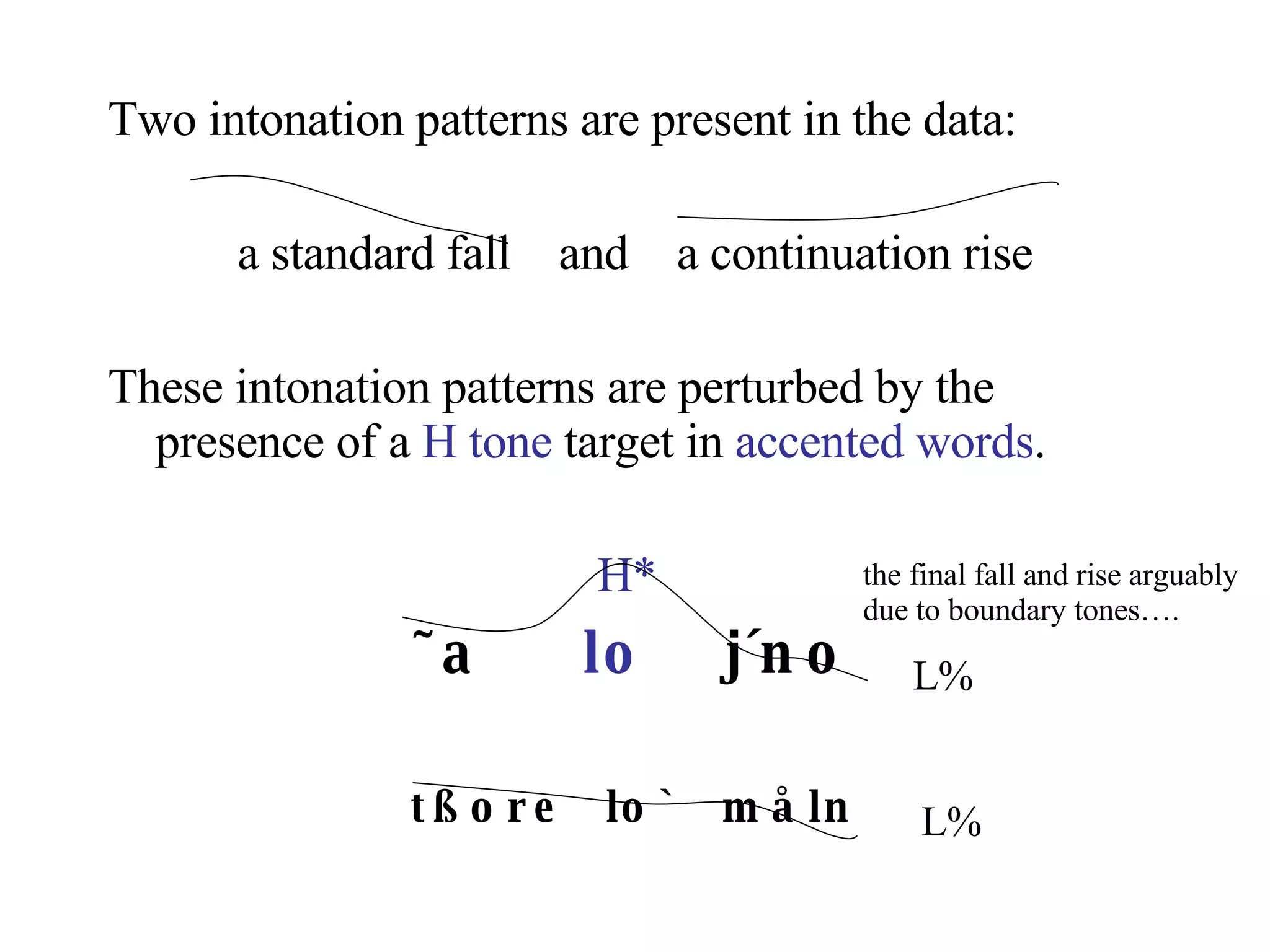
![L Black: / dˆ lo `la / “This is a wall” Red: / tßore lo ` måln / “How old are you?” H Blue: / ˜a lo’ jeno / “I have a cough” Sp4: [lo] contrast in utterances H We see a rise to the H tone /lo/ then a drop vs a falling contour of utterances with the L tone /lo/ . This suggests a pitch accent type system. Words are marked for accent or not. Those with an accent have a H pitch target . * [ lo ] vs [ lo ] H/L contrast in utterances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lsa2sherpa06-1225480748333039-9/75/Lsa2-Sherpa-06-11-2048.jpg)

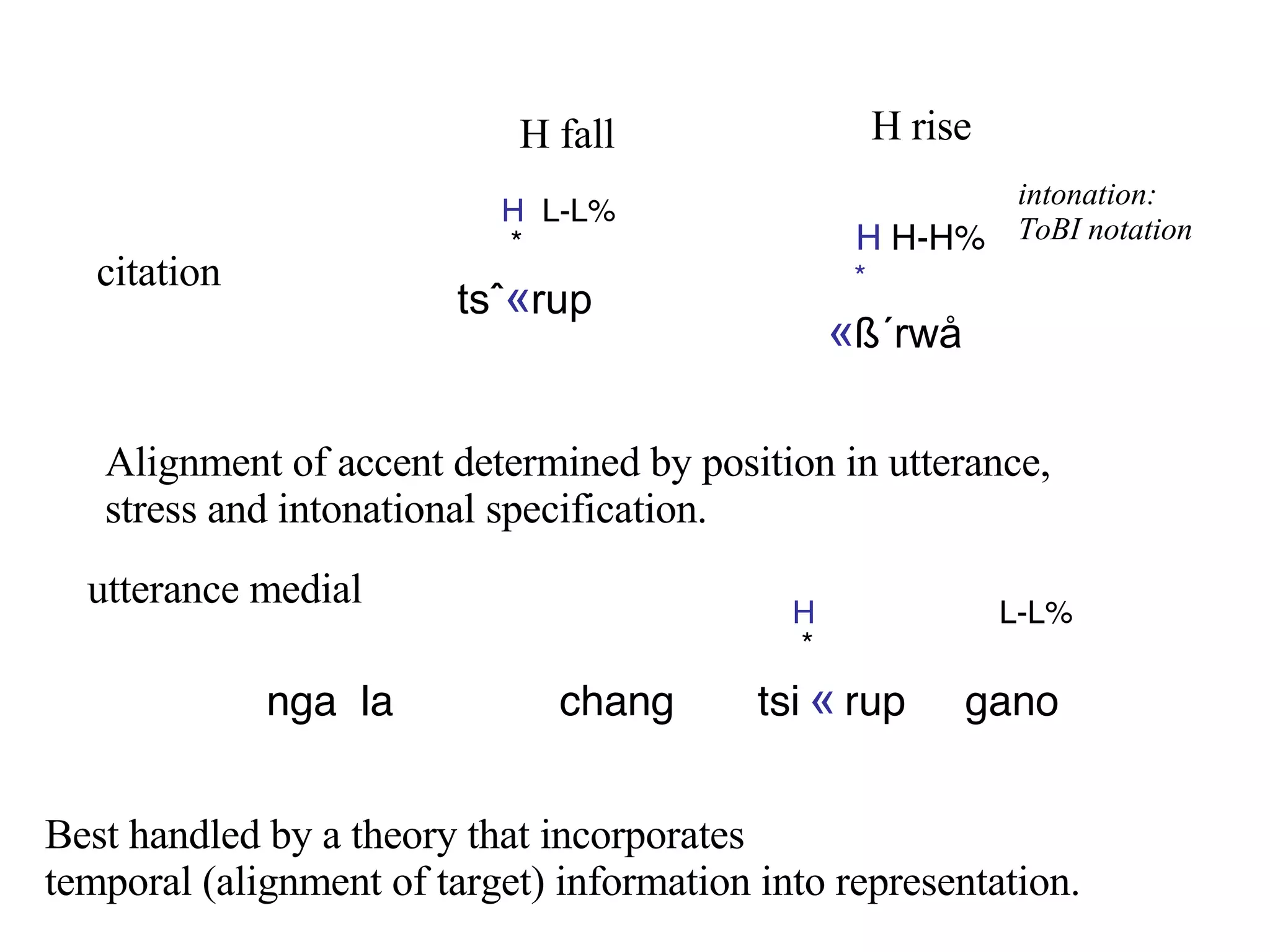
![These ex’s show the first confound: between accent and stress in bisyllables: In all 3 forms: audible stress on the second syllable of accented /tsi « rup/. * [ t߈`«rup ] ‘squeeze’ Note contrast between citation and IP medial contours The stress distinction is also lexical. Gordon et. al. identify a ‘high rising contour’ , contrasting with a ‘ low rising contour’ . as well as high & low falling contours . The tokens differ in the alignment/realization of the H tone target: cit vs medial . ‘ High rising contour’ [ t߈ « rup ] * 3x Sp4 citation (L%) medial nga la chang tsirup gano L% L%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lsa2sherpa06-1225480748333039-9/75/Lsa2-Sherpa-06-15-2048.jpg)