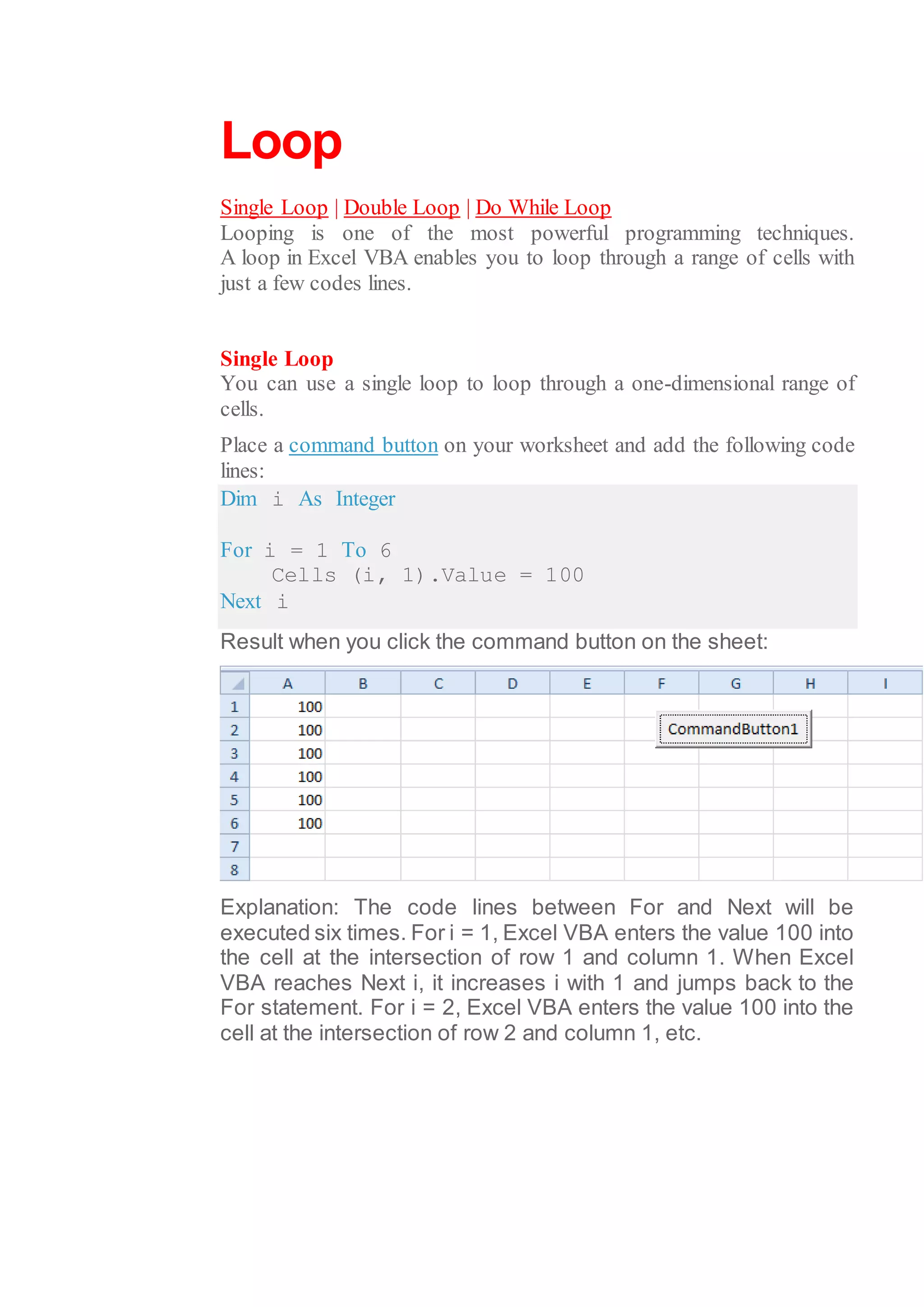
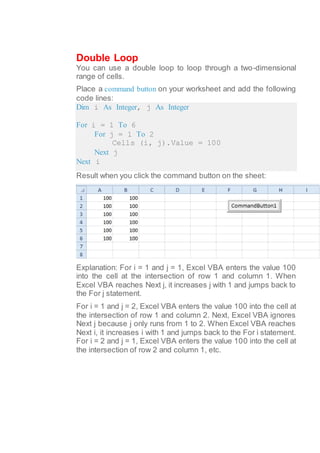
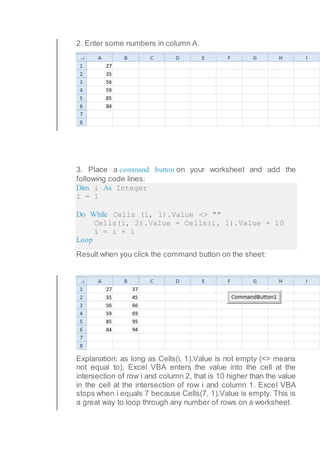
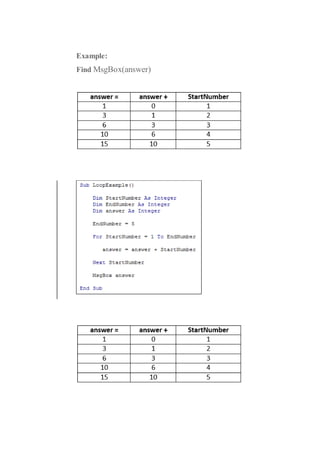
This document discusses different types of loops in Excel VBA including single loops, double loops, do while loops, do until loops. It provides examples of code for each type of loop and explanations of how the code works. Single and double loops are used to loop through one-dimensional and two-dimensional ranges of cells. Do while and do until loops repeat code as long as or until a condition is met. Examples demonstrate using loops to populate cells with values, perform calculations on cell values, and display results in message boxes.