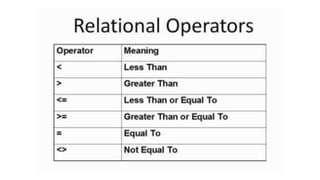
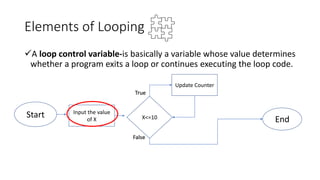
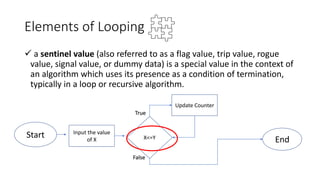
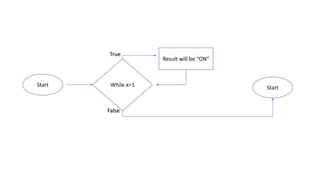
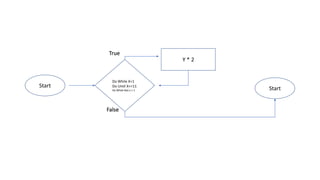
The document explains loops in programming, detailing the structure and purpose of various types of loops in Visual Basic, such as while, do, and for loops. It also covers important looping concepts like loop control variables, sentinel values, and updating loops. The document provides examples for clarity on how each loop operates within programming constructs.