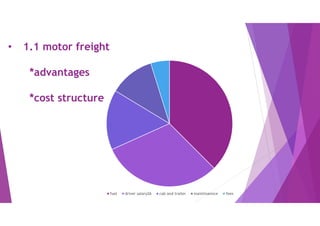
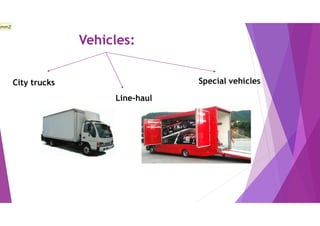
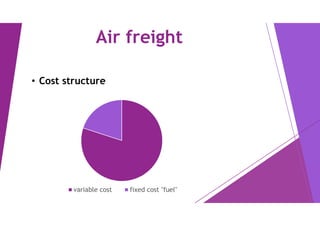
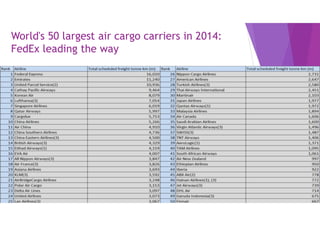
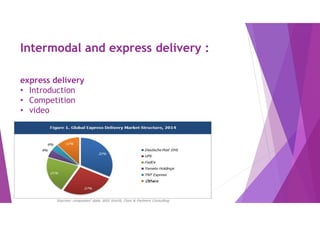
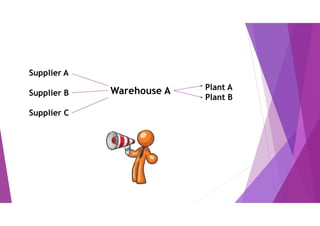
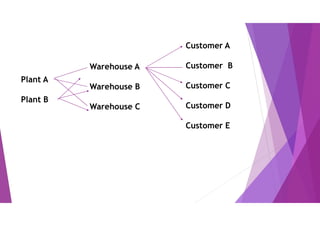
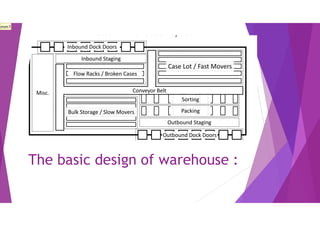
This document provides an overview of key concepts in logistics and supply chain management. It discusses the relationship between logistics and transportation, including motor freight, air freight, and intermodal delivery. For motor freight, it describes vehicle types, terminals, and motor carriers. For air freight, it outlines cost structures, equipment types, and industry statistics. It then explains how intermodal delivery utilizes multiple transportation modes. The document also examines warehouse management, describing basic functions like movement and storage, factors for an effective warehouse, and basic warehouse design.