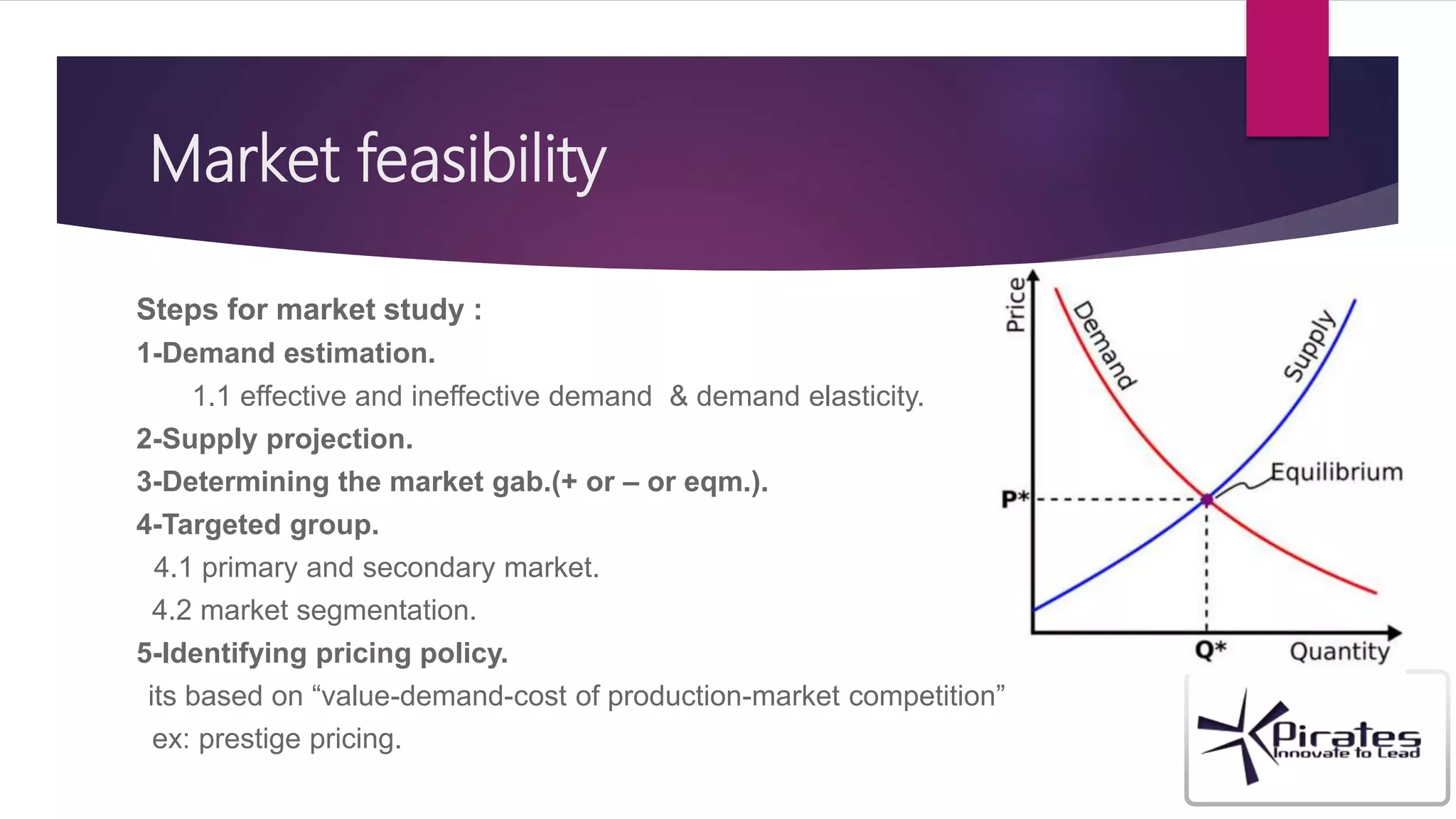
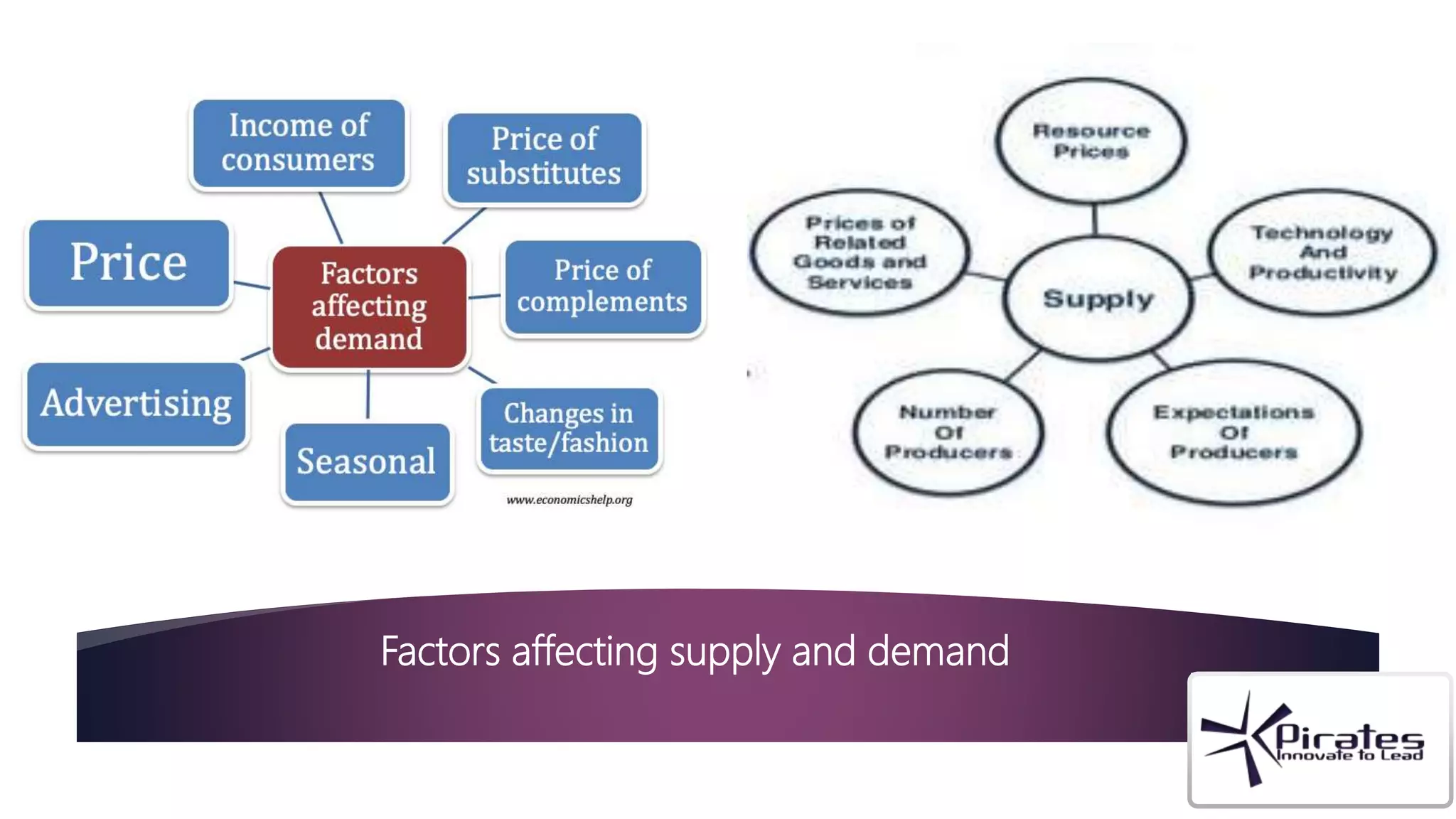
The document discusses the key components of a feasibility study, including technical, financial, market, and legal/environmental feasibility. A feasibility study evaluates whether a proposed project is possible in terms of technical requirements, costs, potential market demand, and legal/regulatory factors. It determines if a project is worth pursuing based on these considerations, while a business plan outlines how a project would be implemented if deemed feasible. The document provides details on assessing feasibility from each of these perspectives.