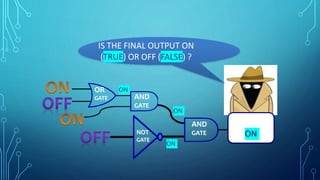
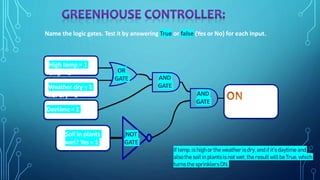
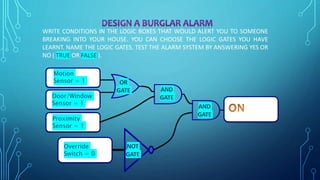
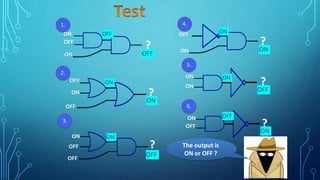
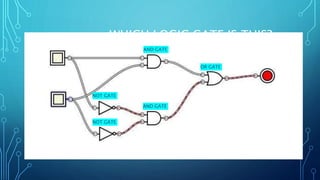
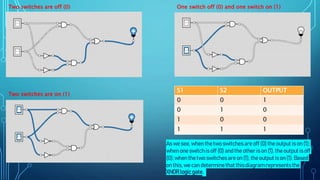
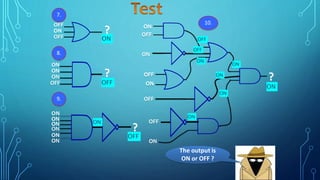
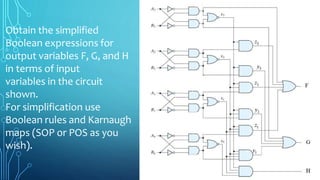
The document discusses the application of logic gates in real-life scenarios, such as controlling sprinklers and alarm systems based on various conditions. It explores the use of AND, OR, NOT, and XNOR logic gates, demonstrating how they can be tested using truth values. Additionally, it includes boolean expression simplifications and Karnaugh map methodologies for circuit analysis.