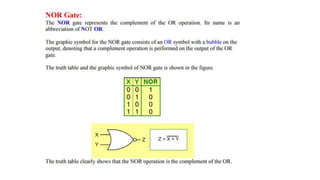
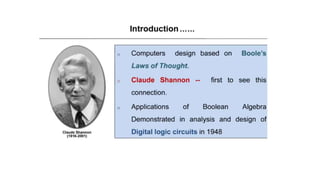
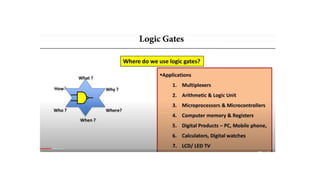
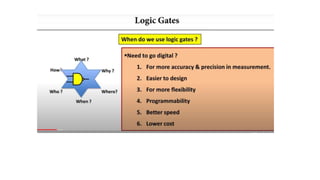
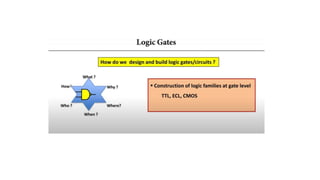
The document provides information about Unit 2 of a course which includes:
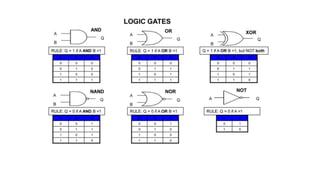
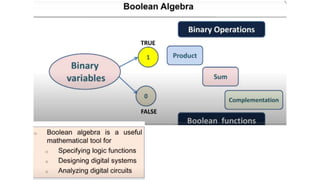
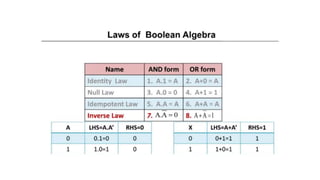
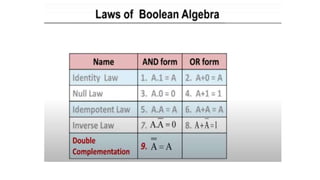
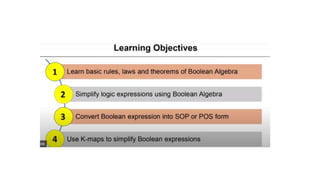
- Boolean algebra rules and laws such as commutative, associative, distributive for AND, OR and inversion. De Morgan's theorem.
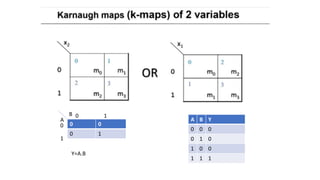
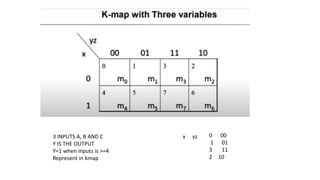
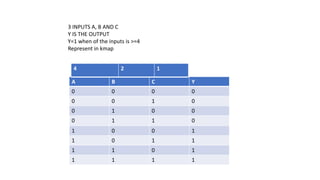
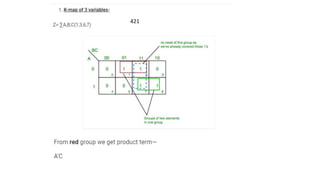
- Simplifying logic equations using Boolean algebra rules and Karnaugh maps up to 4 bits.
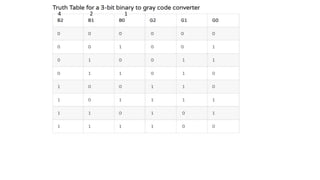
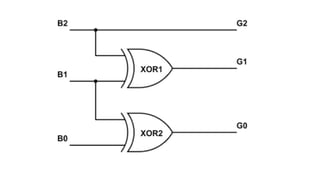
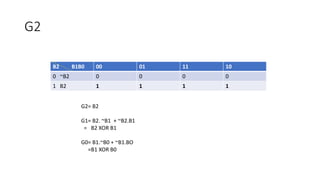
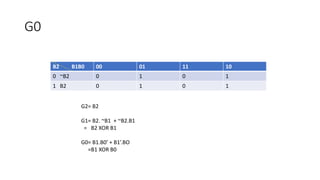
- Converting between binary and gray codes.
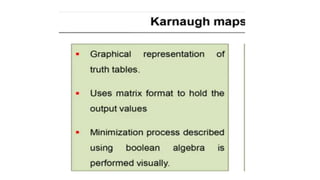
- Minimizing logic expressions using Karnaugh maps.







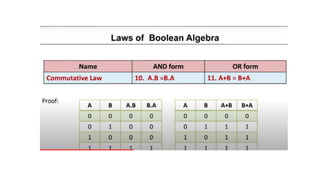

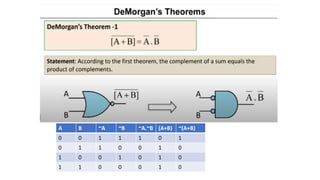
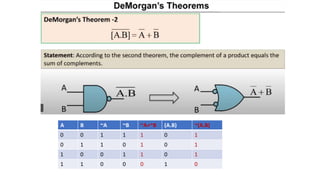
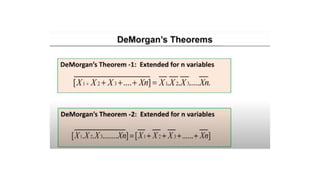

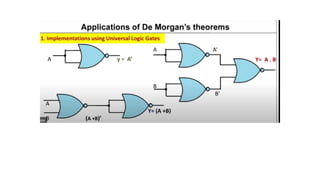


















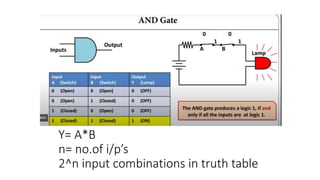
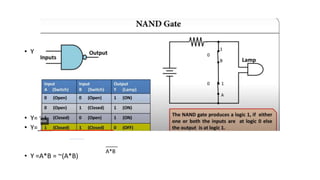

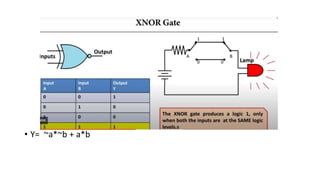
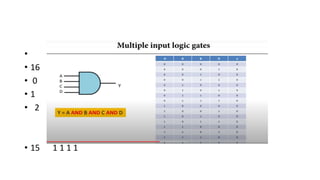
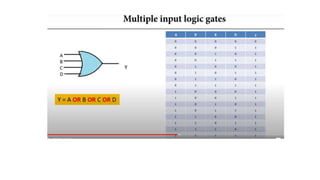
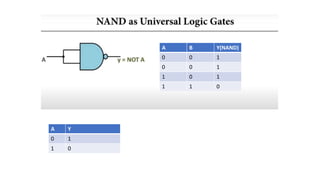
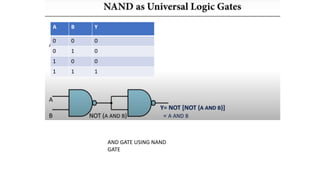
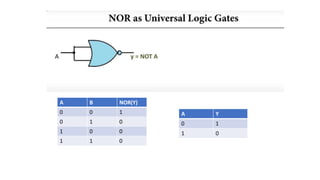
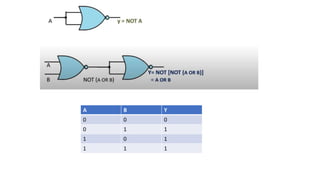
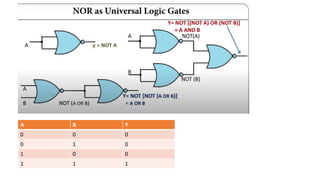
![• Y= NOT[(NOT A).(NOT B)]
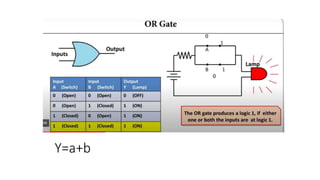
• Y=A+B
OR GATE
A B Y
0 0 .0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
OR GATE USING NAND GATE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hz5t12k9sneawkbn18id-unit-2-boolean-algebra-and-karnaugh-maps-240208132606-3b959371/85/Unit_2_Boolean_algebra_and_Karnaugh_maps-pptx-73-320.jpg)