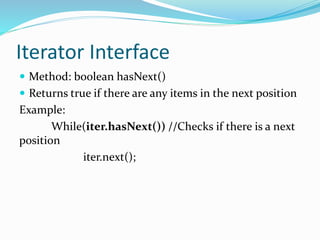
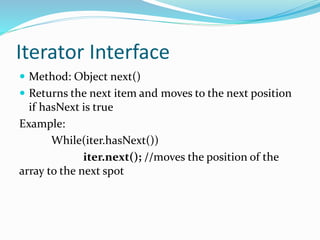
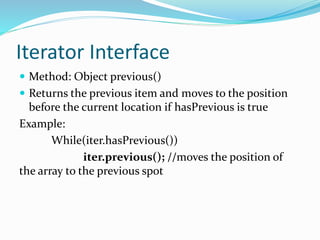
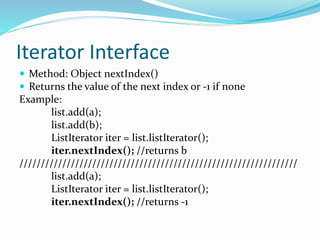
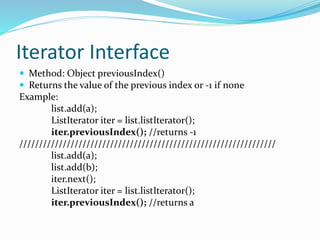
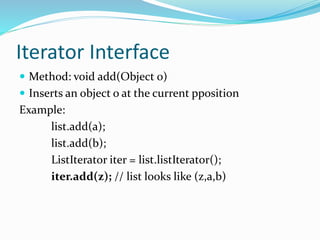
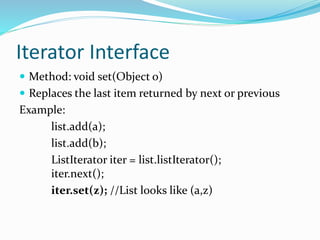
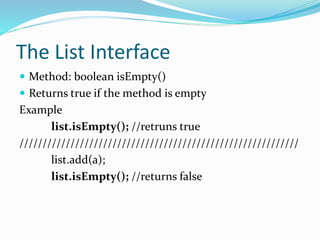
The document describes the methods available in the List and Iterator interfaces in Java. It provides examples of how to use each method, including adding, removing, and accessing elements in a list; iterating through a list using an iterator; and getting information about the iterator's current position. Some key methods covered are add, remove, contains, get, size, iterator, and next for the List interface and hasNext, next, remove for the Iterator interface.





















![The List Interface
Method: Object[] toArray()
Returns an array containg all of the elements in the
list
Example:
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
int[] array = list.toArray(); //Creates an array
conating all of lists elements: 1, 2, and 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javacollections-150113100129-conversion-gate01/85/Java-collections-24-320.jpg)
![The List Interface
Method: Object[] toArray(Object a)
Returns an array containg all of the elements in the
list, witht the runtime/ size of the array according to
the object
Example:
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
int[] array = list.toArray(list); //Creats an array
conating all of lists elements: 1, 2, and 3 with size of list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javacollections-150113100129-conversion-gate01/85/Java-collections-25-320.jpg)