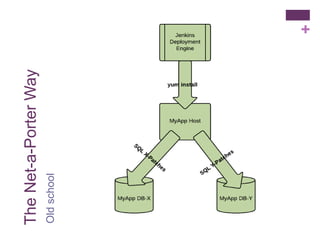
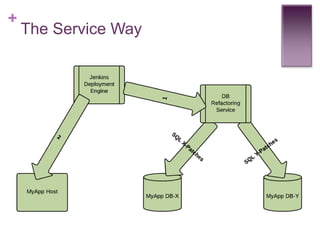
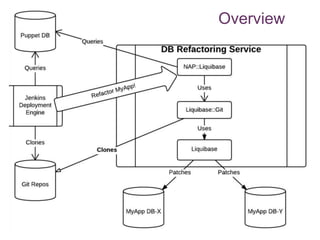
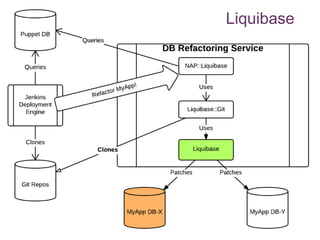
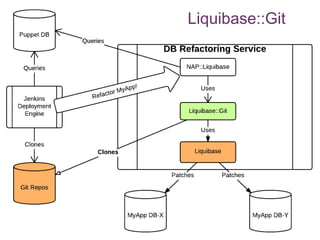
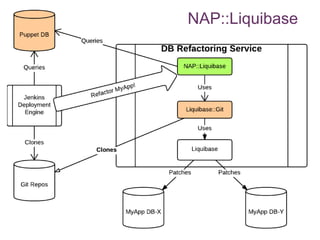
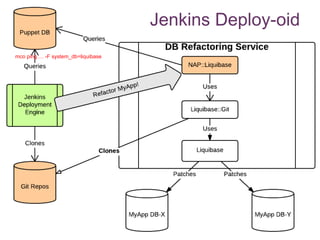
The document discusses database change management as a service, focusing on safe refactoring principles and the use of tools like Liquibase for version control and patch management. It highlights the importance of backward compatibility and the need for a rollback mechanism with each patch. Additionally, it suggests avoiding redundant refactoring code across applications and treating database management as a service rather than a one-off process.