The document provides information about a meetup on integrating Liquibase with MuleSoft. It includes:
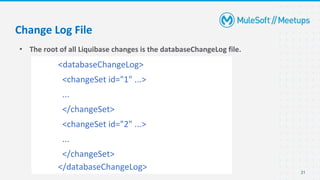
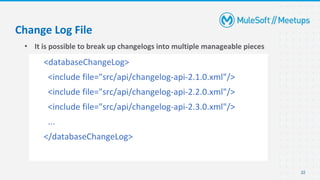
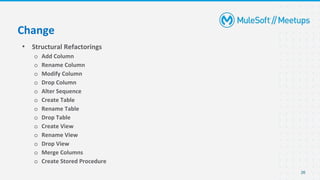
- An introduction and overview of Liquibase, including its major concepts like changesets and tracking tables.
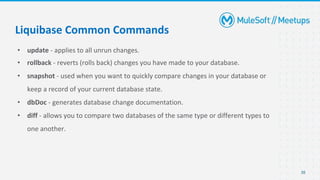
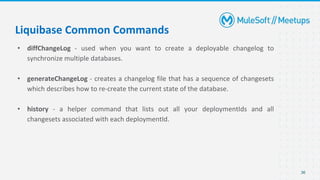
- Details on how Liquibase works and its key features like supporting multiple databases and rollback of changes.
- A demonstration of integrating Liquibase with MuleSoft.
- Information on an upcoming advanced integrations meetup and a request for feedback on the current session.