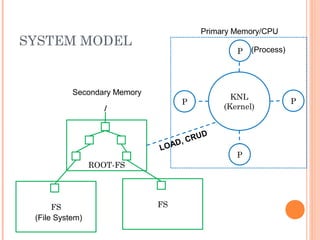
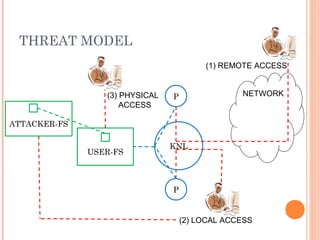
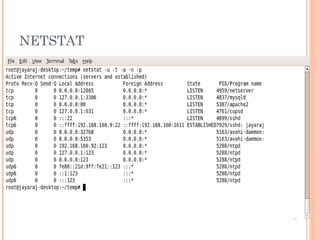
The document discusses elements of Linux security. It outlines threats like remote access attacks, local access attacks, and post-exploit activities. It also discusses countermeasures like minimizing exploit potential through patching and firewalls, minimizing post-exploit damage through privileges and capabilities, and maximizing discovery through auditing and monitoring. Security elements covered include authentication, access control, availability, integrity, and confidentiality.