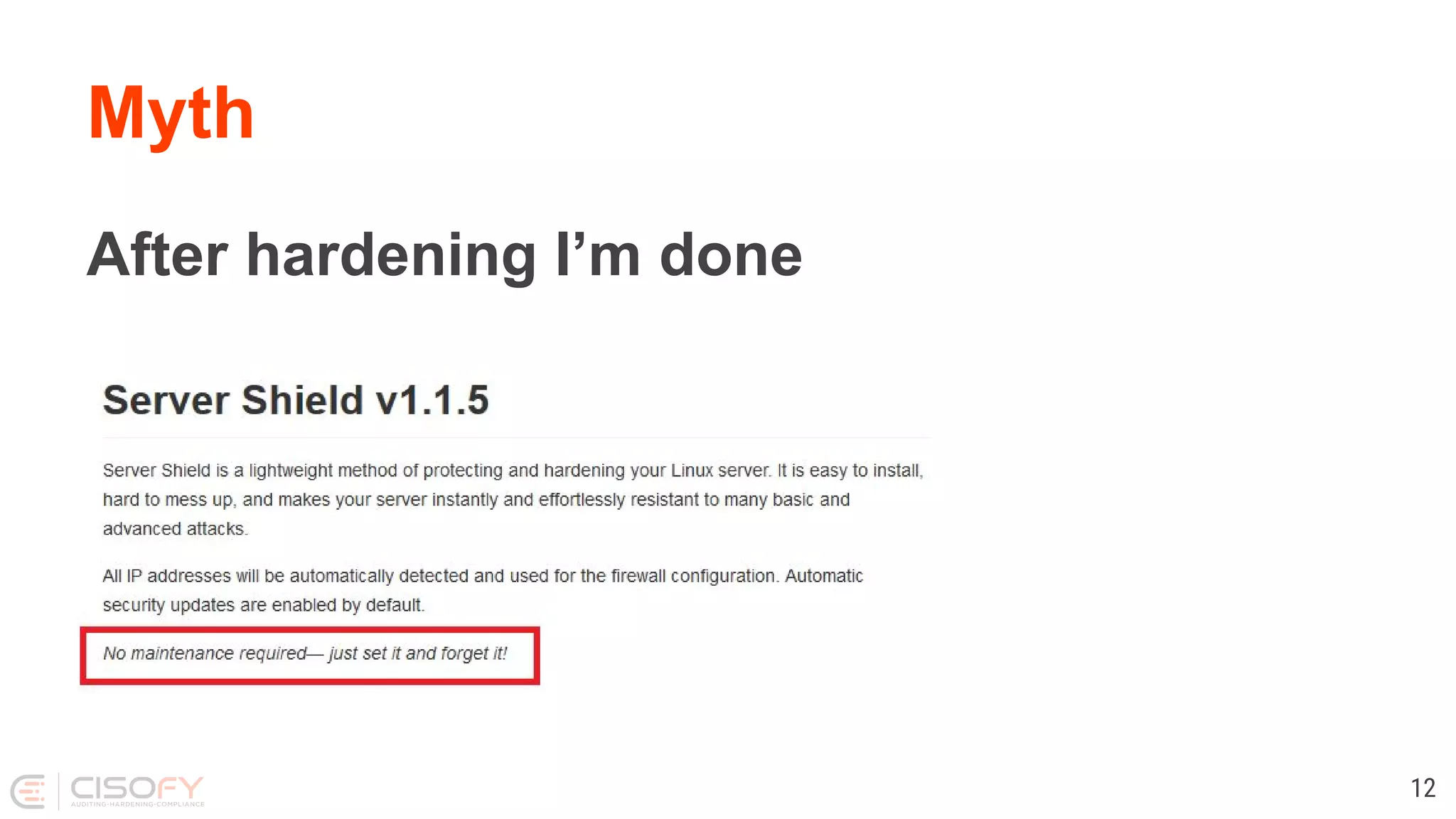
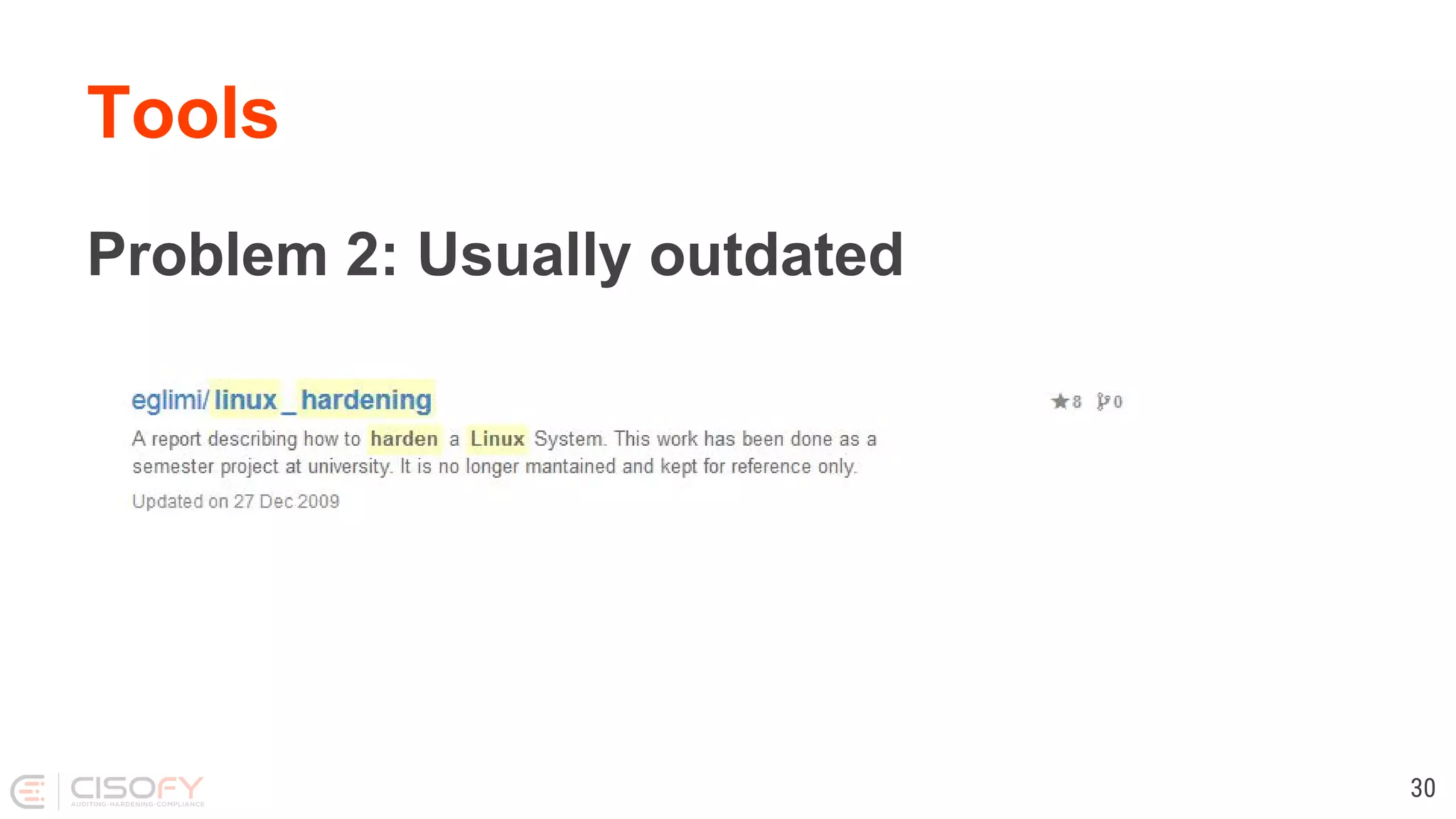
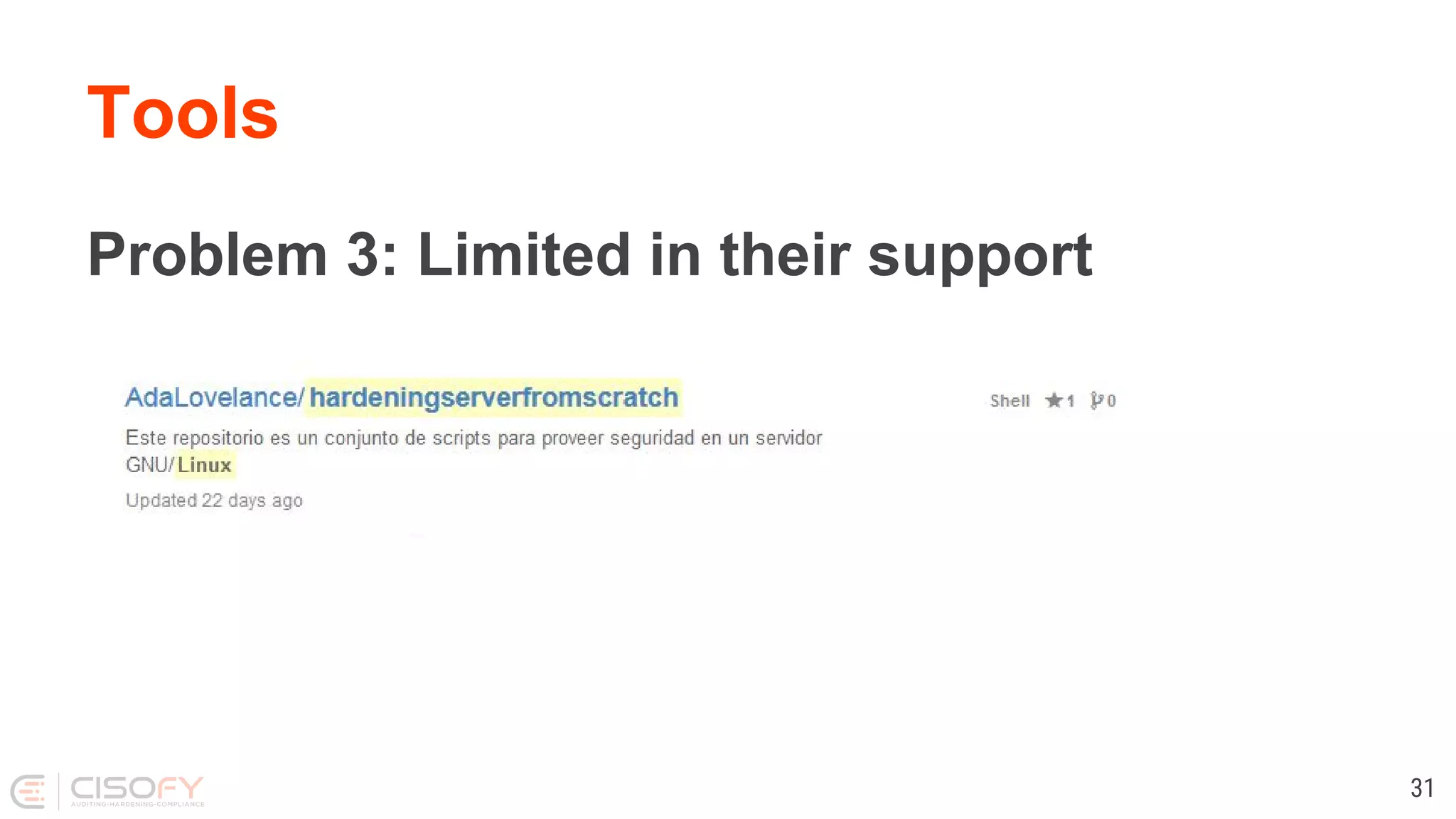
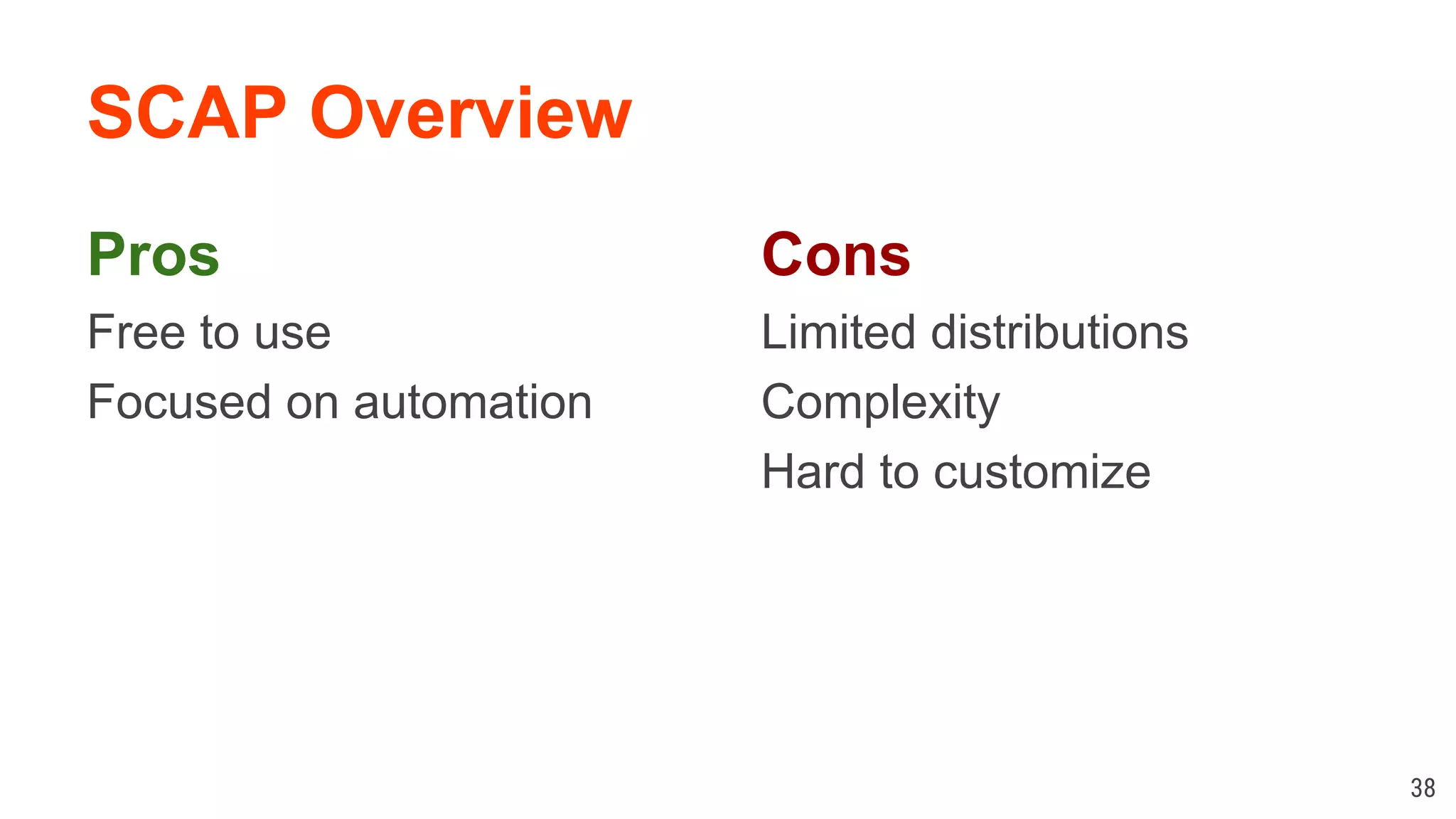
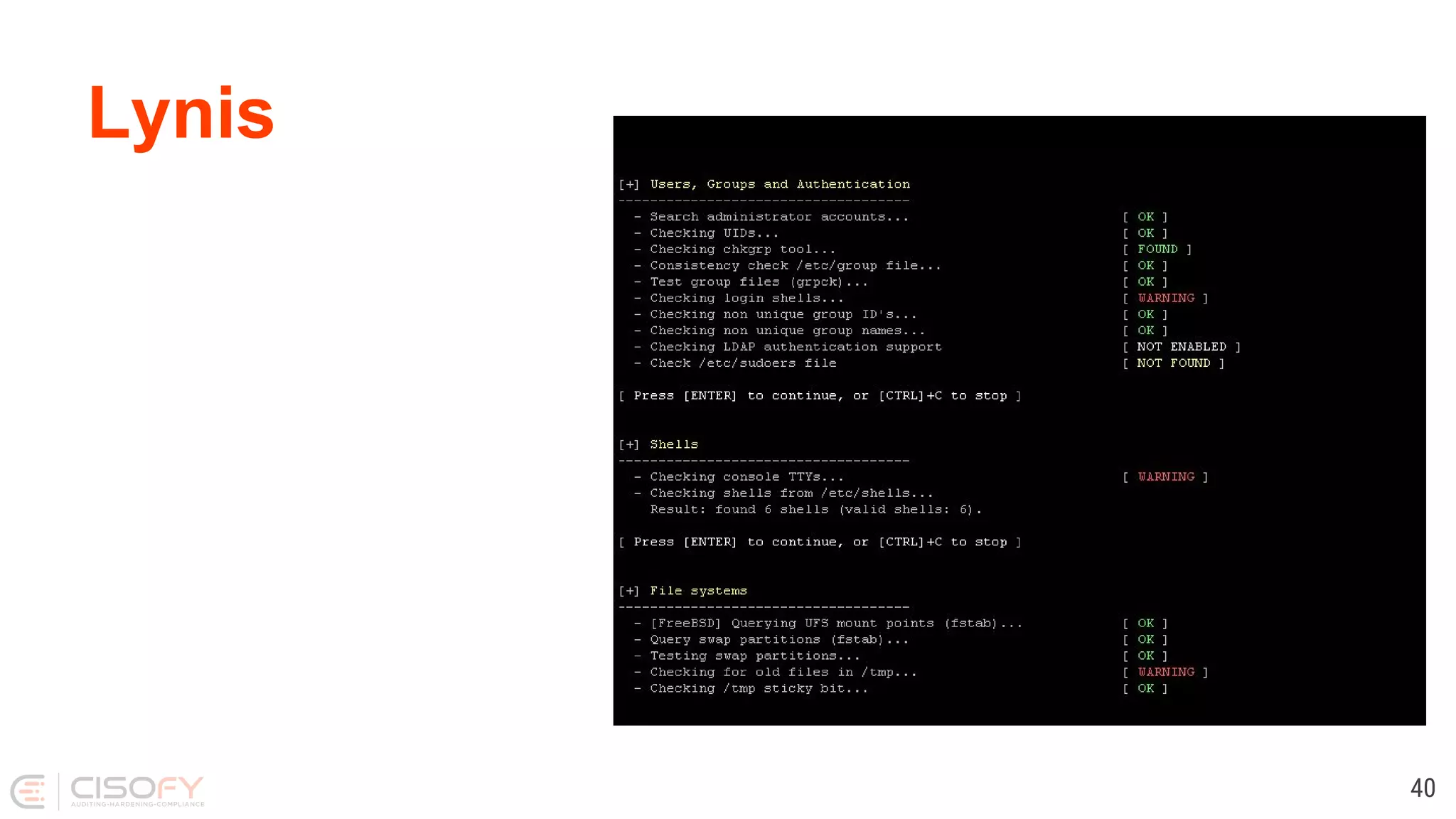
The document discusses Linux security practices, focusing on hardening, auditing, and available tools, particularly emphasizing the importance of ongoing security measures. It introduces the SCAP and Lynis tools for auditing and hardening, outlining their features, pros, and cons. The presentation concludes with recommendations for continuous protection and regular checks.