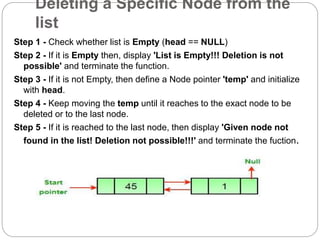
A linked list is a linear data structure where elements are linked using pointers. Each element contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. Linked lists allow for dynamic sizes and easy insertion/deletion. They are less cache friendly than arrays due to non-contiguous memory allocation. Common operations include insertion/deletion at the beginning, middle, or end which have time complexities ranging from O(1) to O(n) depending on the operation and presence of additional pointers. Doubly linked lists contain pointers to both the next and previous nodes, enabling traversal in both directions but using more memory.