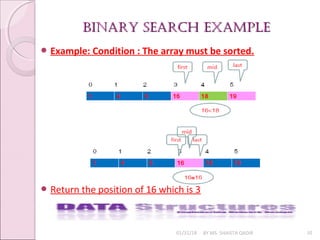
The document discusses searching algorithms, focusing on sequential and binary search methods. Sequential search examines elements one by one and has a time complexity of O(n), while binary search is more efficient, with a time complexity of O(log n), as it divides the array into halves. Examples of both algorithms and their respective program logic are provided.






![SEQUENTIAL SEARCH pROGRAmSEQUENTIAL SEARCH pROGRAm
LOGICLOGIC
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 7
PROGRAM LOGIC:
public int seqsearch(int [ ]arr, int x)
{
for(int i=0; i< arr.length; i++)
if(arr [ i ] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
Time Complexity of Sequential search algorithm is: O(n)3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture6-180131100803/85/Searching-7-320.jpg)



![BINARY SEARCH pROGRAmBINARY SEARCH pROGRAm
lOGIClOGIC
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 12
PROGRAM LOGIC:
public static int binarysearch(int[ ] a, int x) {
int lo = 0; int hi = a.length;
while (lo < hi) {
int i = (lo + hi) / 2;
if (a[i] == x)
return i;
else if (a[i] < x)
lo = i+1;
else hi = I; }
return -1; }
Time Complexity of binary search algorithm is: O(logn)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture6-180131100803/85/Searching-12-320.jpg)
