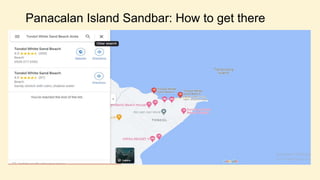
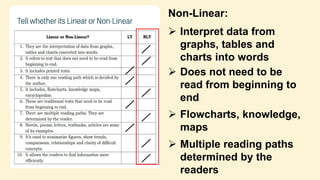
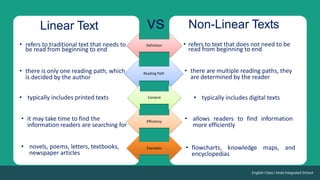
The document discusses linear and non-linear texts. It defines linear text as traditional text that must be read from beginning to end, like novels and textbooks. Non-linear text does not need to be read sequentially and can be interpreted in multiple ways, including through charts, graphs and diagrams. Examples given of non-linear texts are maps, directories and infographics. The document also contains examples of activities and assessments for students to practice distinguishing between linear and non-linear texts and extracting information from non-linear sources.