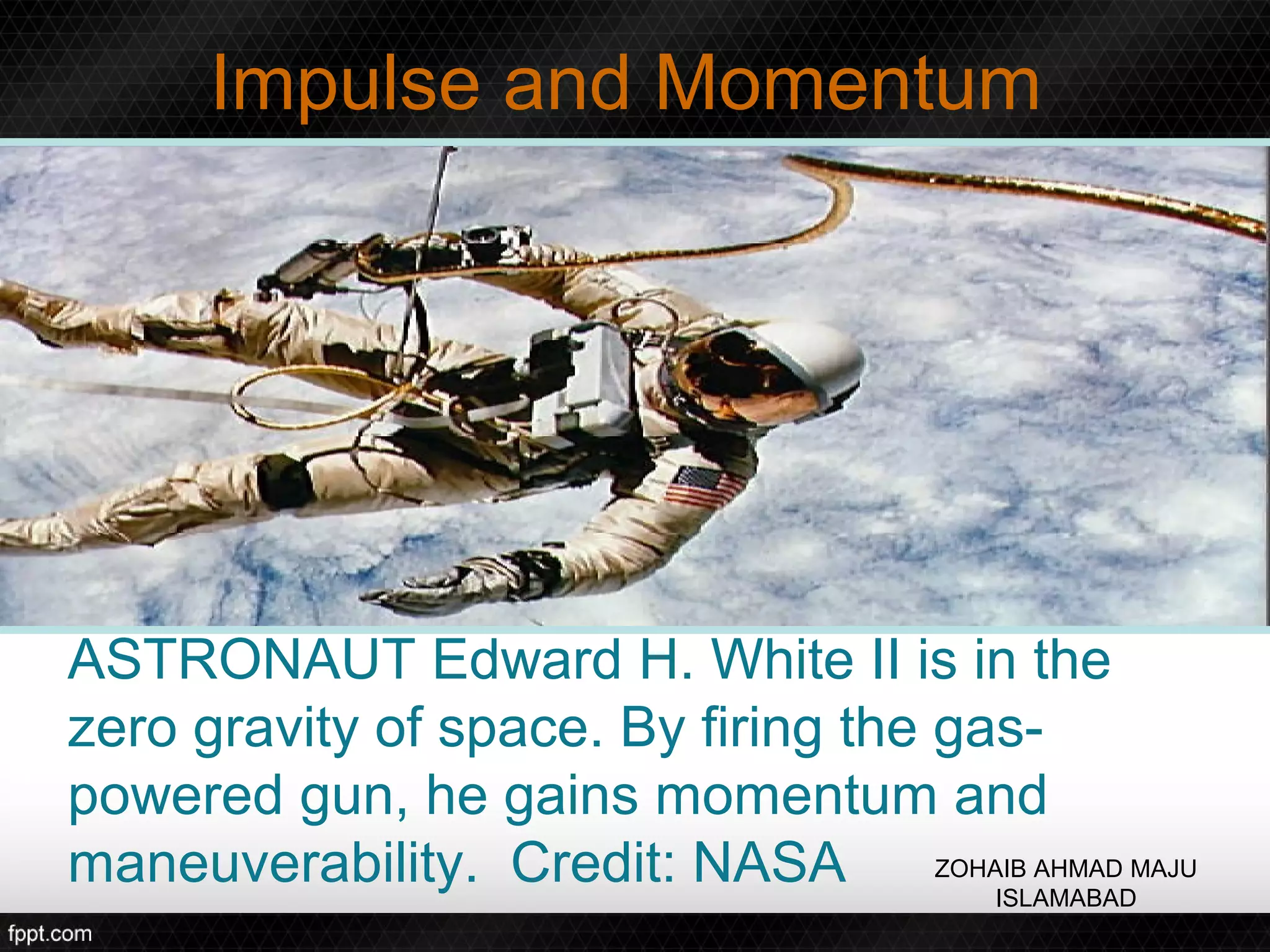
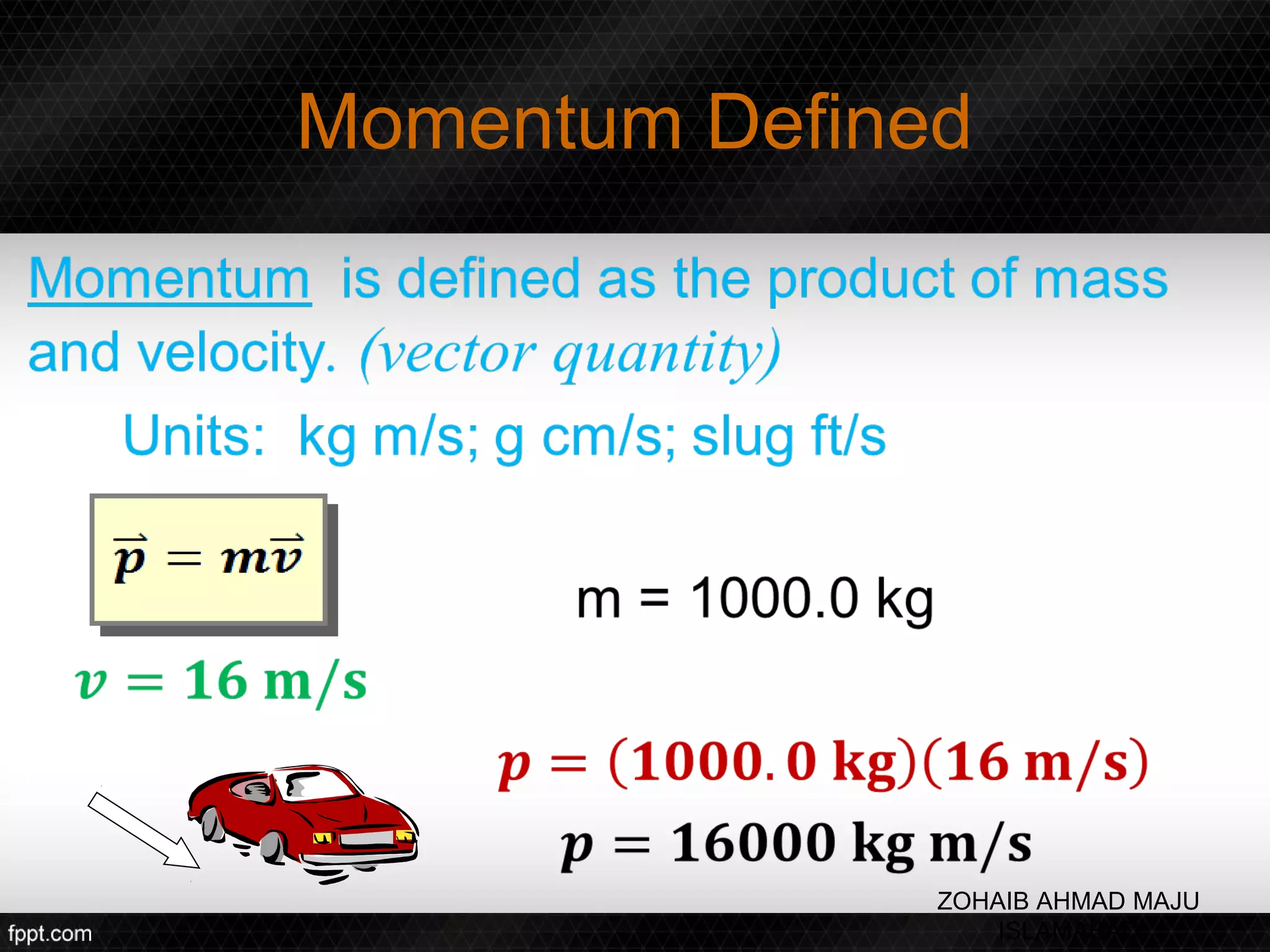
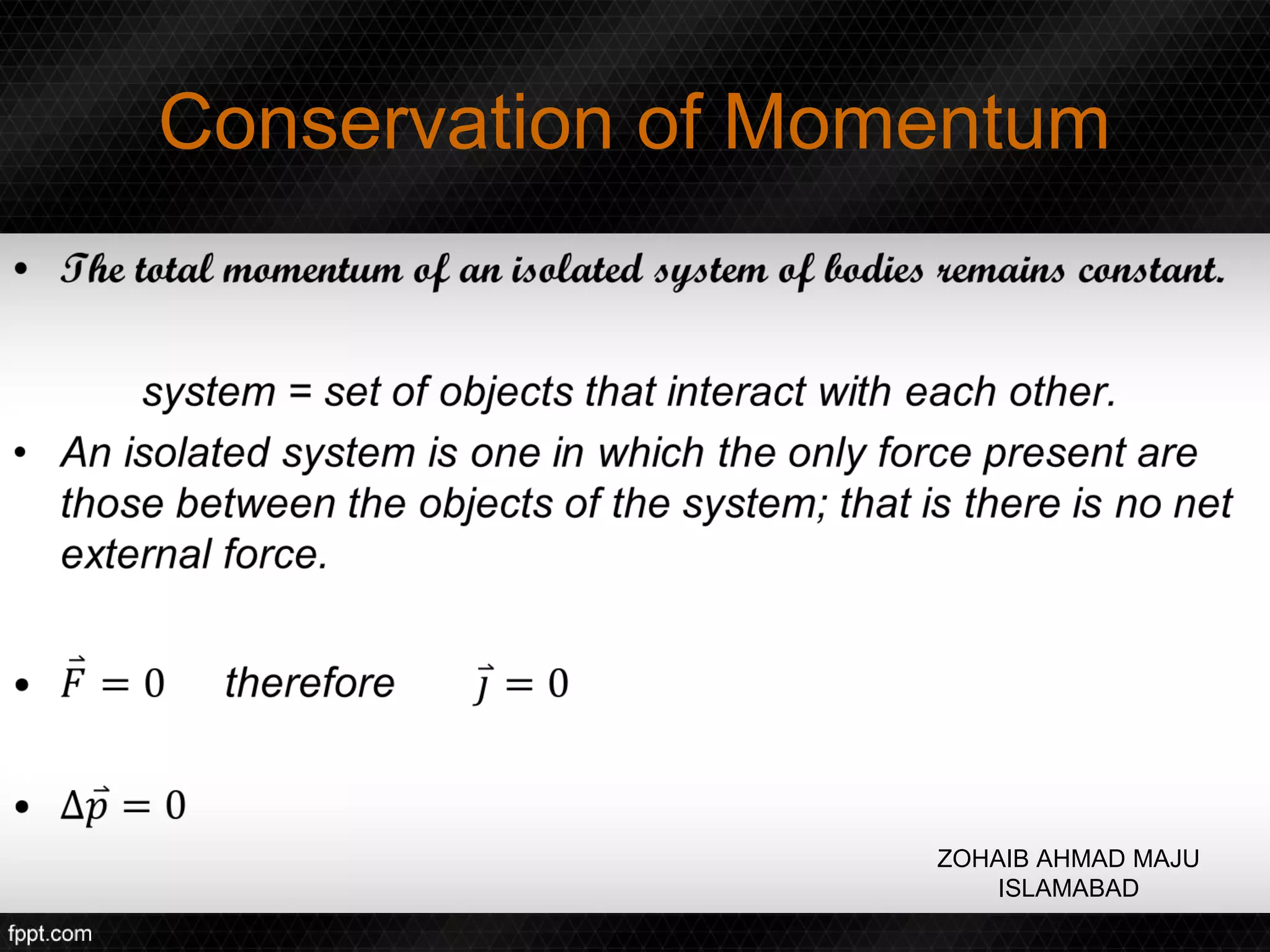
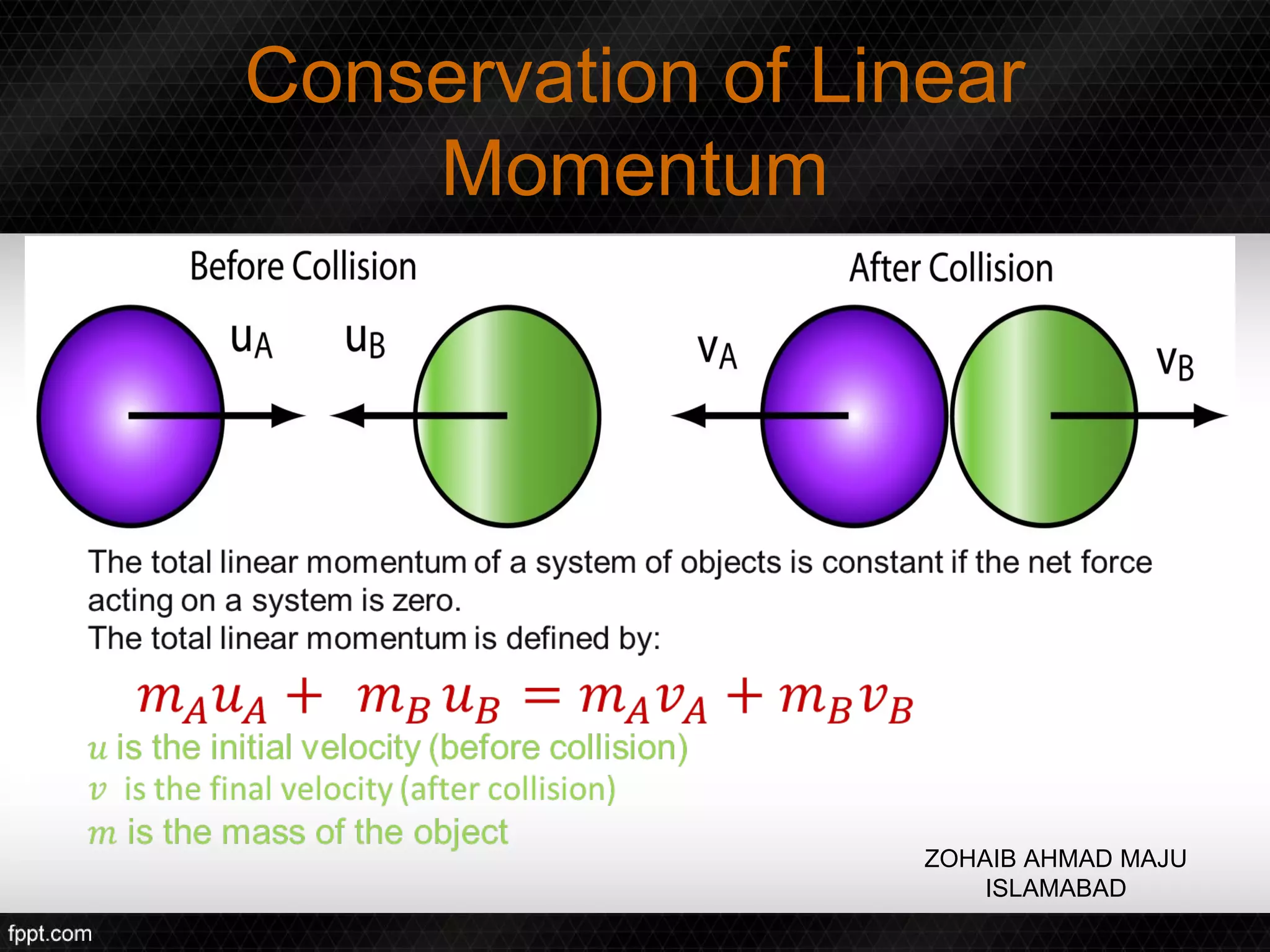
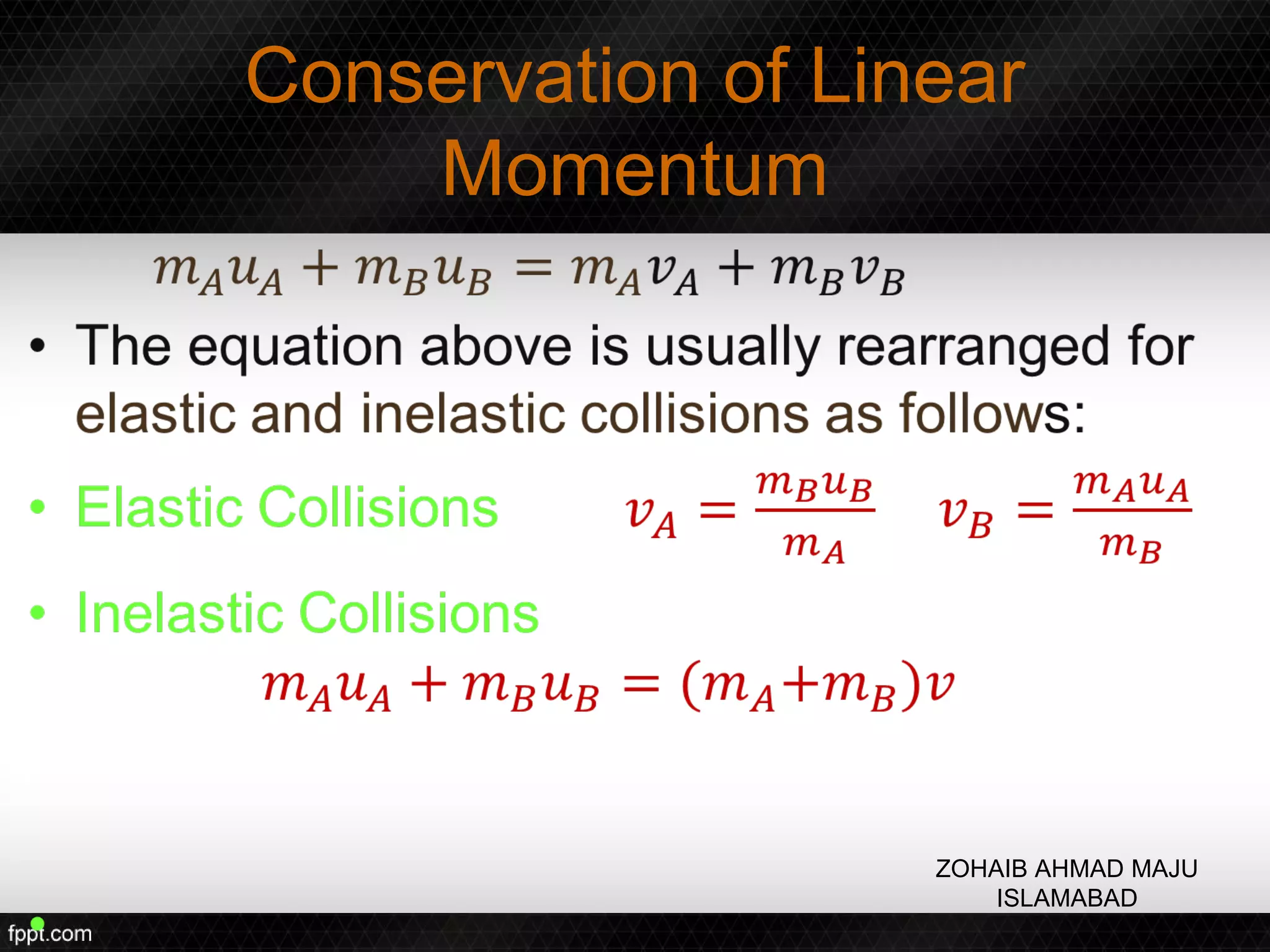
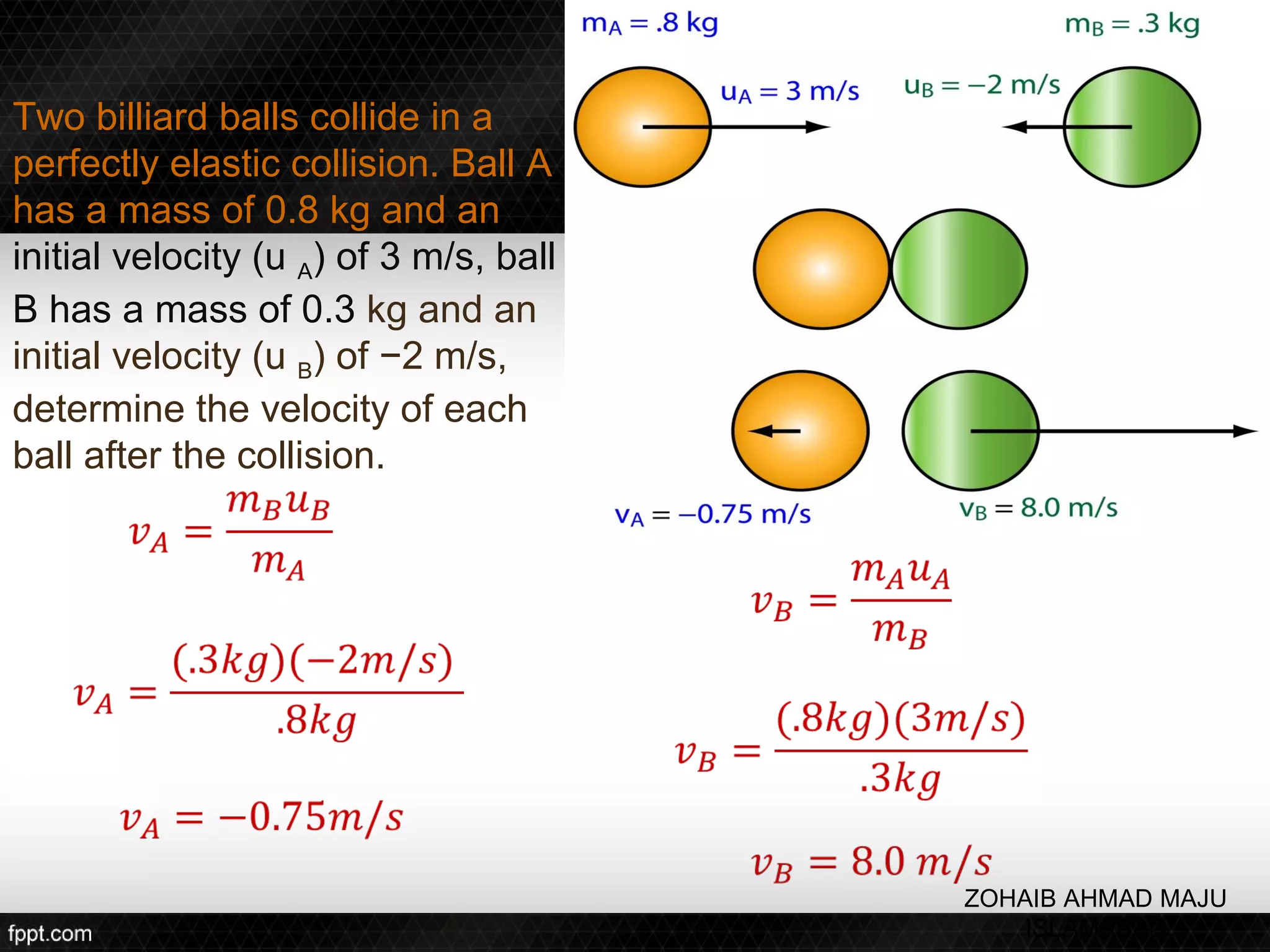
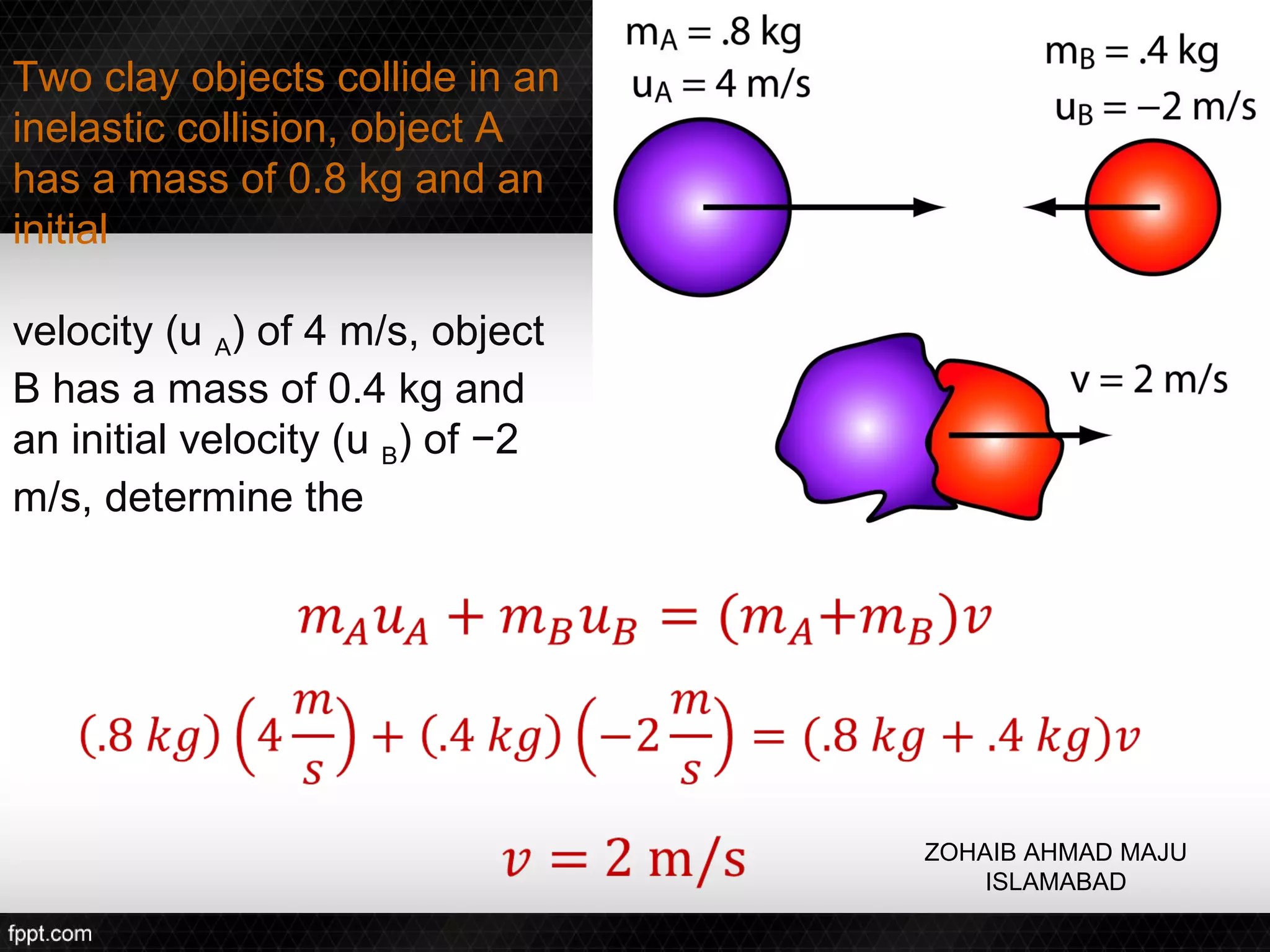
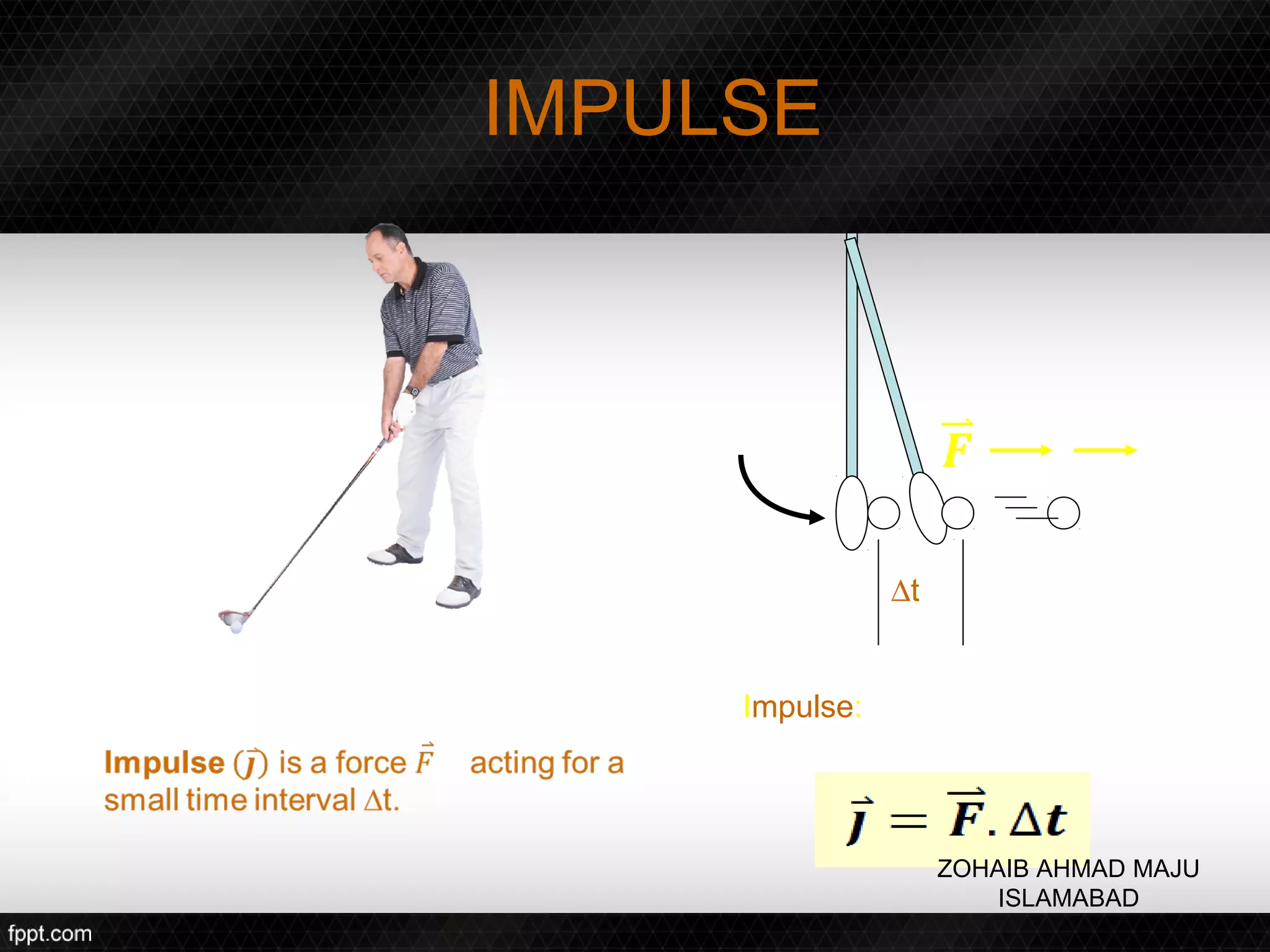
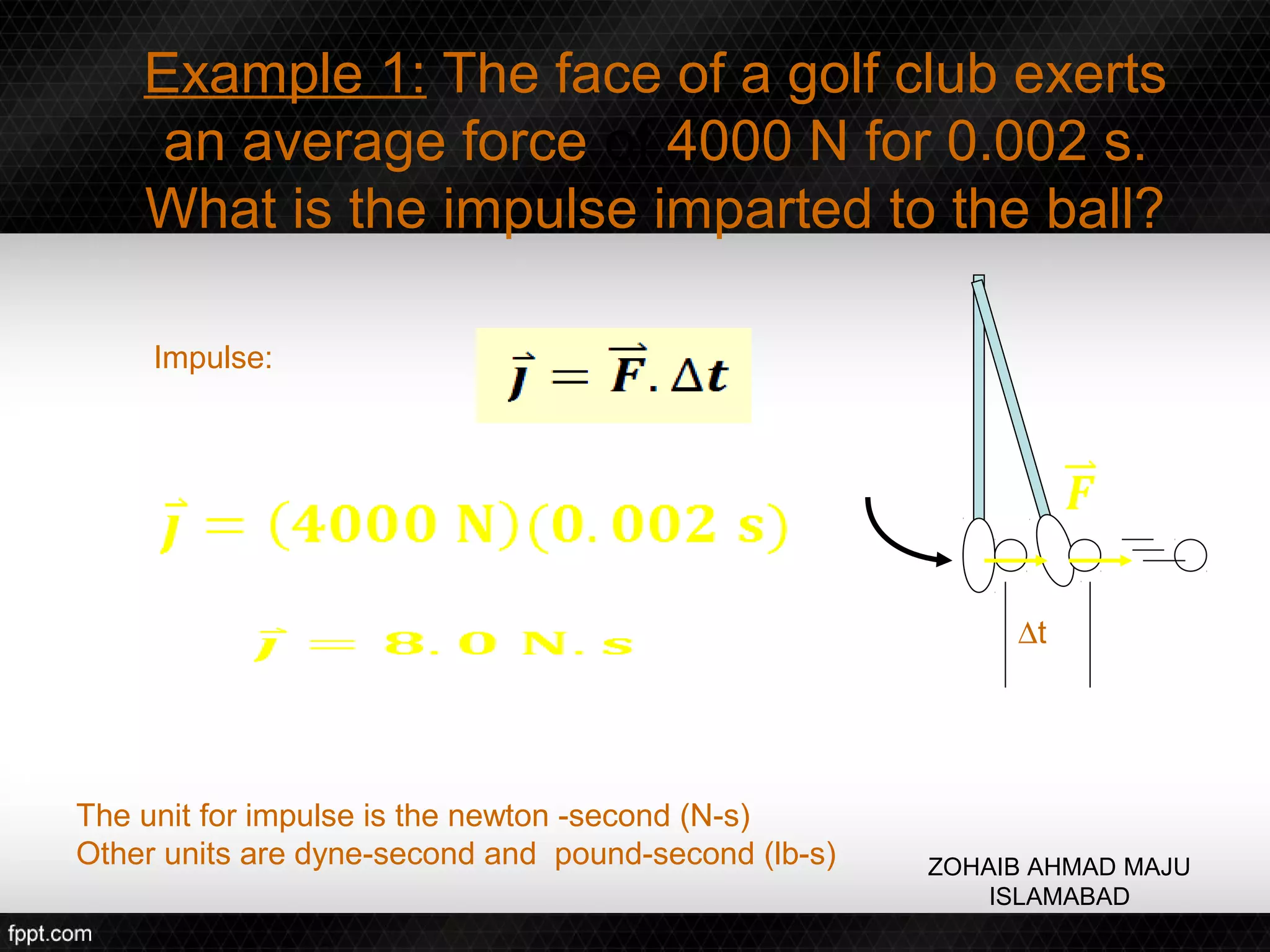
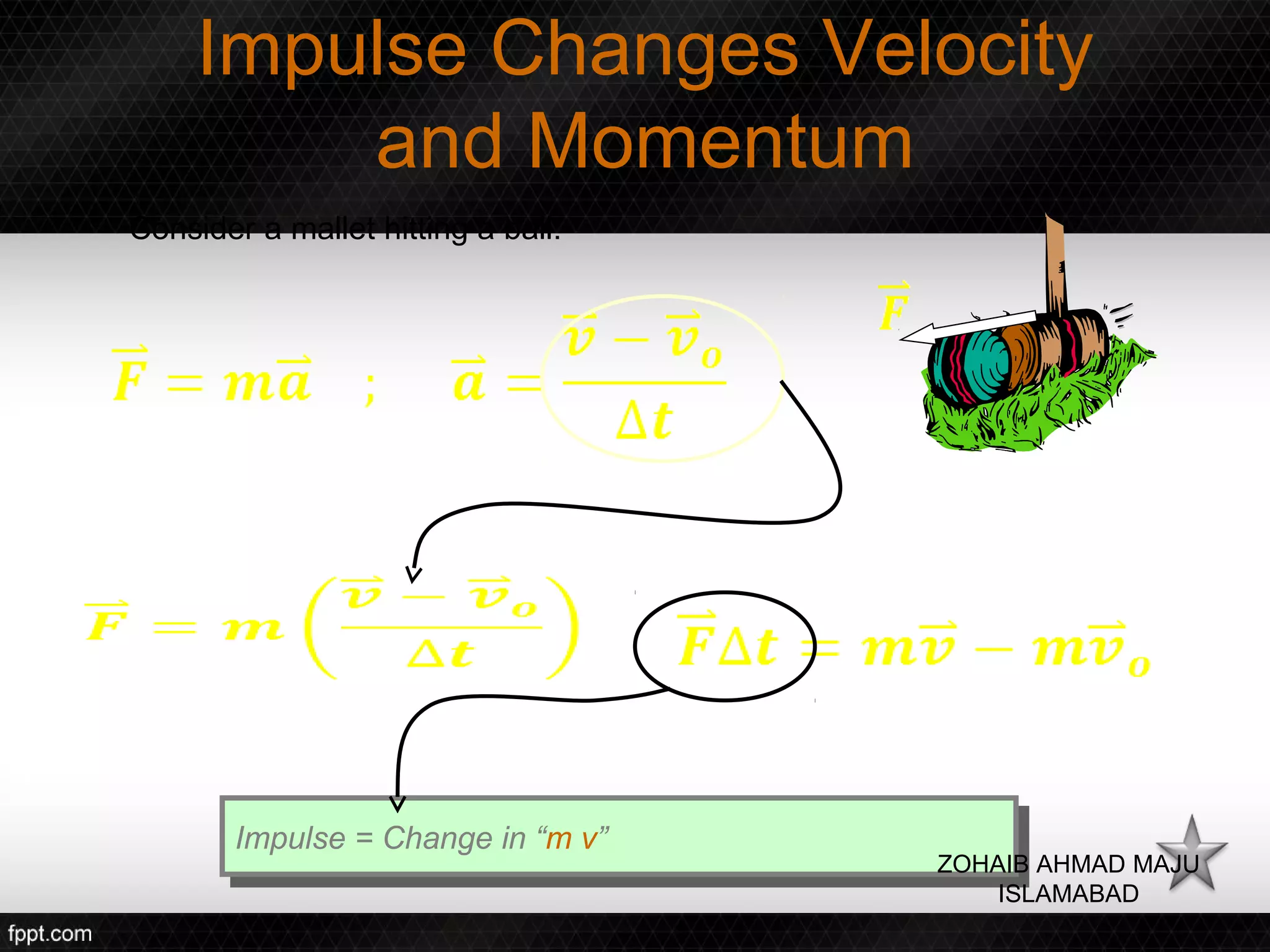
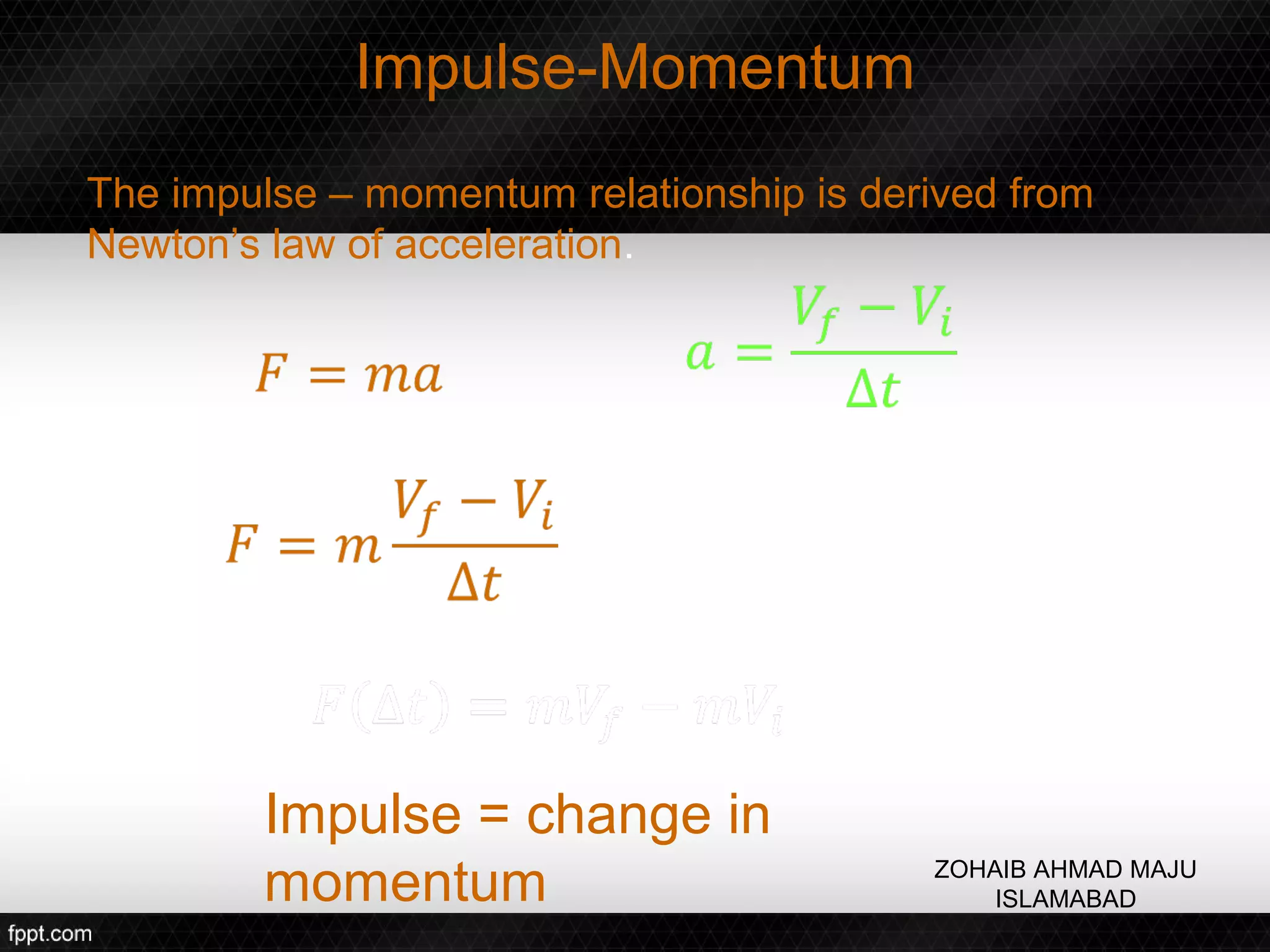
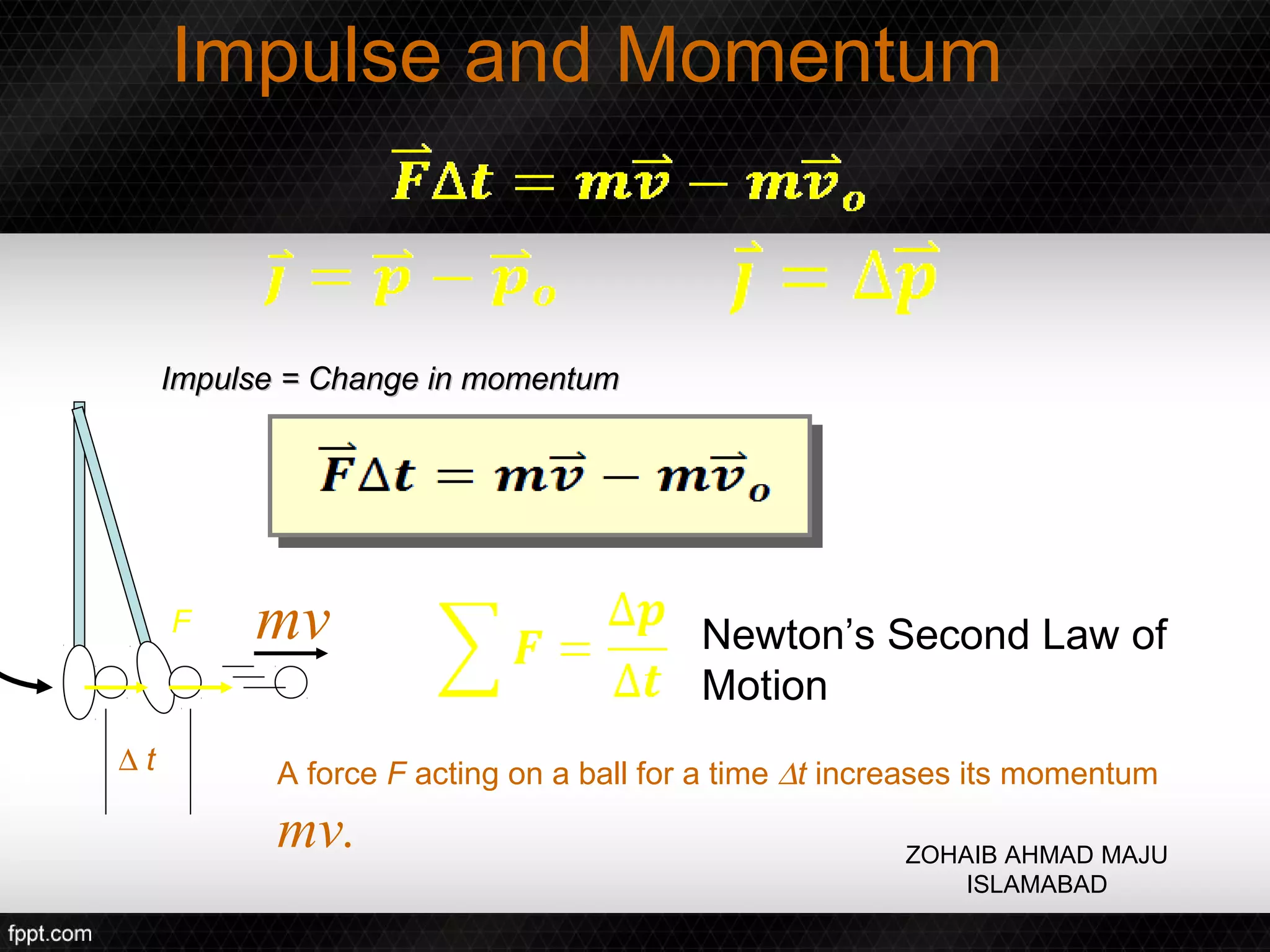
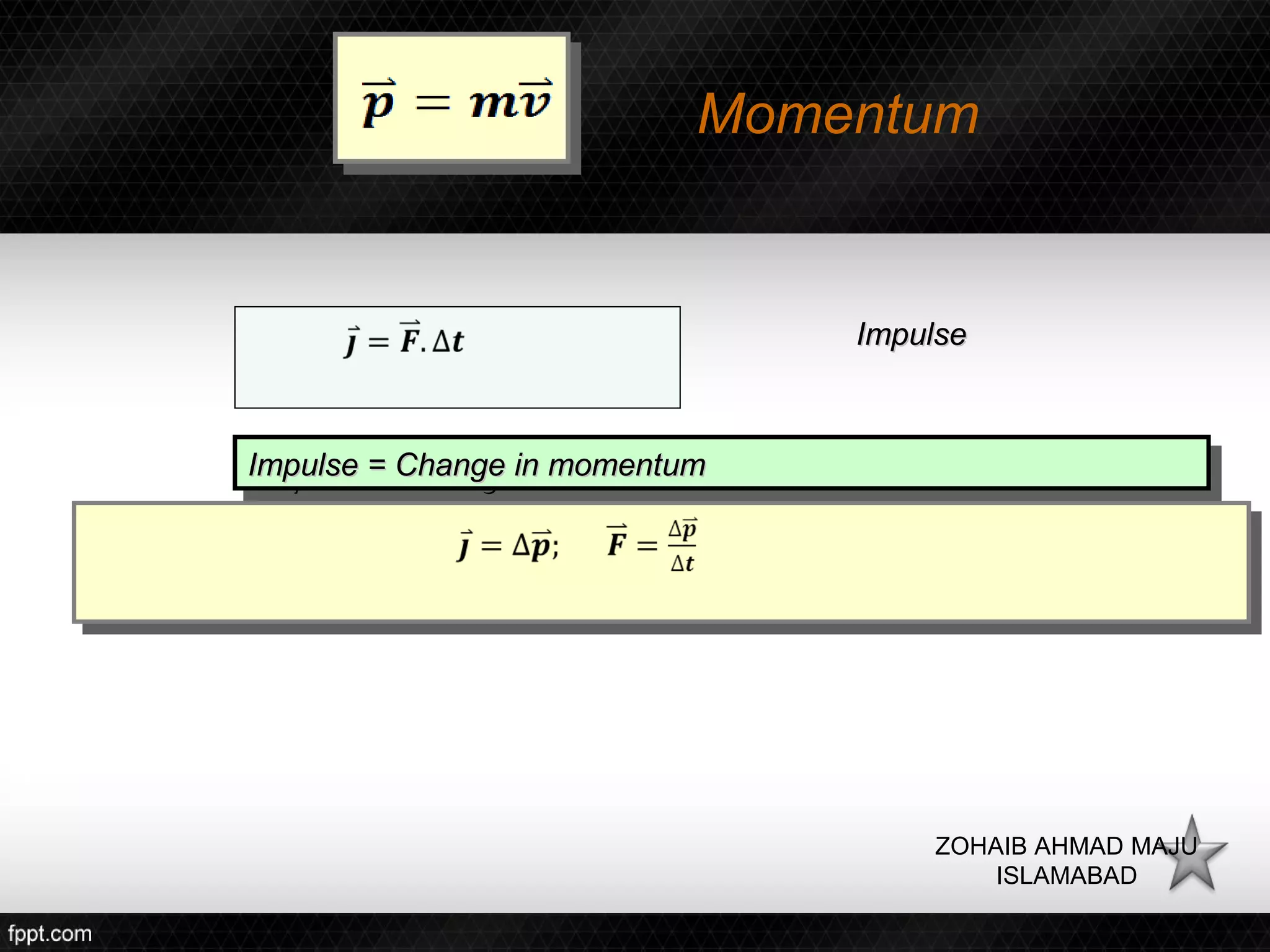
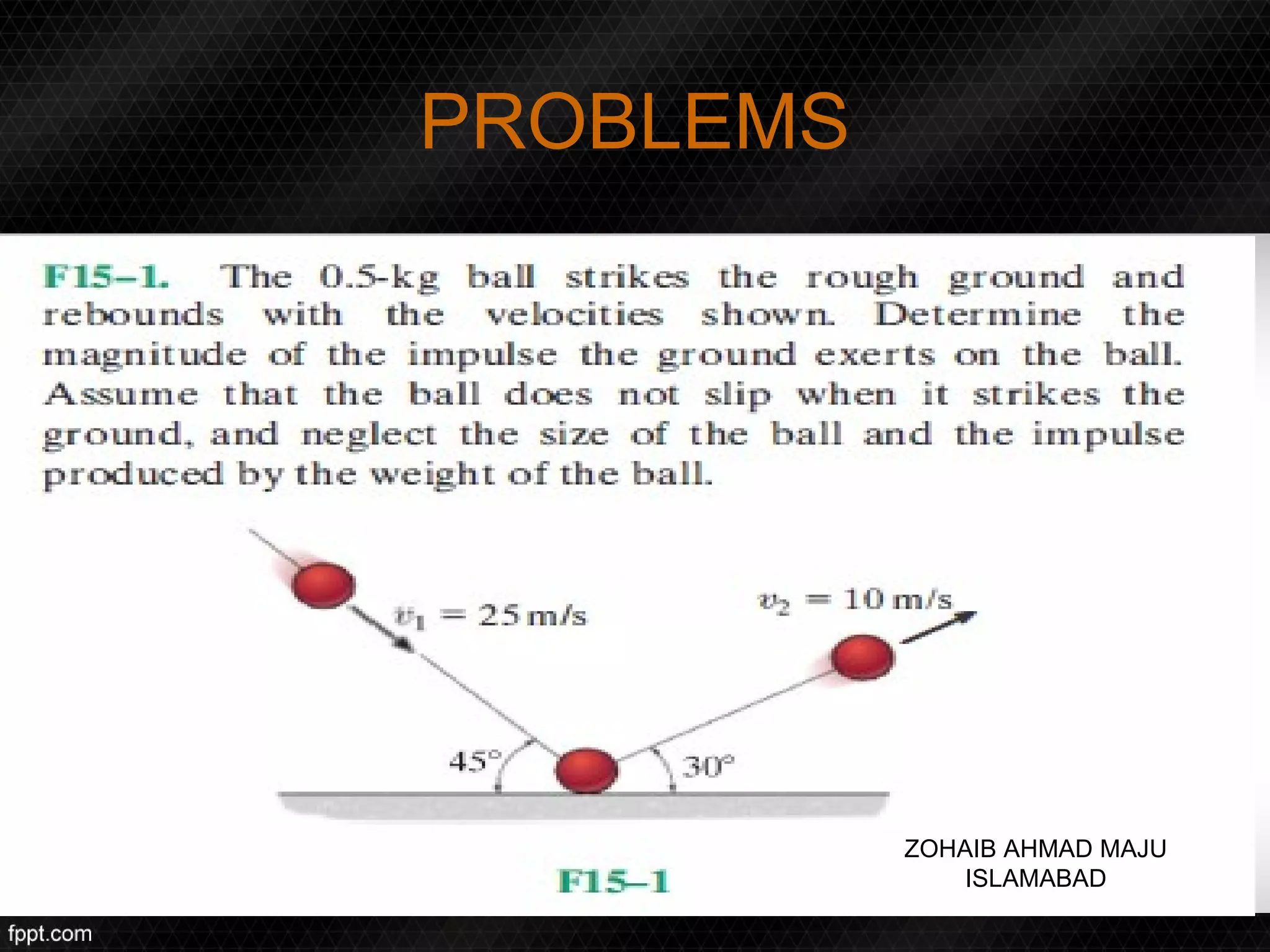
This document discusses linear impulse and momentum. It defines momentum and explores the conservation of linear momentum, stating that the total linear momentum of a system is constant if the net force is zero. Collision classifications are also discussed, including elastic versus inelastic collisions. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculations of momentum and impulse-momentum relationships for various physical situations. The key relationships emphasized are that impulse equals change in momentum, and momentum is conserved in systems where the net force is zero.