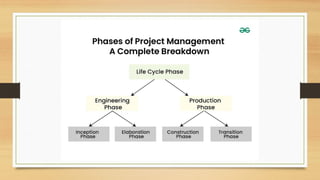
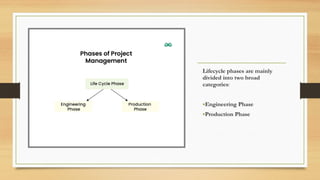
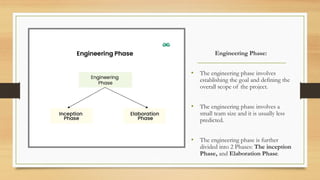
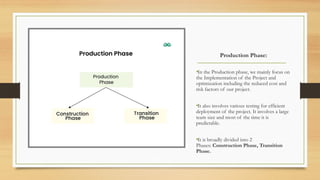
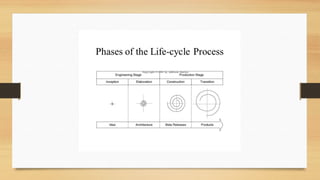
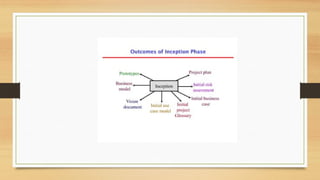
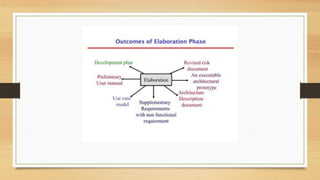
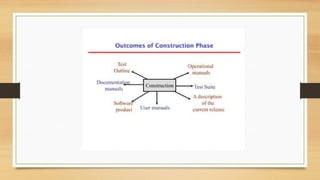
The document outlines the life cycle phases in software project management, categorized into engineering and production phases. The engineering phase includes inception and elaboration, focusing on project goals, requirements, architecture, and risk assessment, while the production phase encompasses construction and transition, emphasizing implementation, testing, and deployment. Key activities and objectives are described for each sub-phase, ensuring a structured approach to software development.