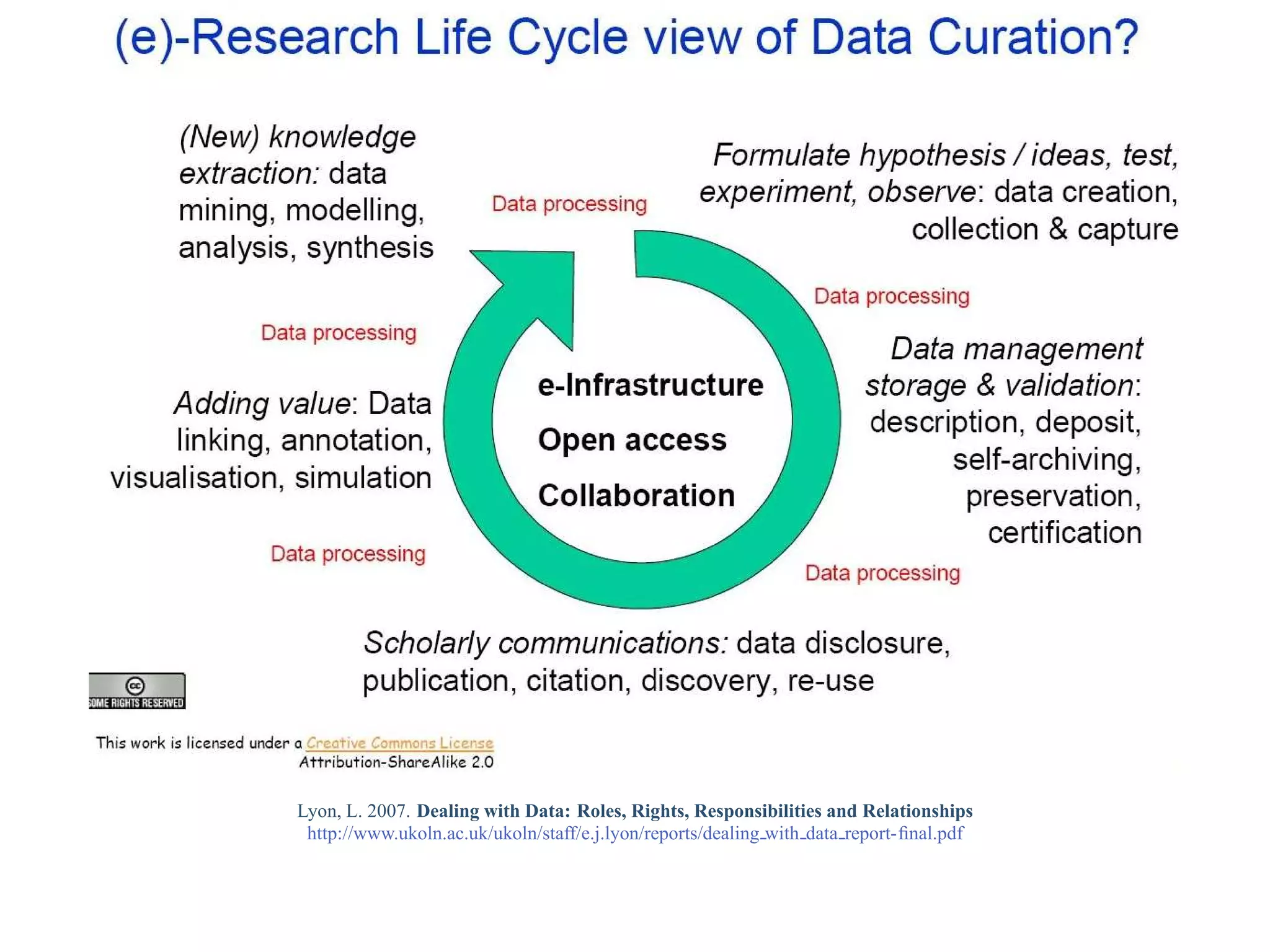
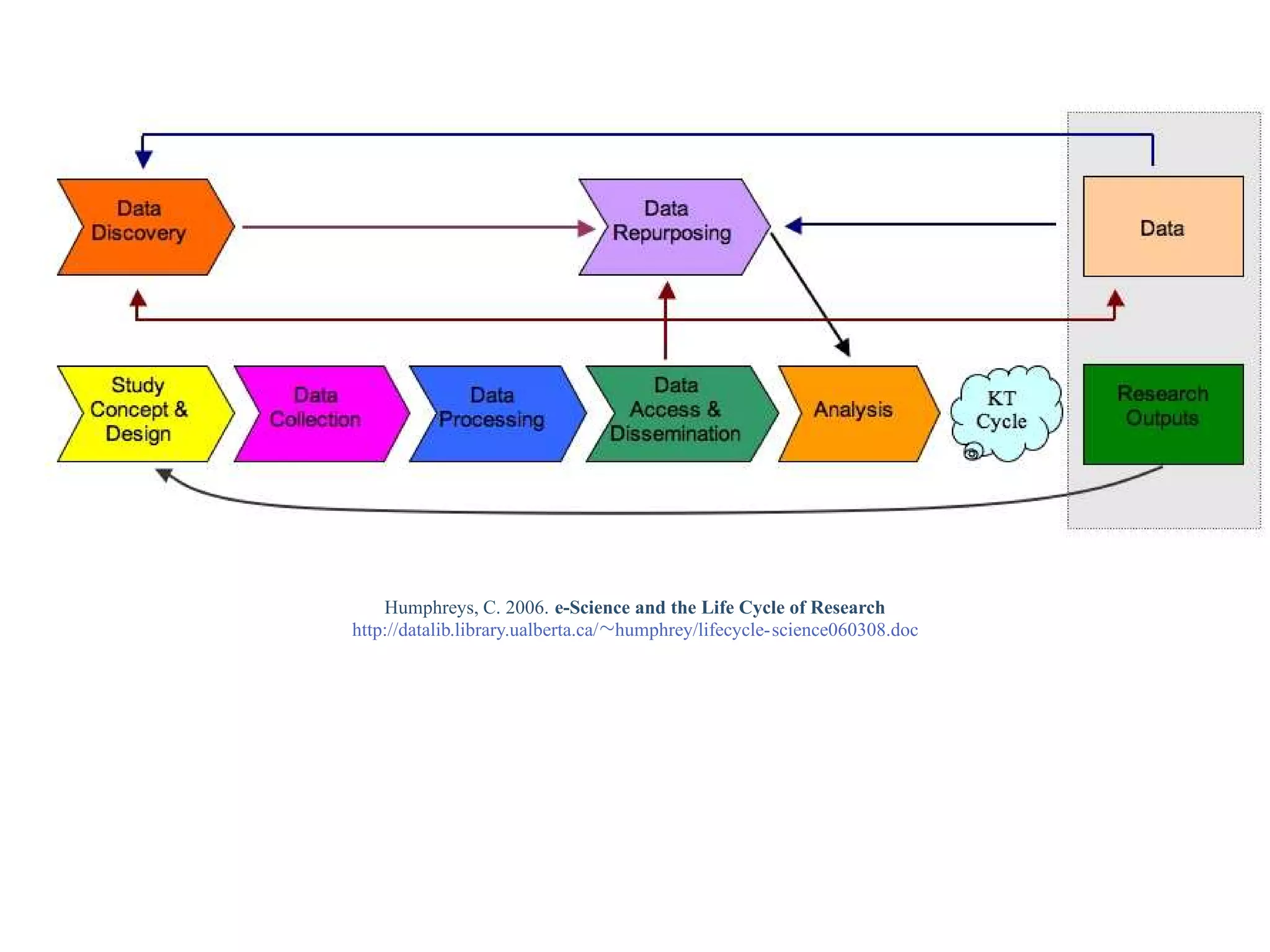
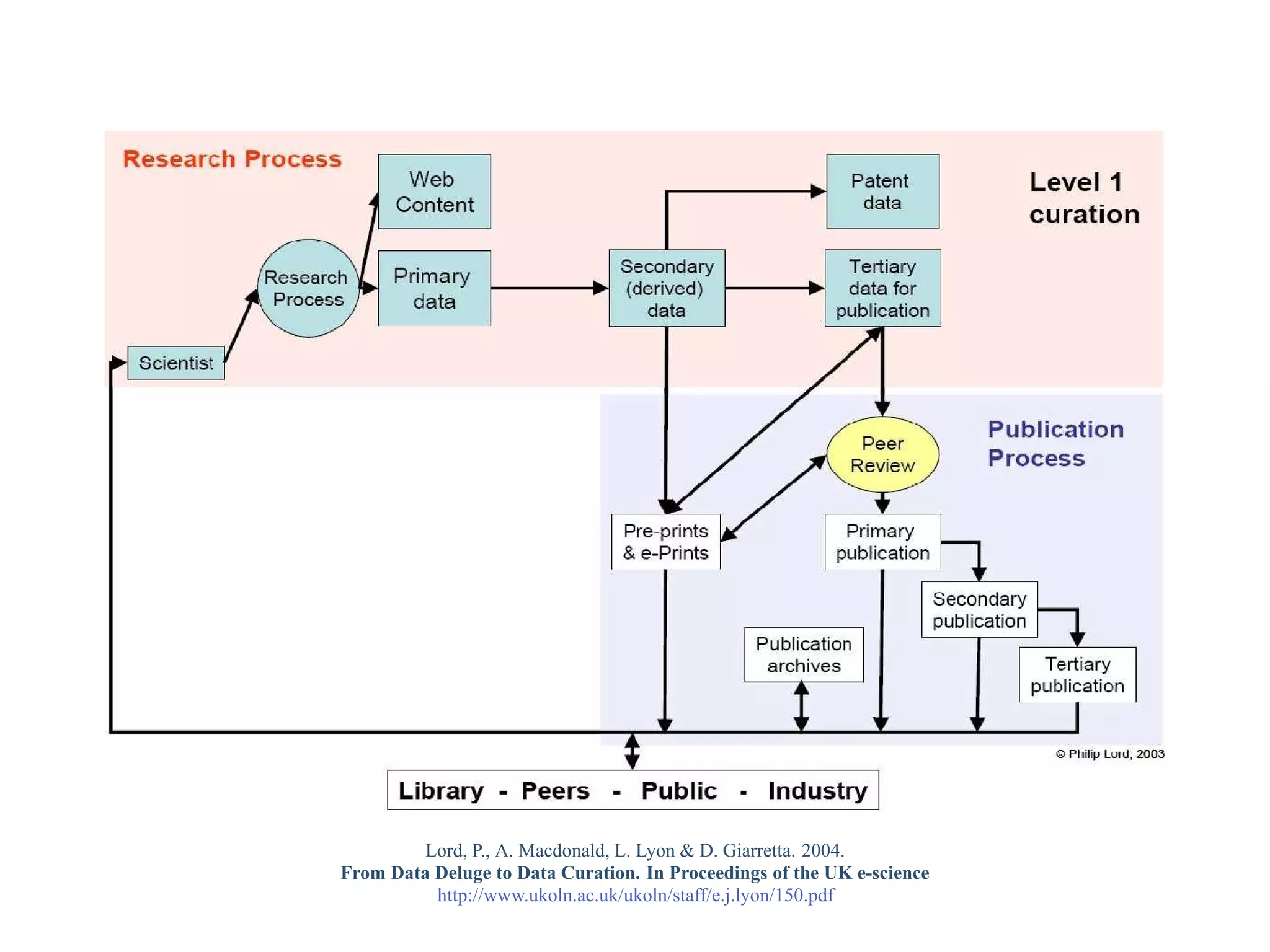
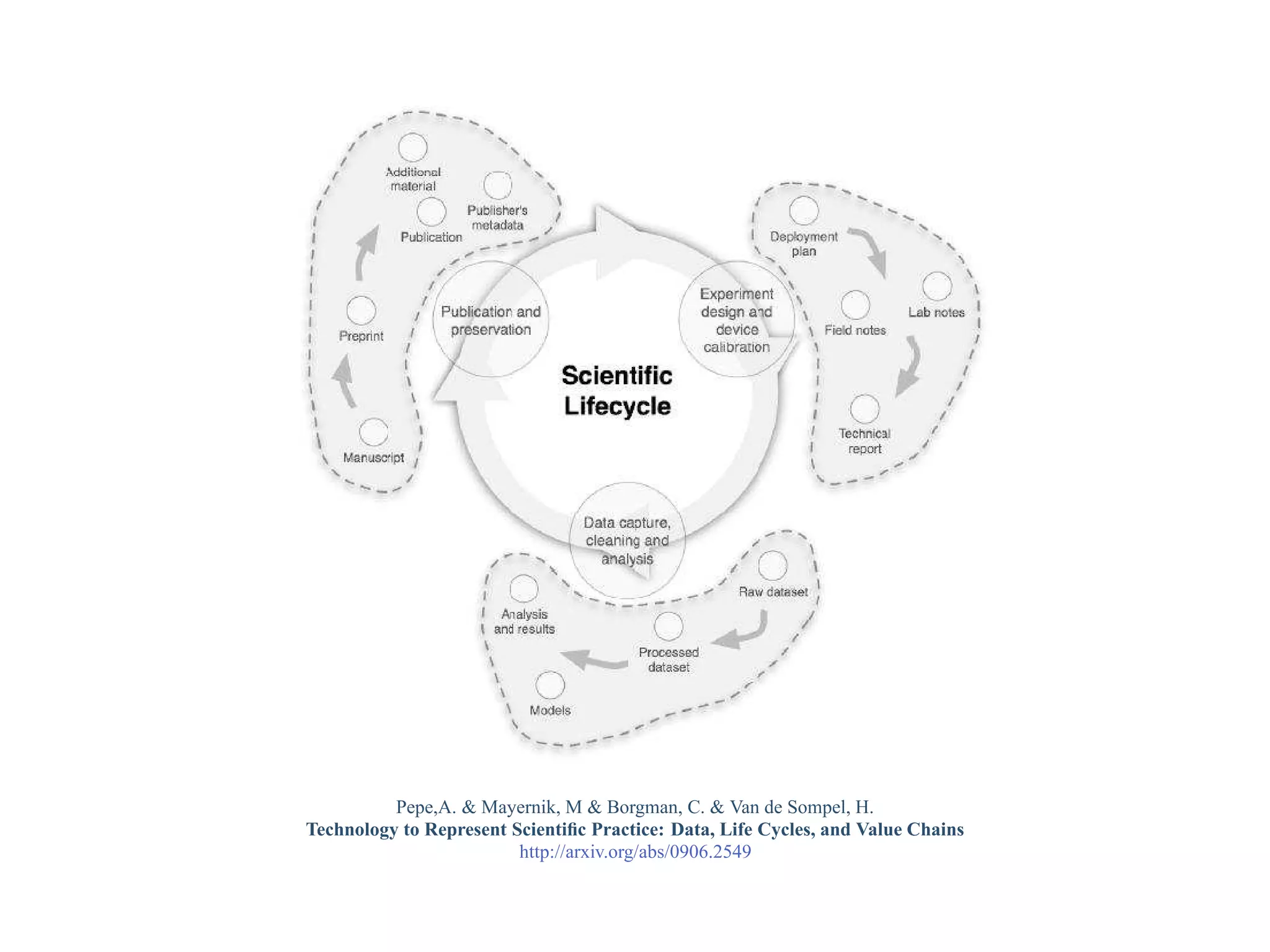
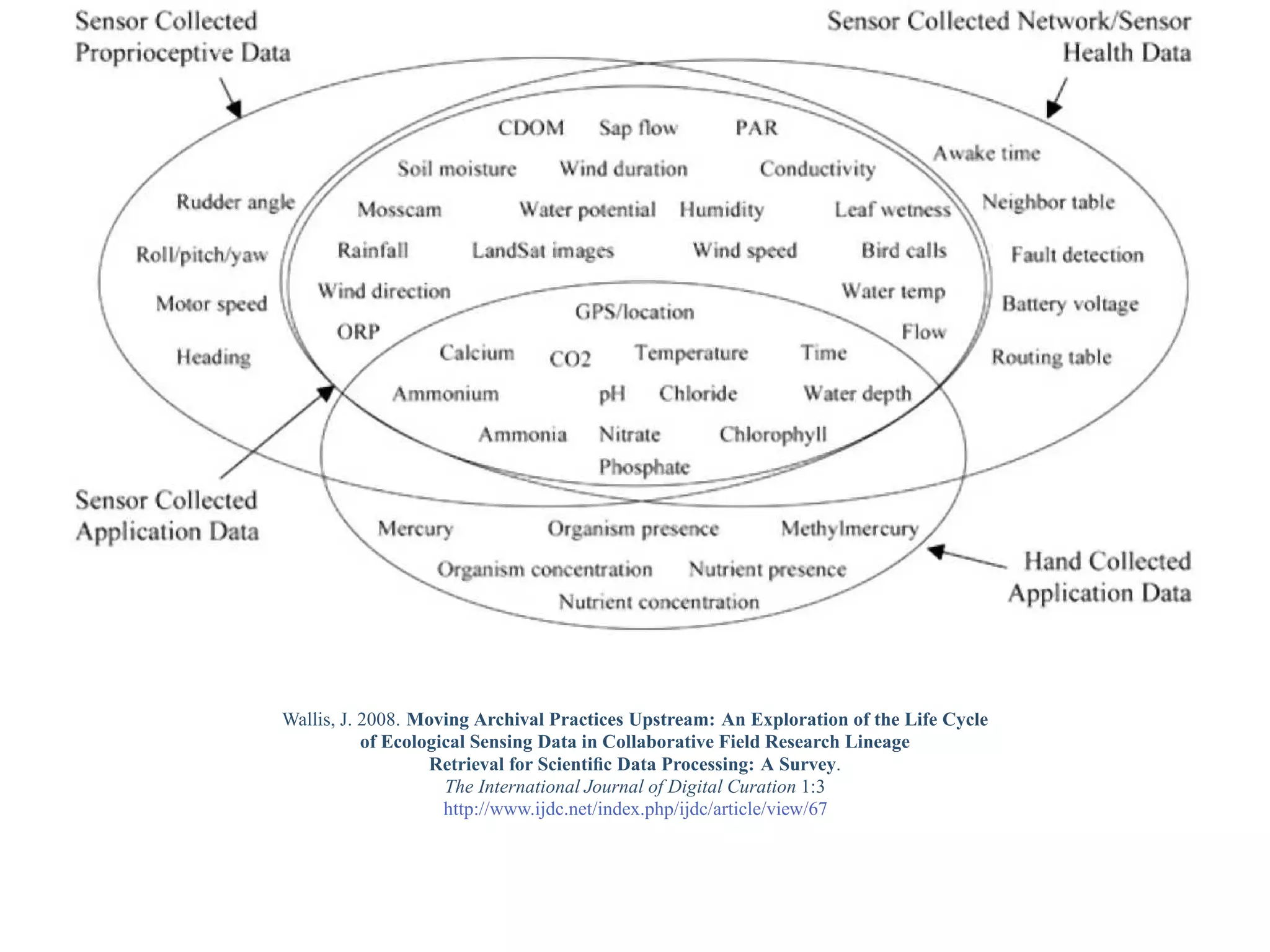
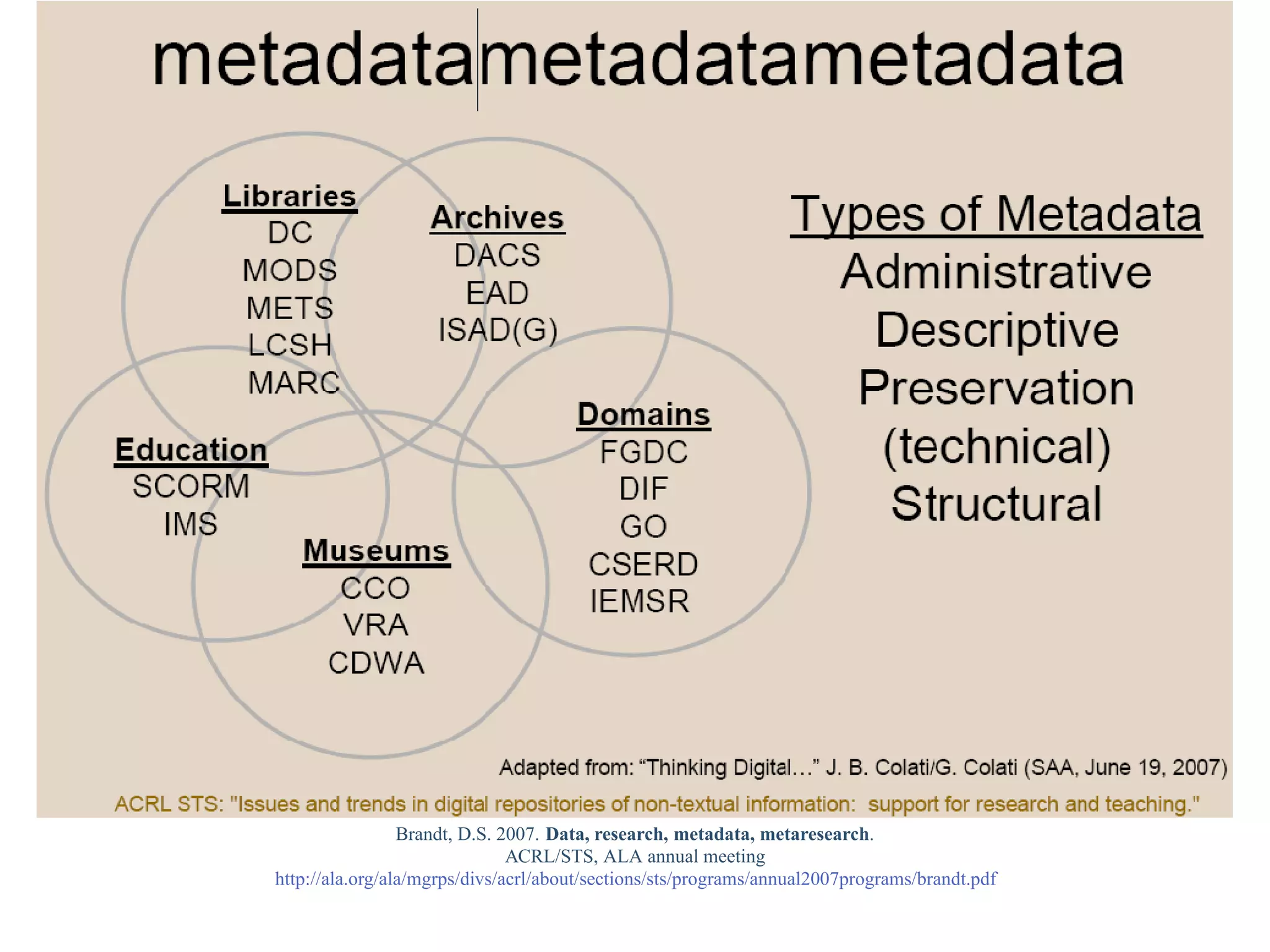
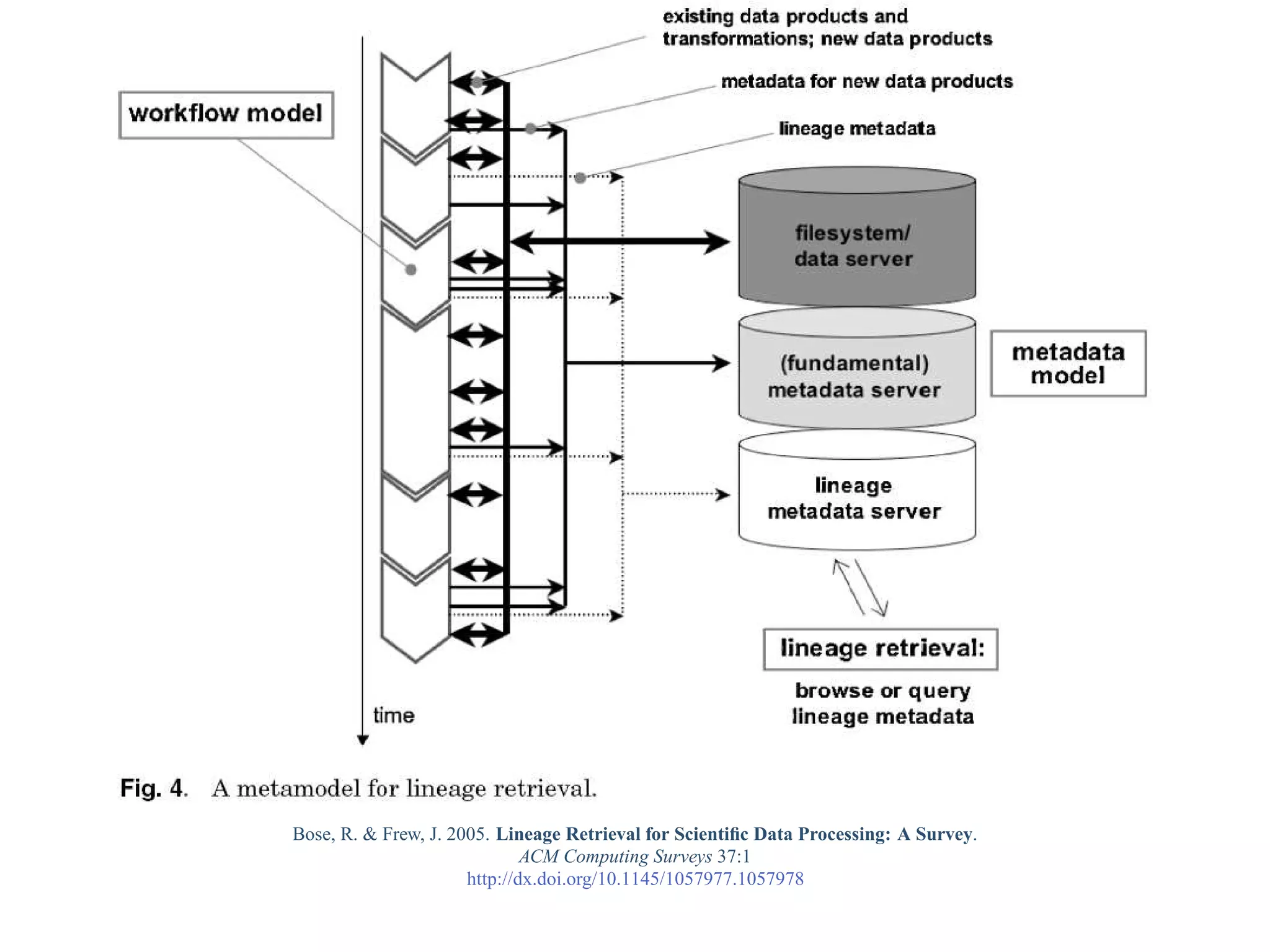
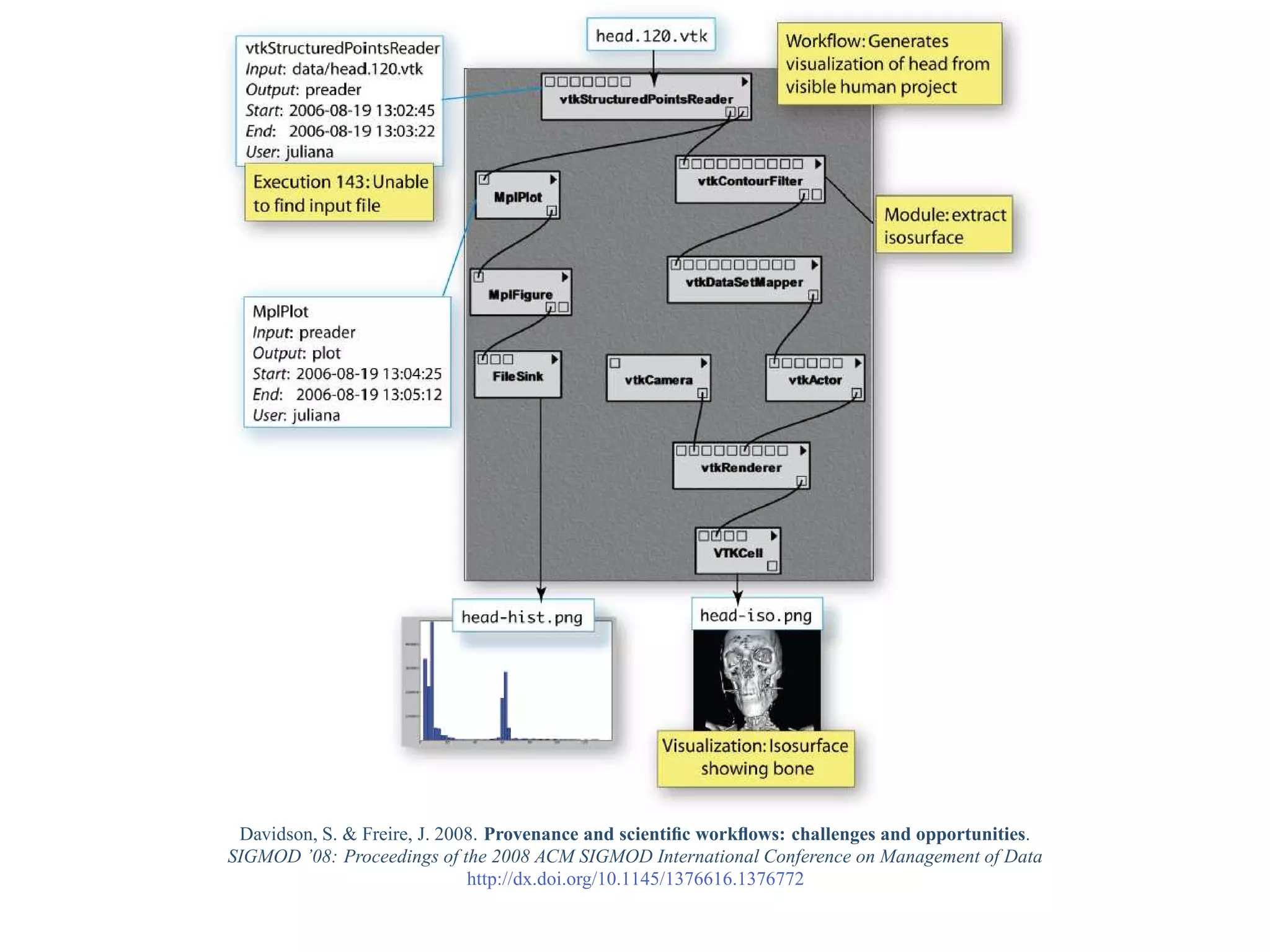
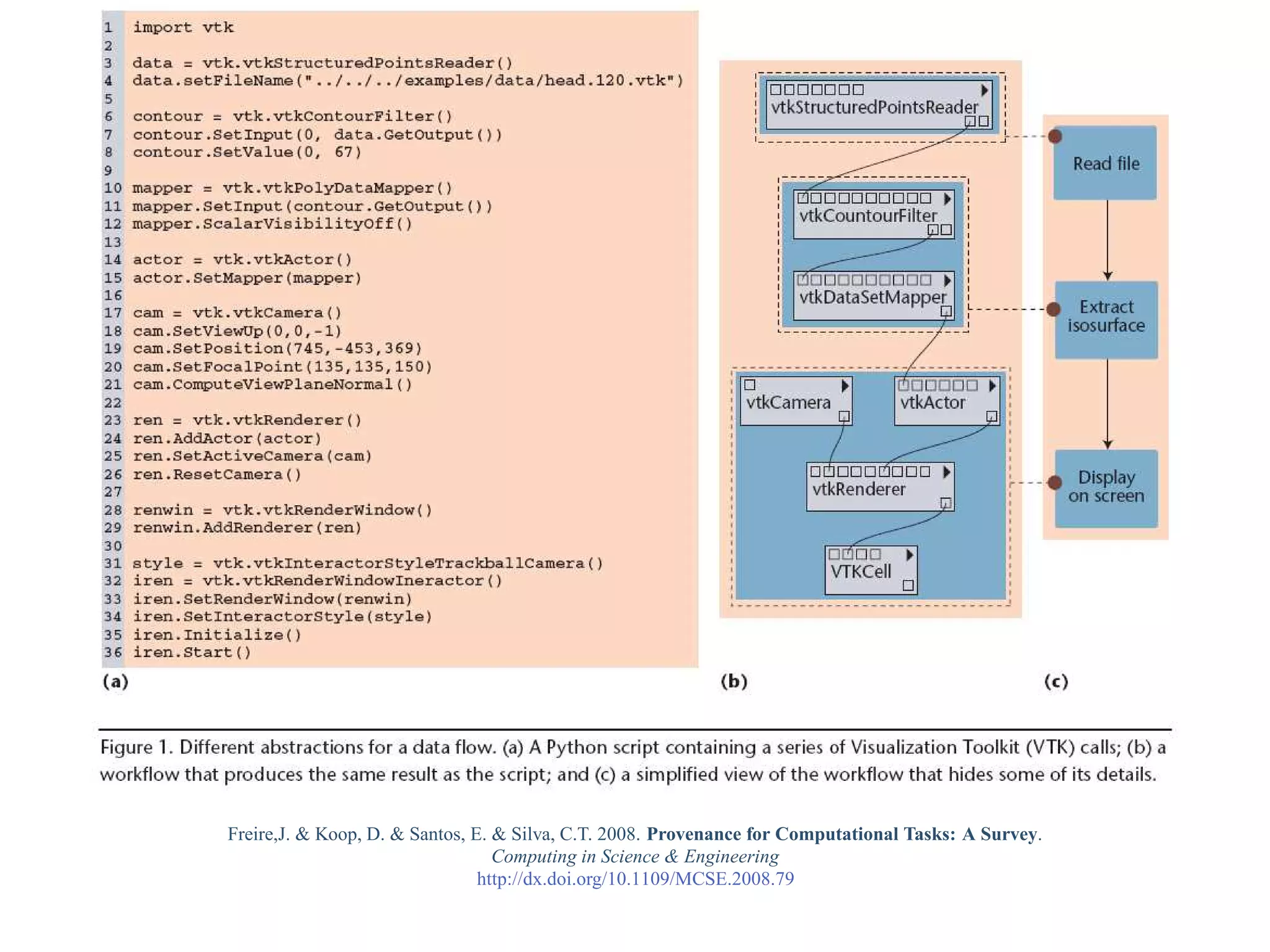
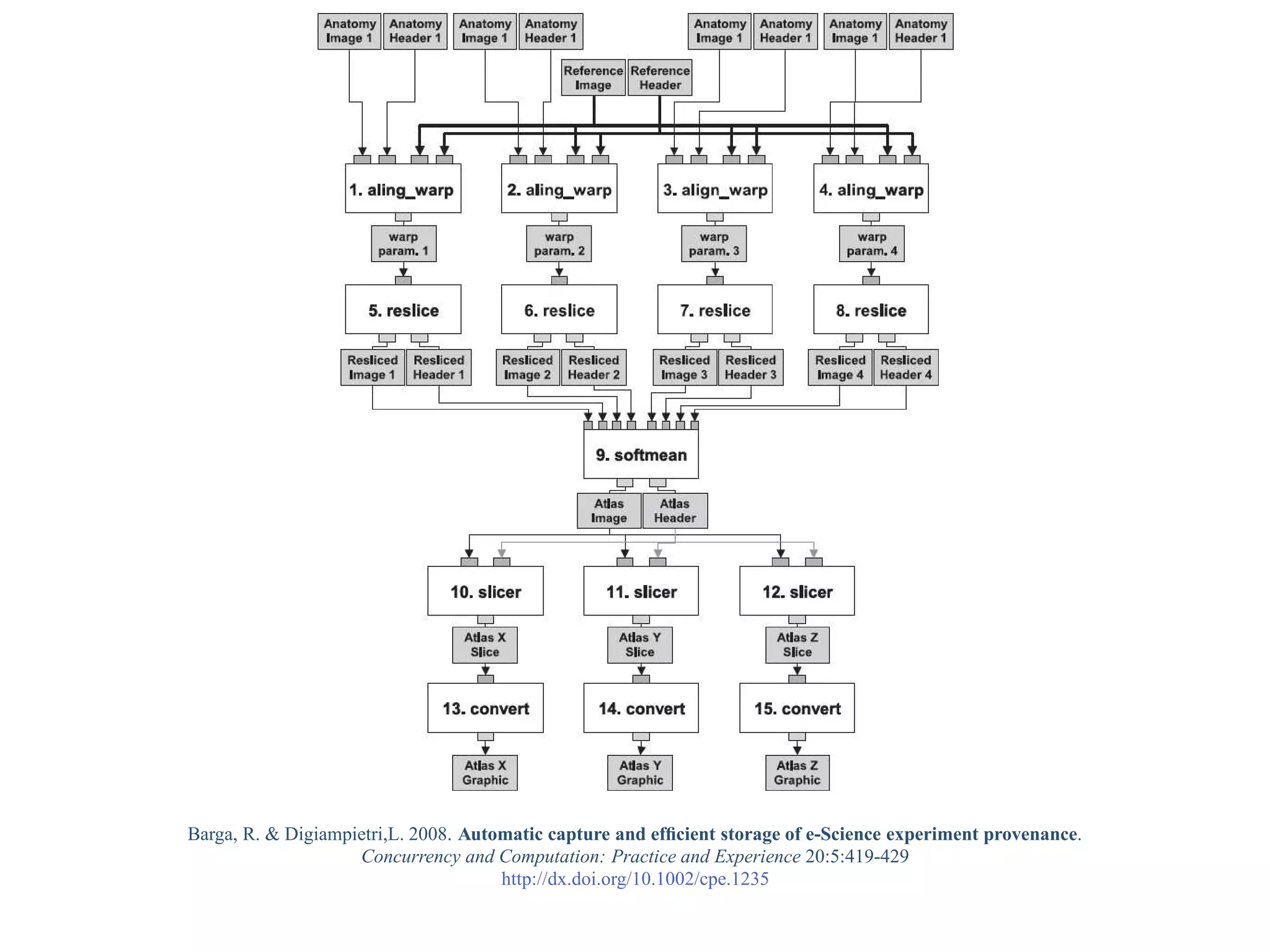
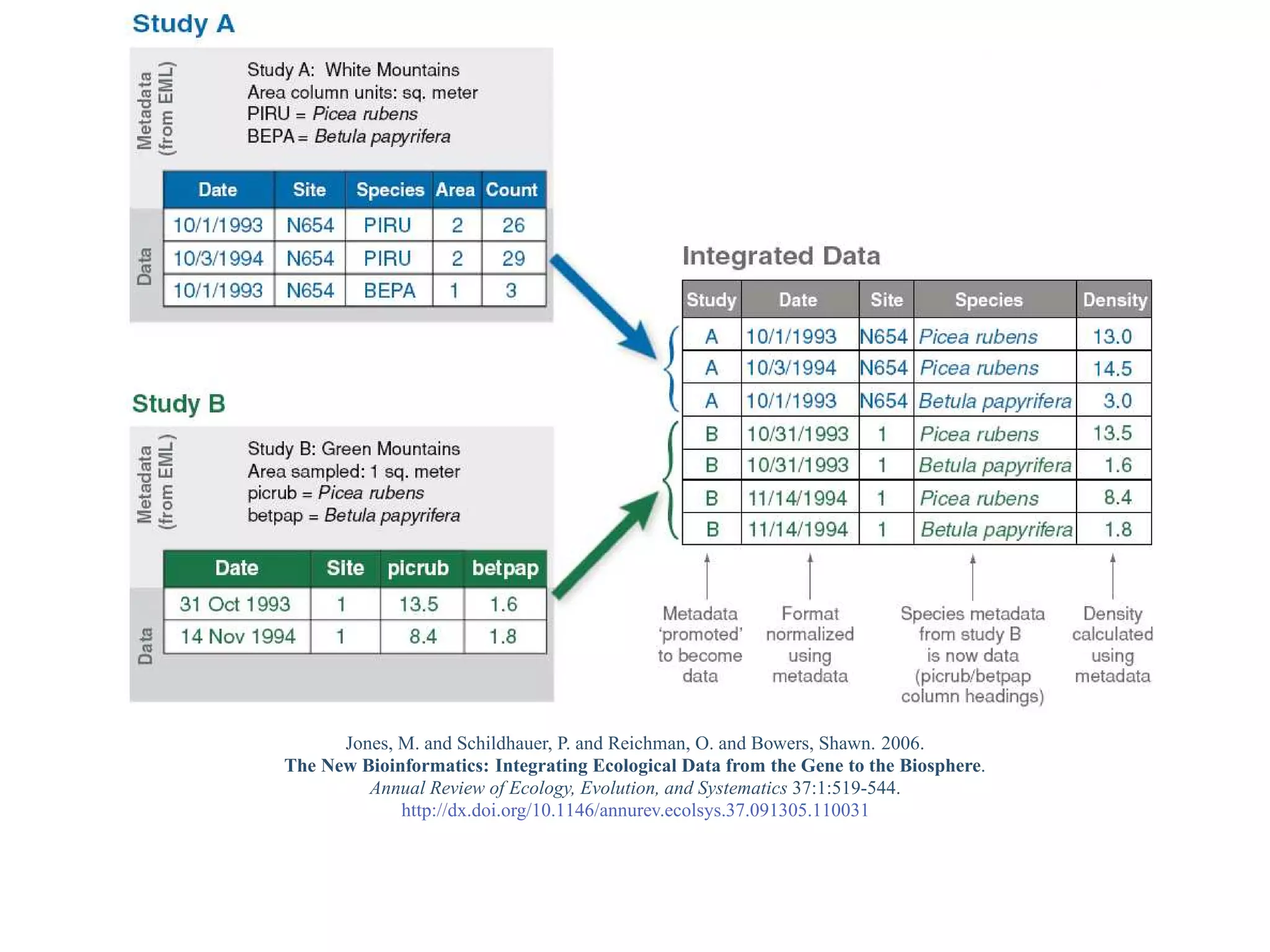
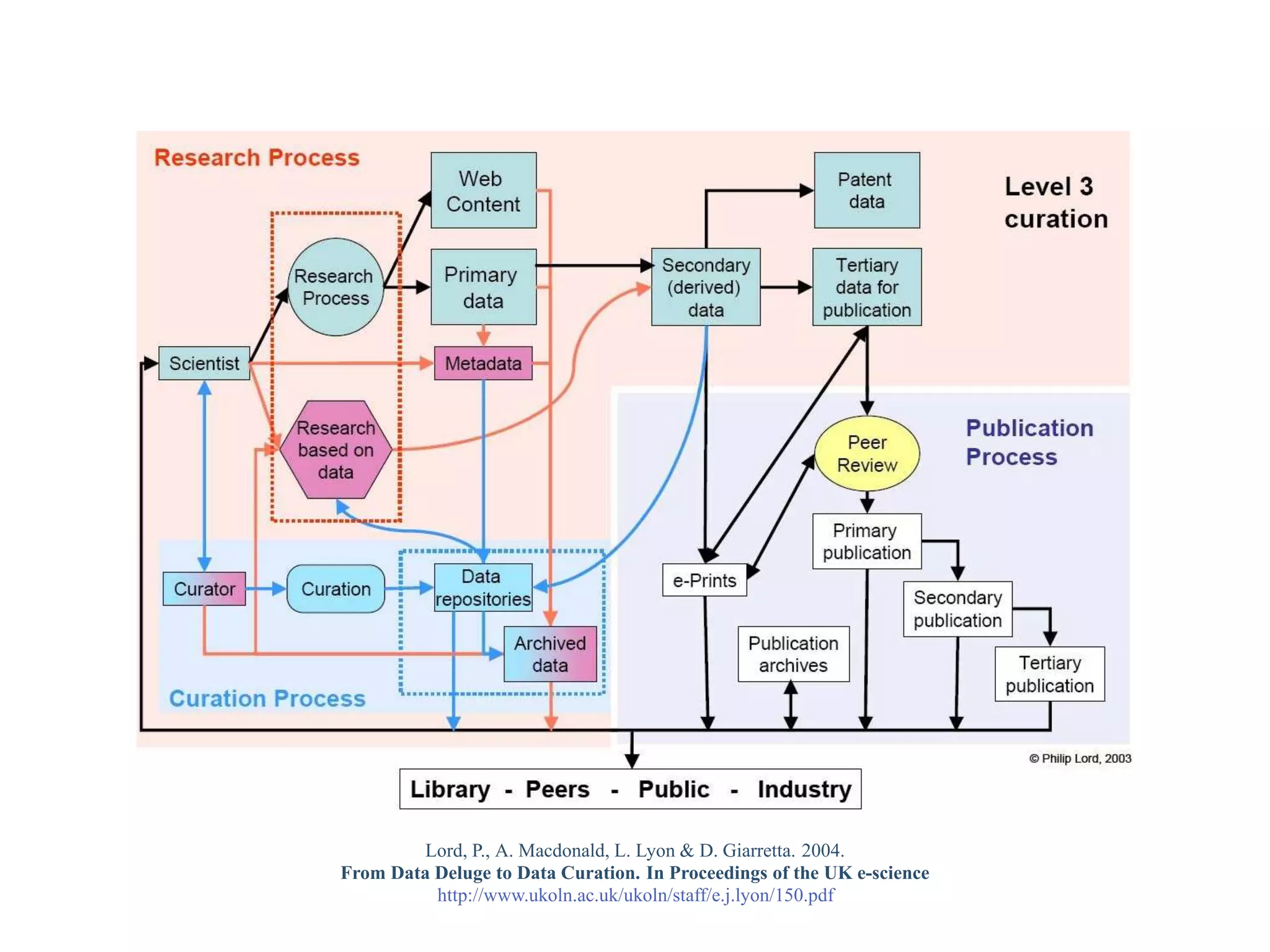
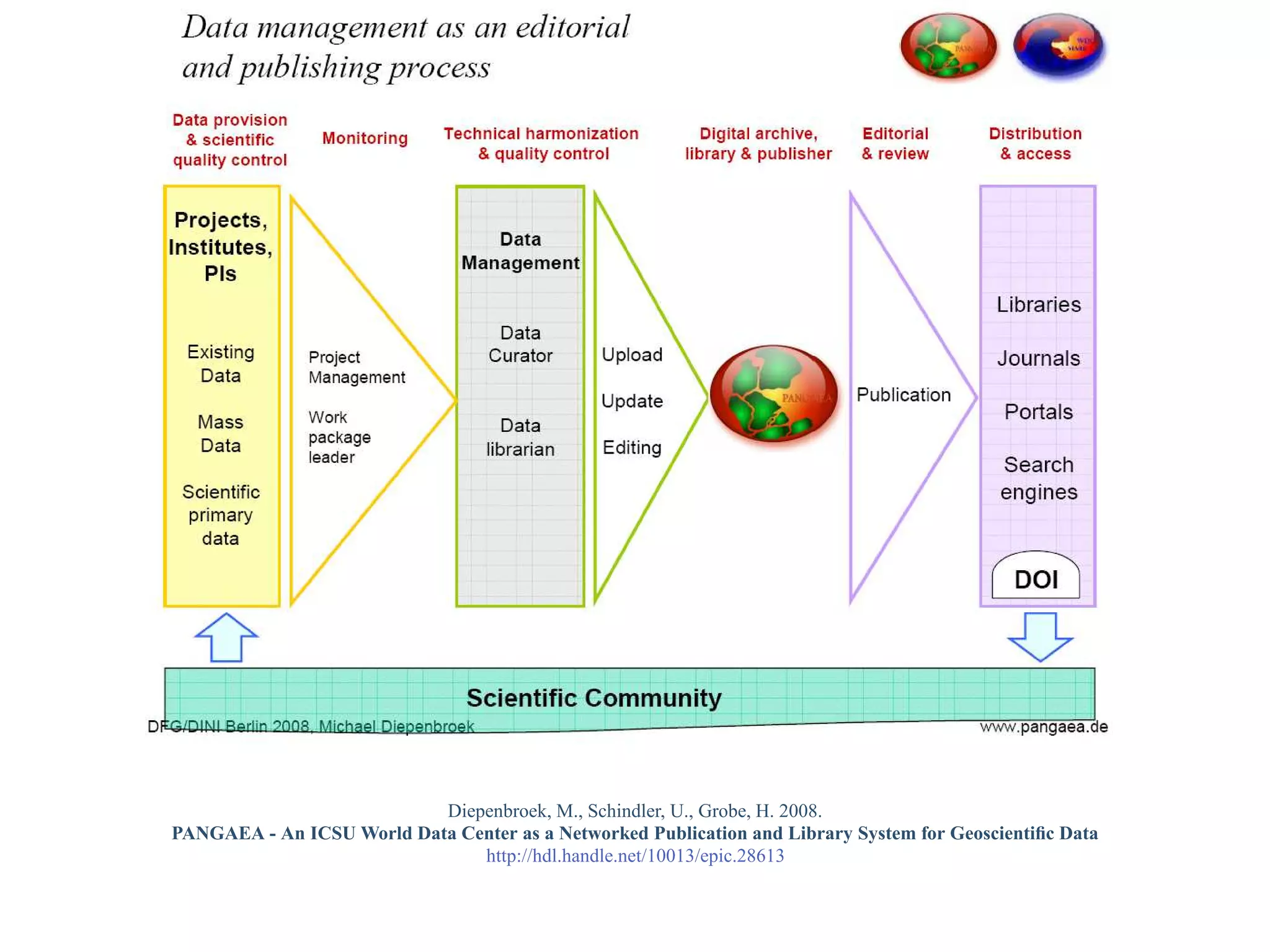
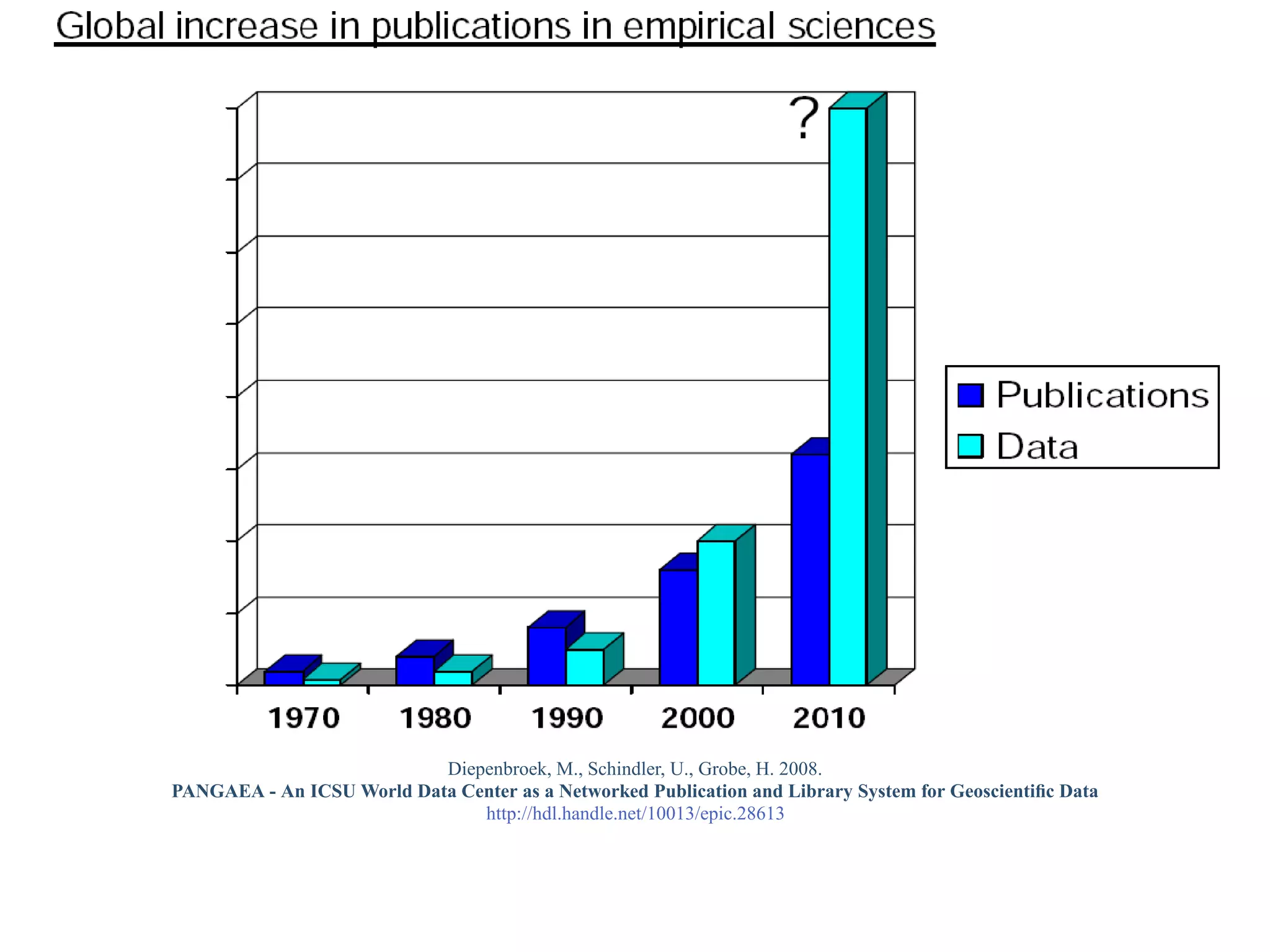
This document provides a gentle introduction to research data management and the research data lifecycle. It defines key terms like research, research data, and research data lifecycles. It discusses the benefits of data sharing, including enabling new research and testing new hypotheses. Research data can be complex with data, metadata, transformations, and combinations. The document outlines the research data lifecycle from collection to archiving and roles in data management.




![Degradation in information content associated with data and metadata over time
Status quo
Time of publication
Information Content of Data and Metadata
Specific details about problems with individual items or specific
dates of collection are lost relatively rapidly
General details about the data collection are lost
through time
Retirement or career change makes access by
scientists to “mental storage” difficult or unlikely
Accident may destroy Death of investigator and subse-
data and documentation quent loss of remaining records
Time
Newton, G. 2009. After Michener et al. 1997, Ecological Applications 7:1:330-342
DOI 10.1890/1051-0761(1997)007[0330:NMFTES]2.0.CO;2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libschool20091126-100415132500-phpapp02/75/Research-Data-Management-and-the-Research-Data-Lifecycle-a-Gentle-Introduction-8-2048.jpg)













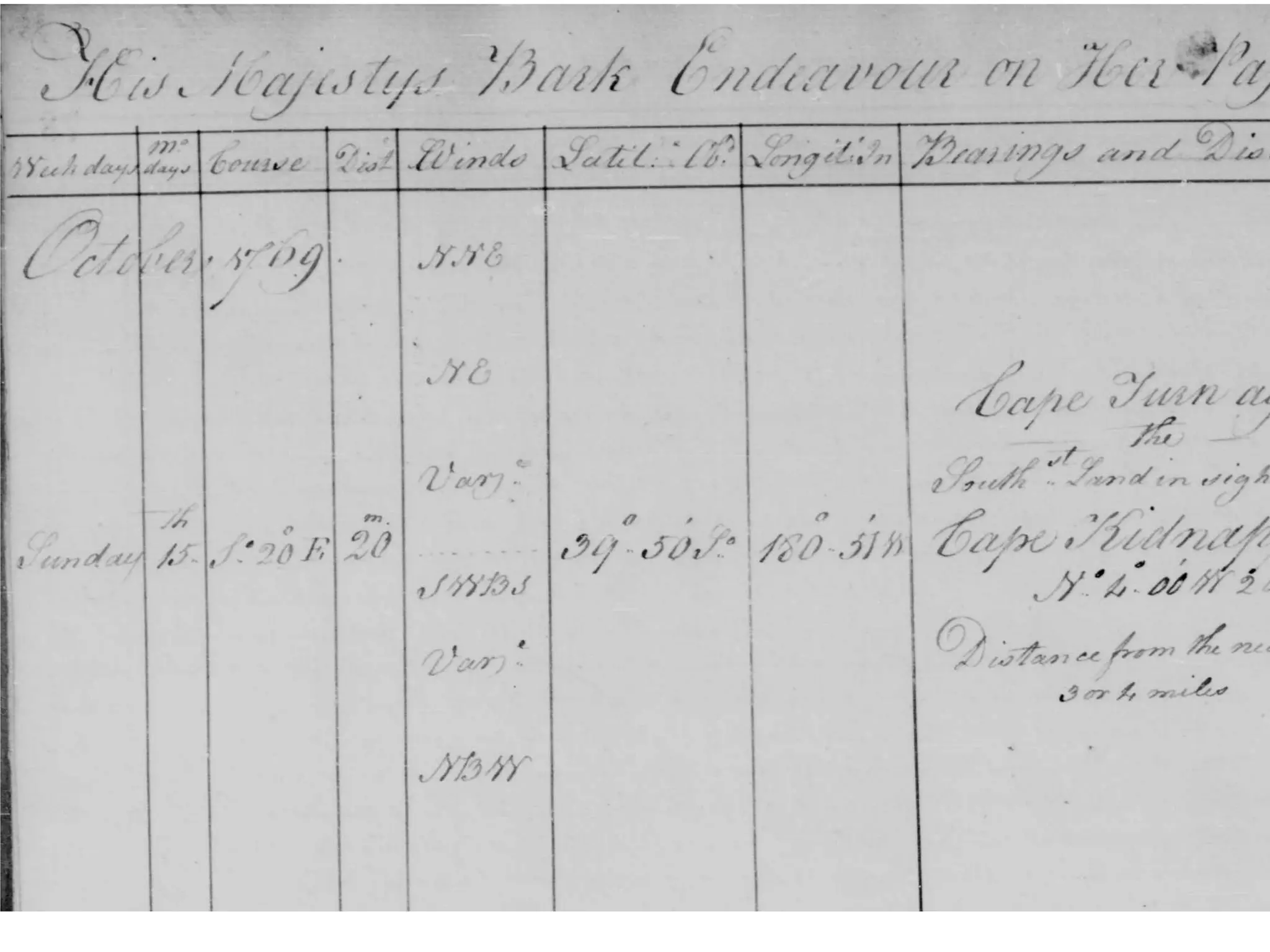

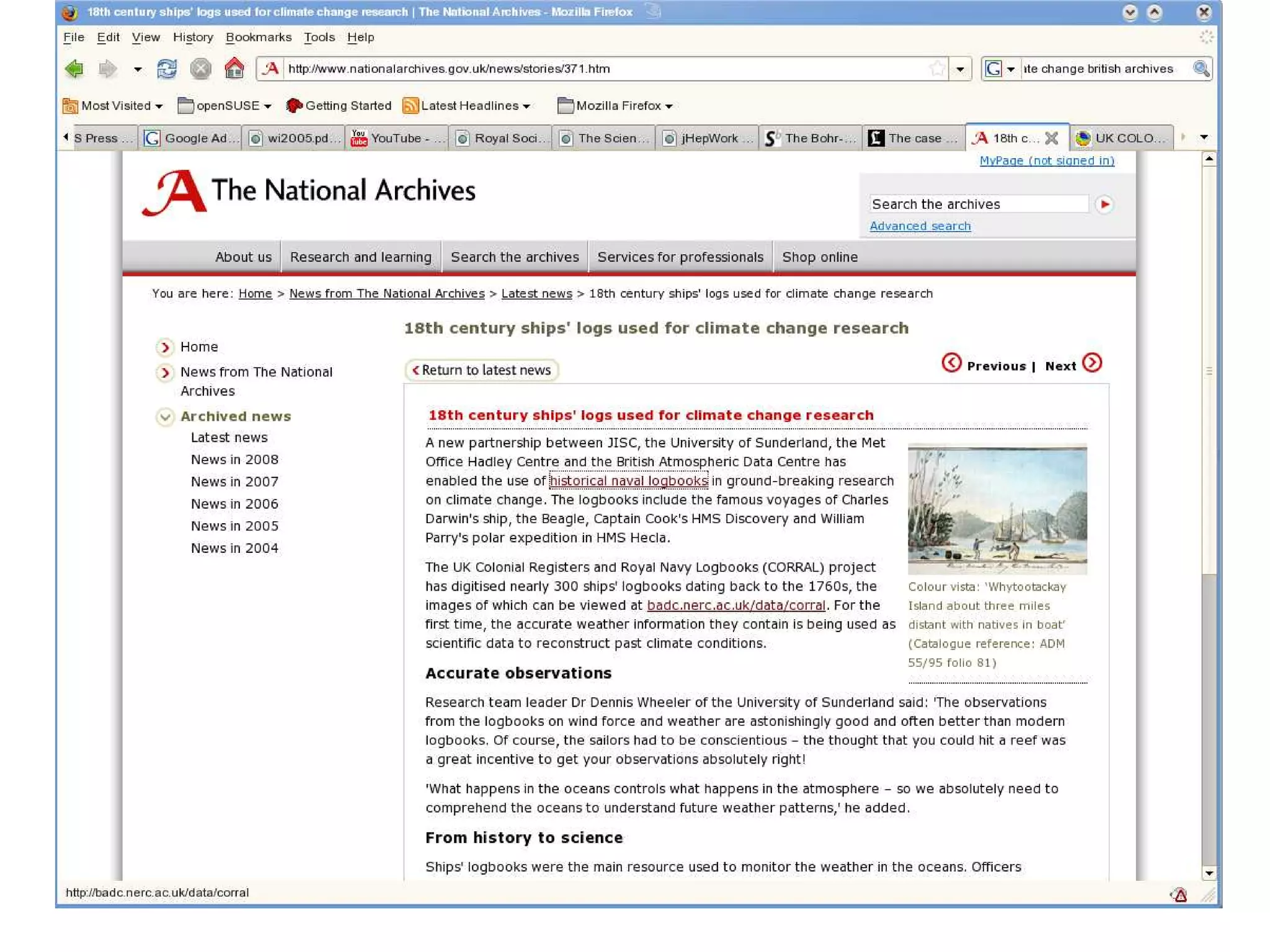
![Captain Cook’s logs
Some definitions
His Majestys Bark [a type of ship] Endeavour on Her Passage On
Data Sharing
the Coast of New Zealand from Poverty Bay to Southw
Research & Research
Data Lifecycle October 15th 1769; Course: S 20 ◦ E; Winds: Vary; Location:
Research Data 39◦ 50′ 180◦ 51′ ; Moderate and fair weather...thunder and spitting
Complexity
Data Archiving
rain... — Log 39, page 79. UK National Archives
Data Management
Roles
s Record of date, time, location (lat/long), the sea conditions and
Conclusion
local weather conditions
s Now being mined by JISC, the University of Sunderland, the
Met Office Hadley Centre and the British Atmospheric Data
Centre for climate change research
—http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/news/stories/371.htm
17 / 66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libschool20091126-100415132500-phpapp02/75/Research-Data-Management-and-the-Research-Data-Lifecycle-a-Gentle-Introduction-26-2048.jpg)