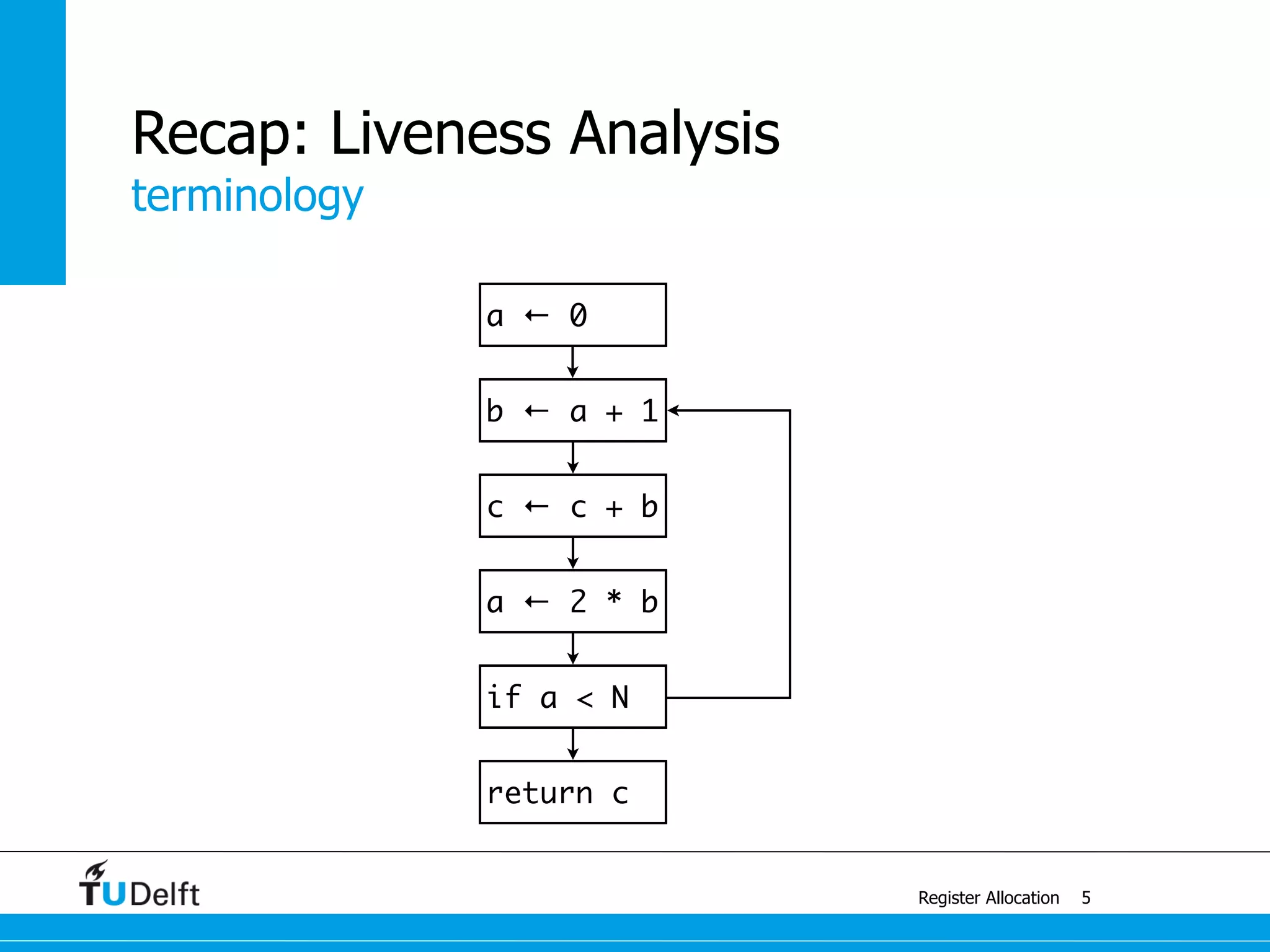
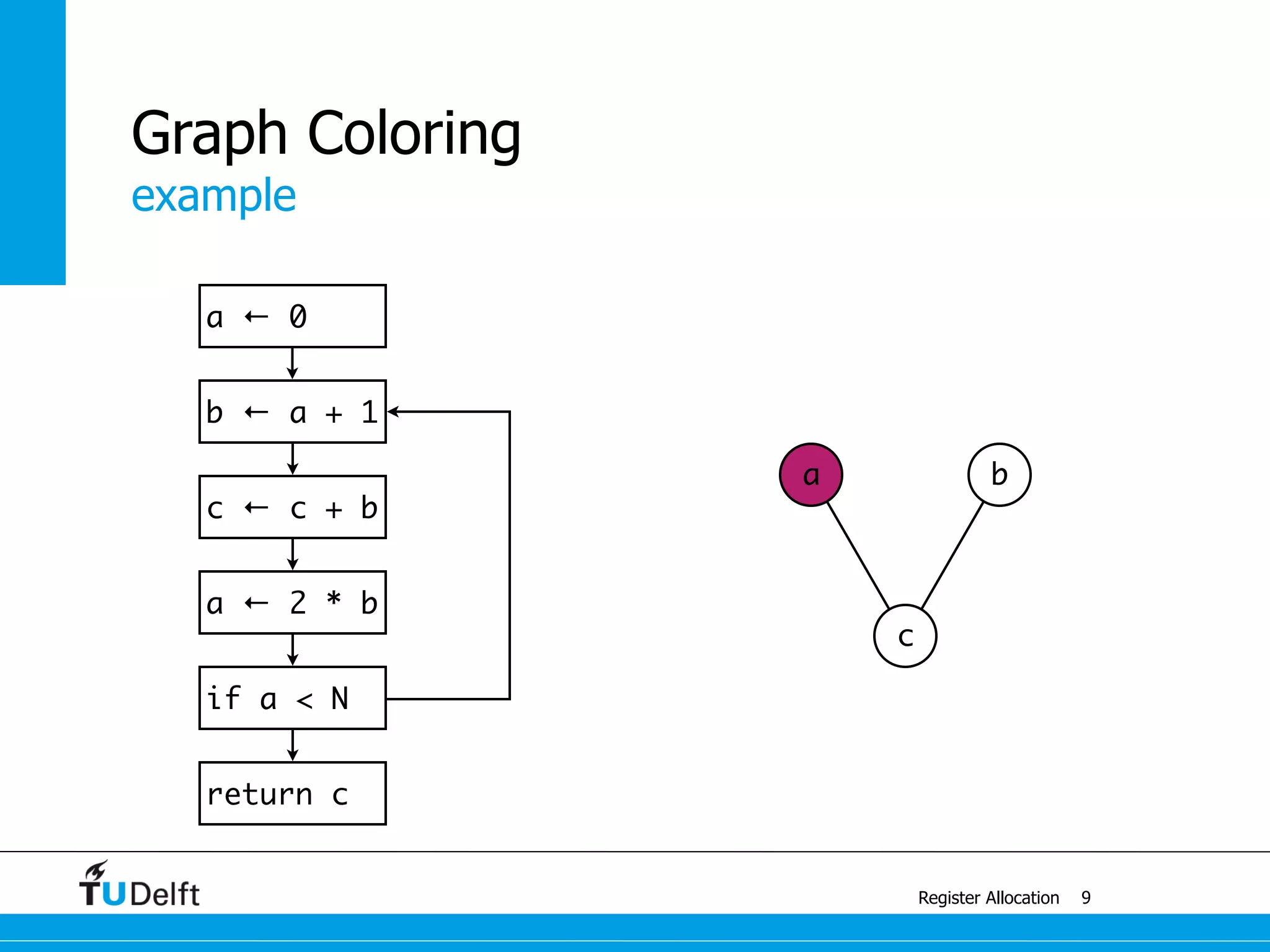
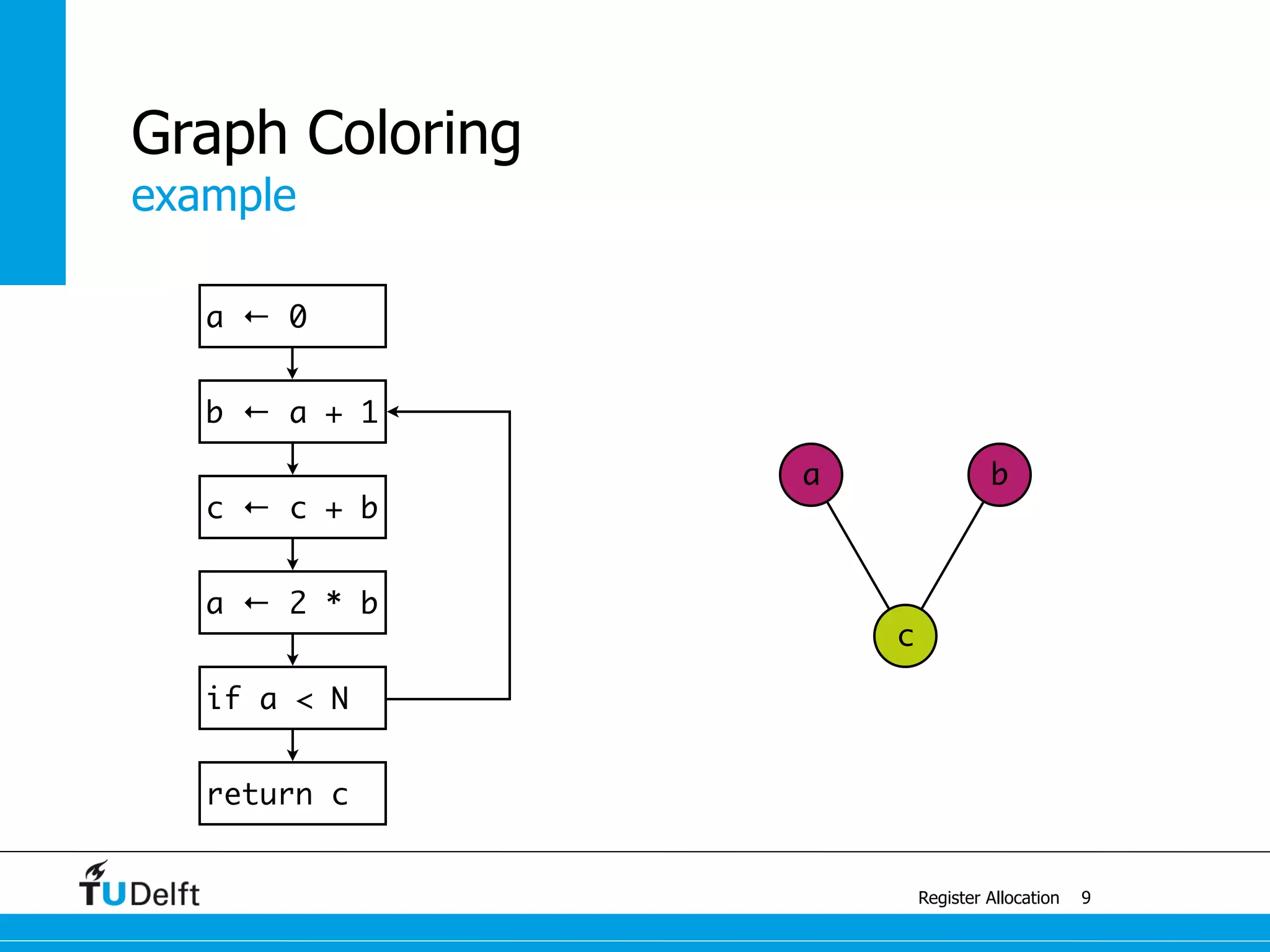
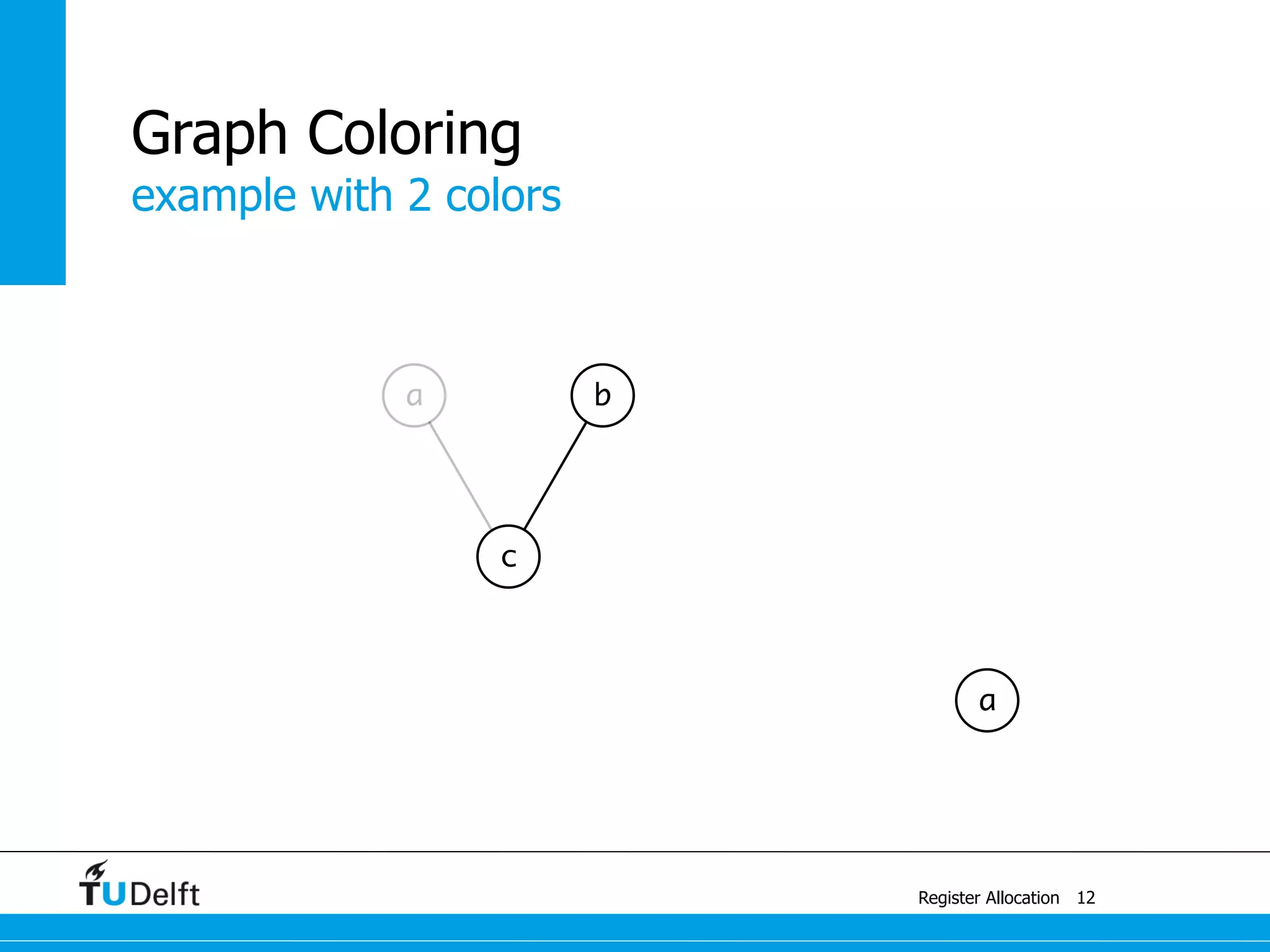
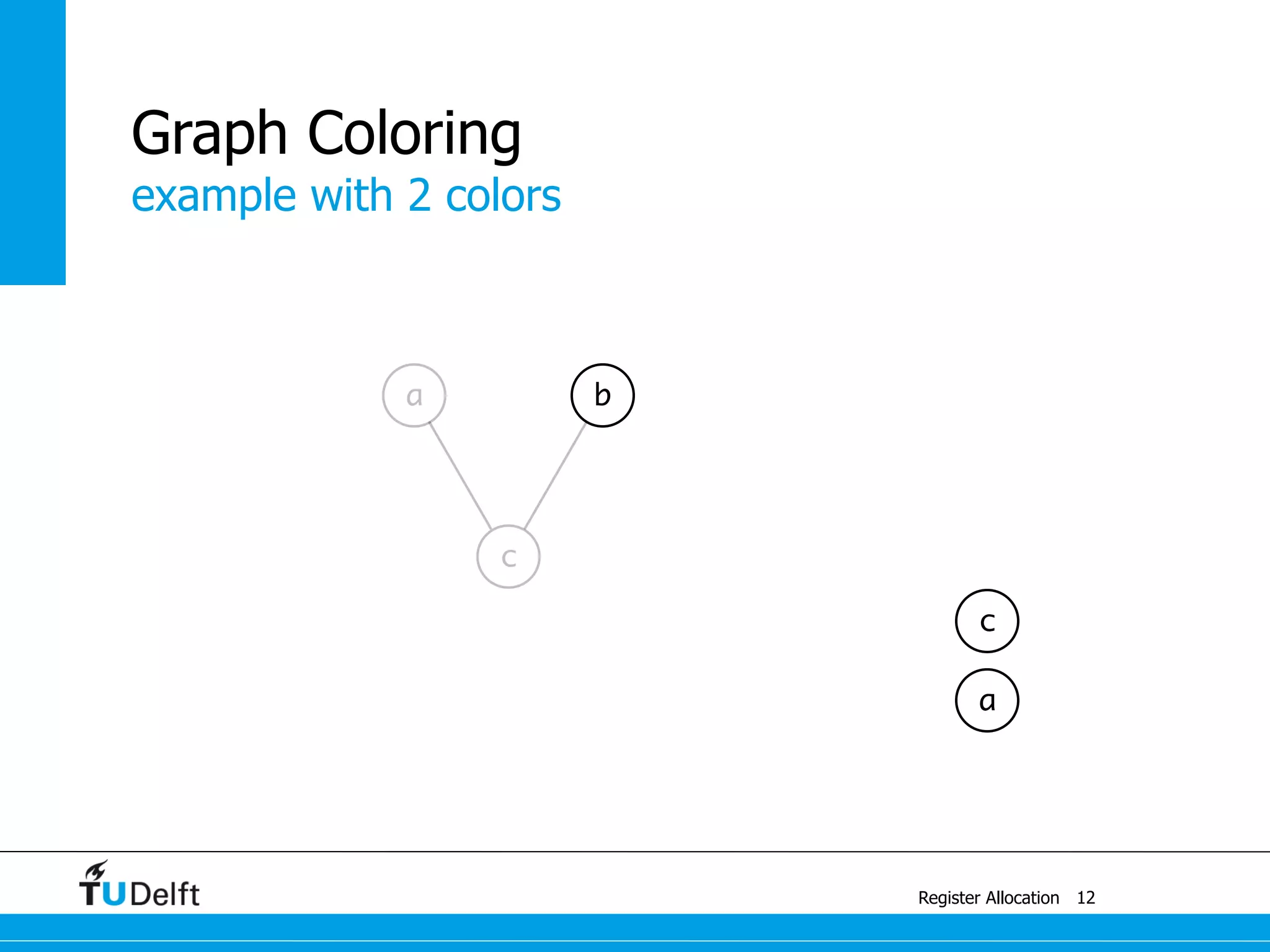
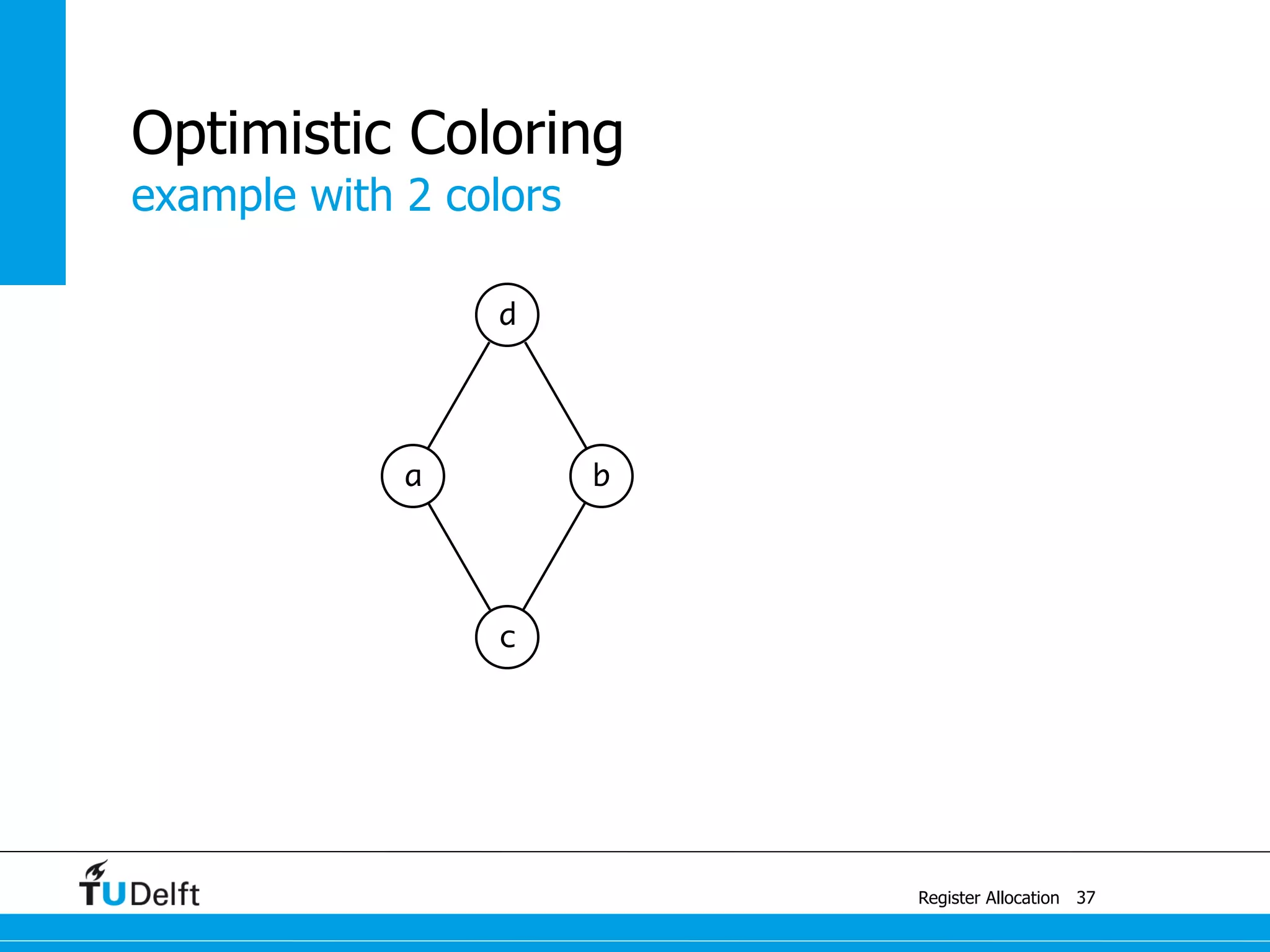
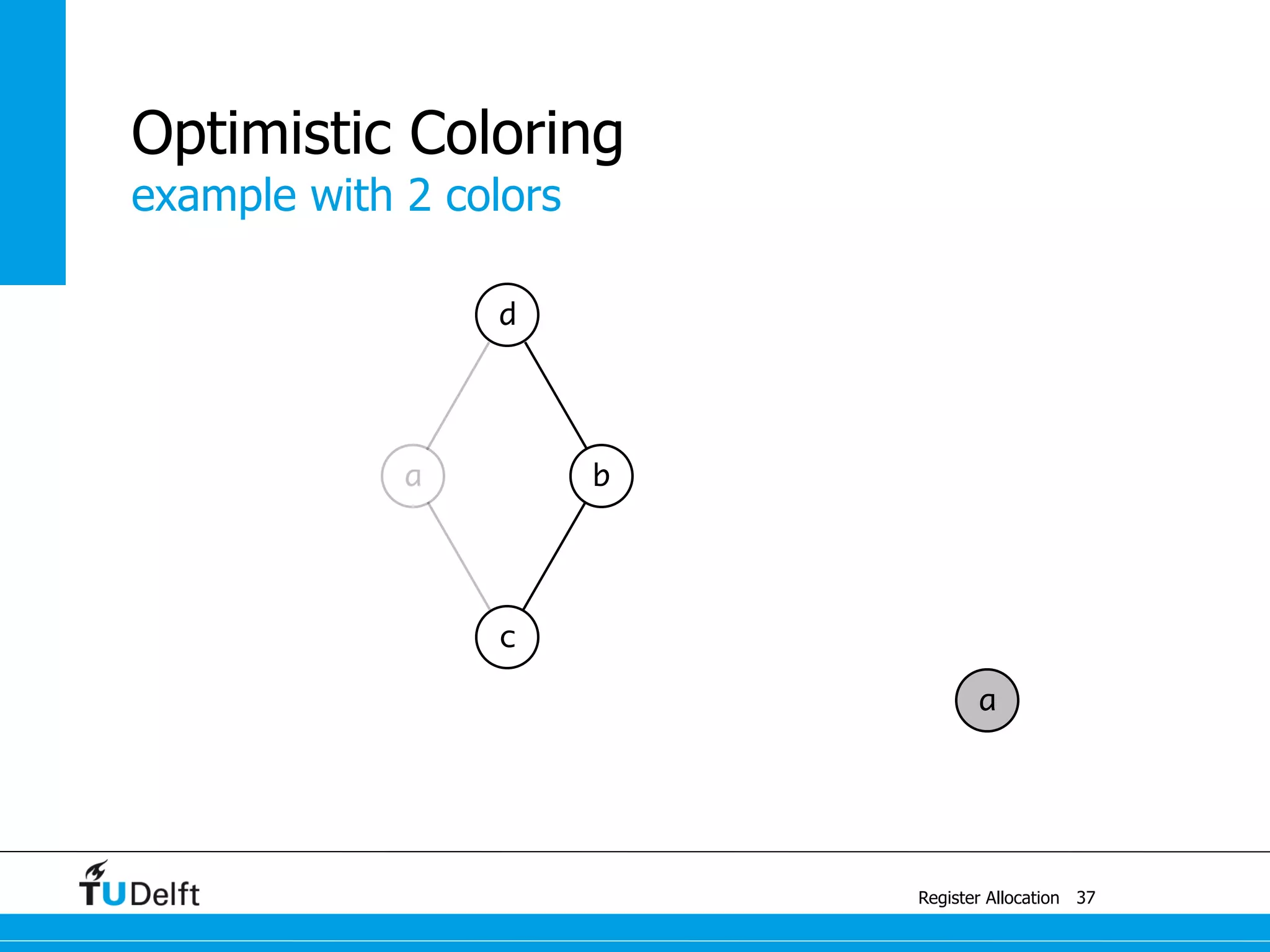
This document discusses register allocation in compiler construction. It begins with an example of constructing an interference graph from a code snippet during liveness analysis. It then covers the main steps of register allocation: constructing interference graphs from liveness analysis, graph coloring to assign registers while minimizing spills, and handling move instructions through coalescing. It provides examples demonstrating graph coloring on interference graphs with different numbers of available registers.

![exercise
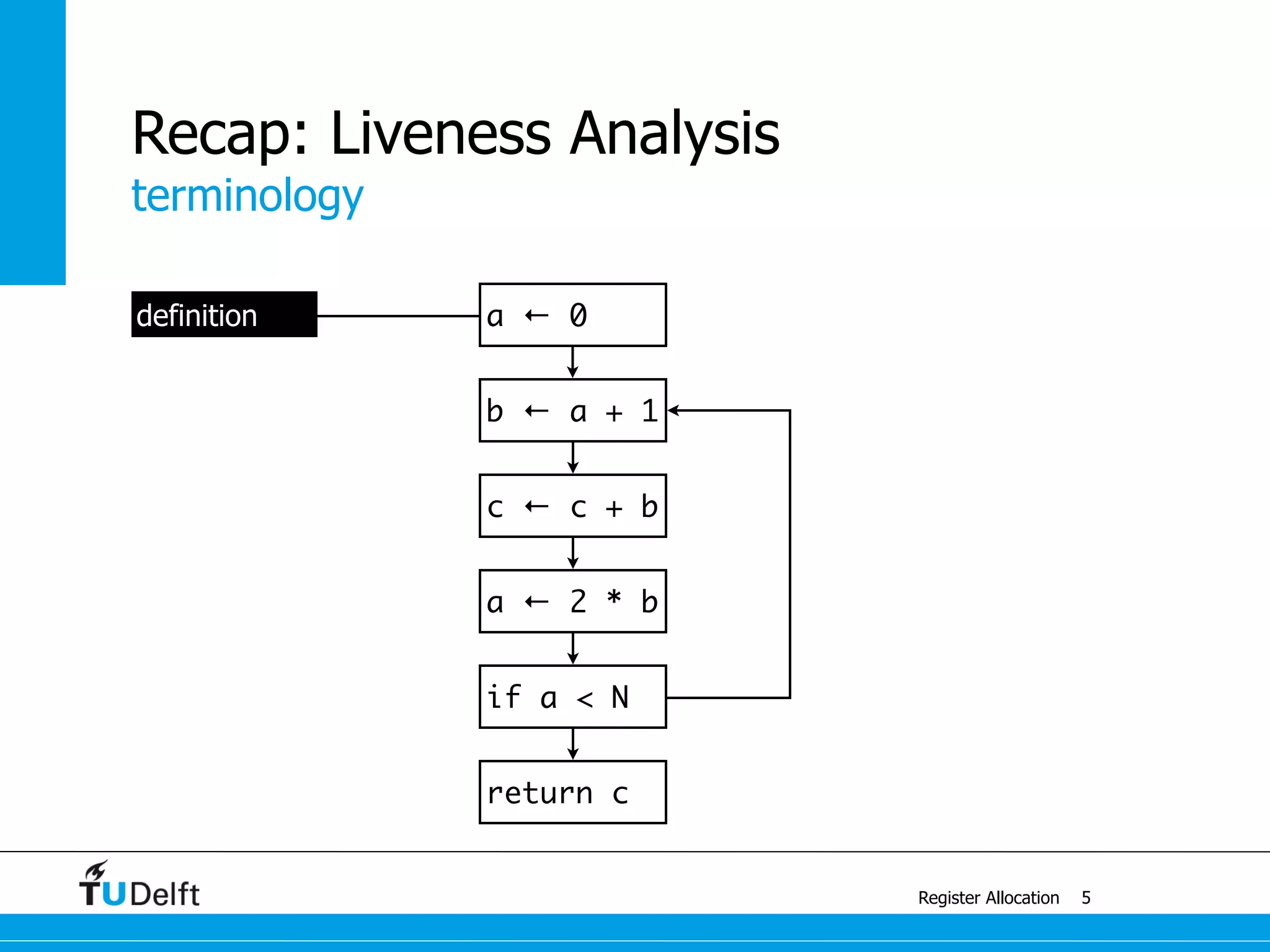
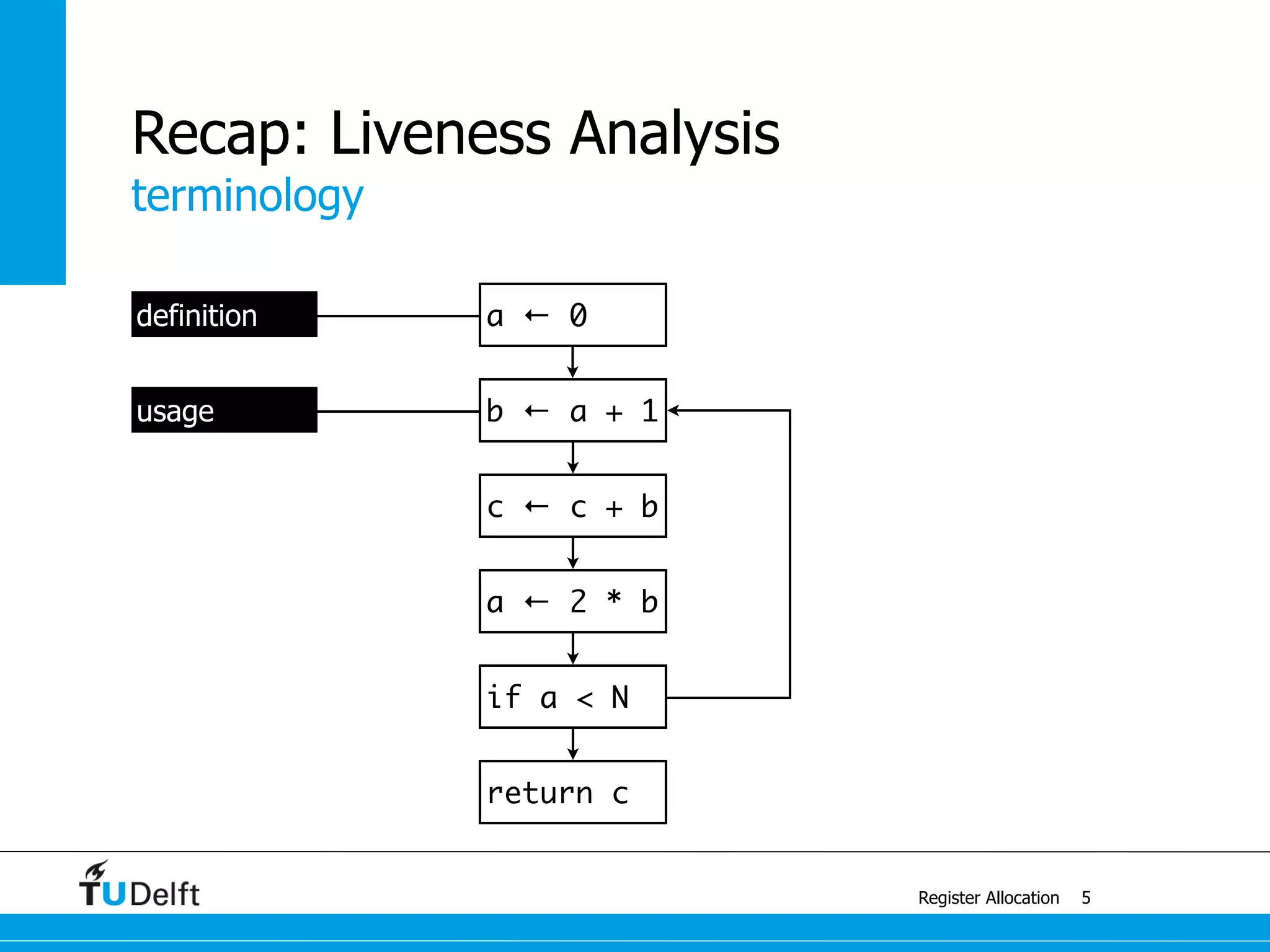
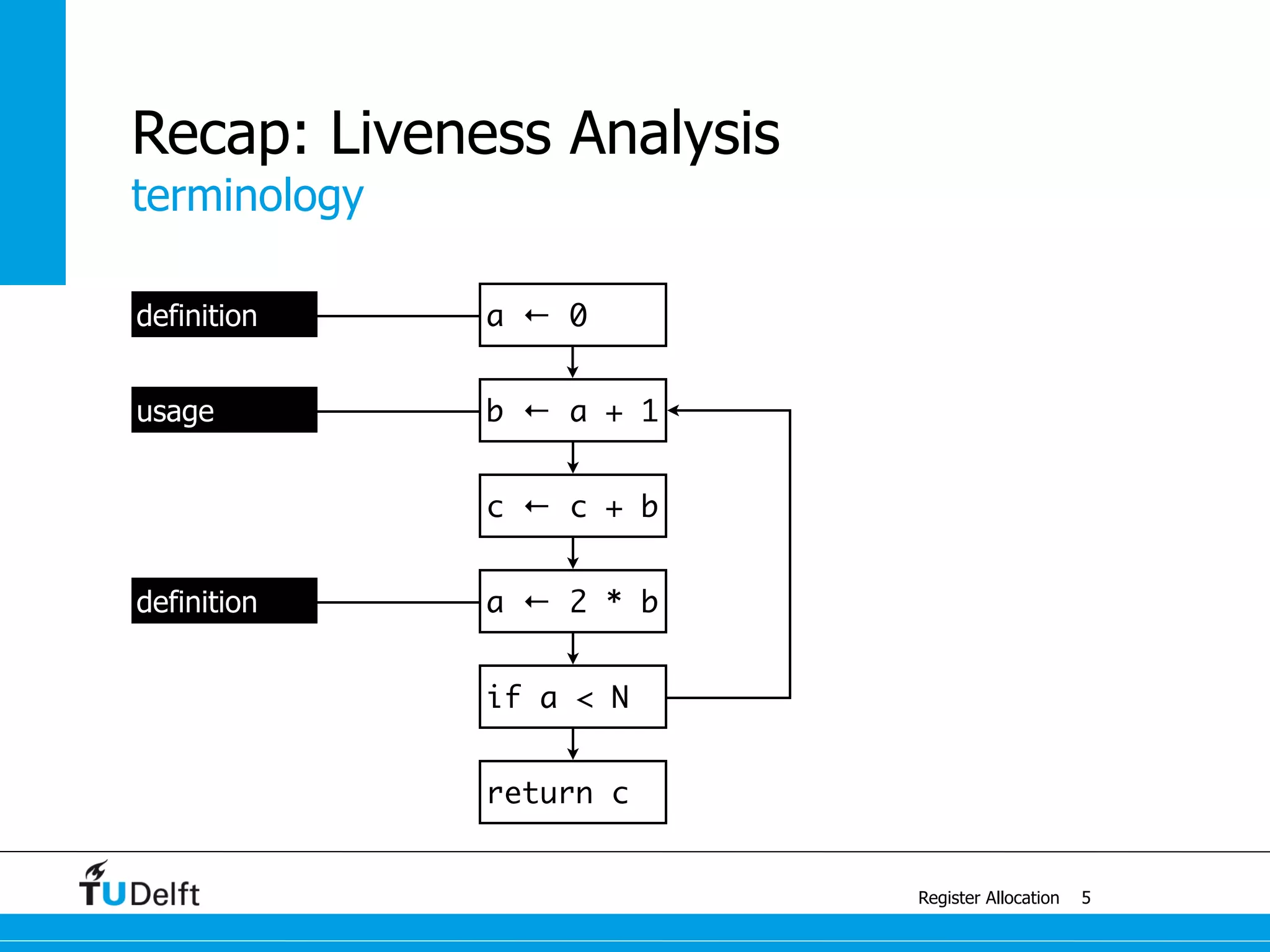
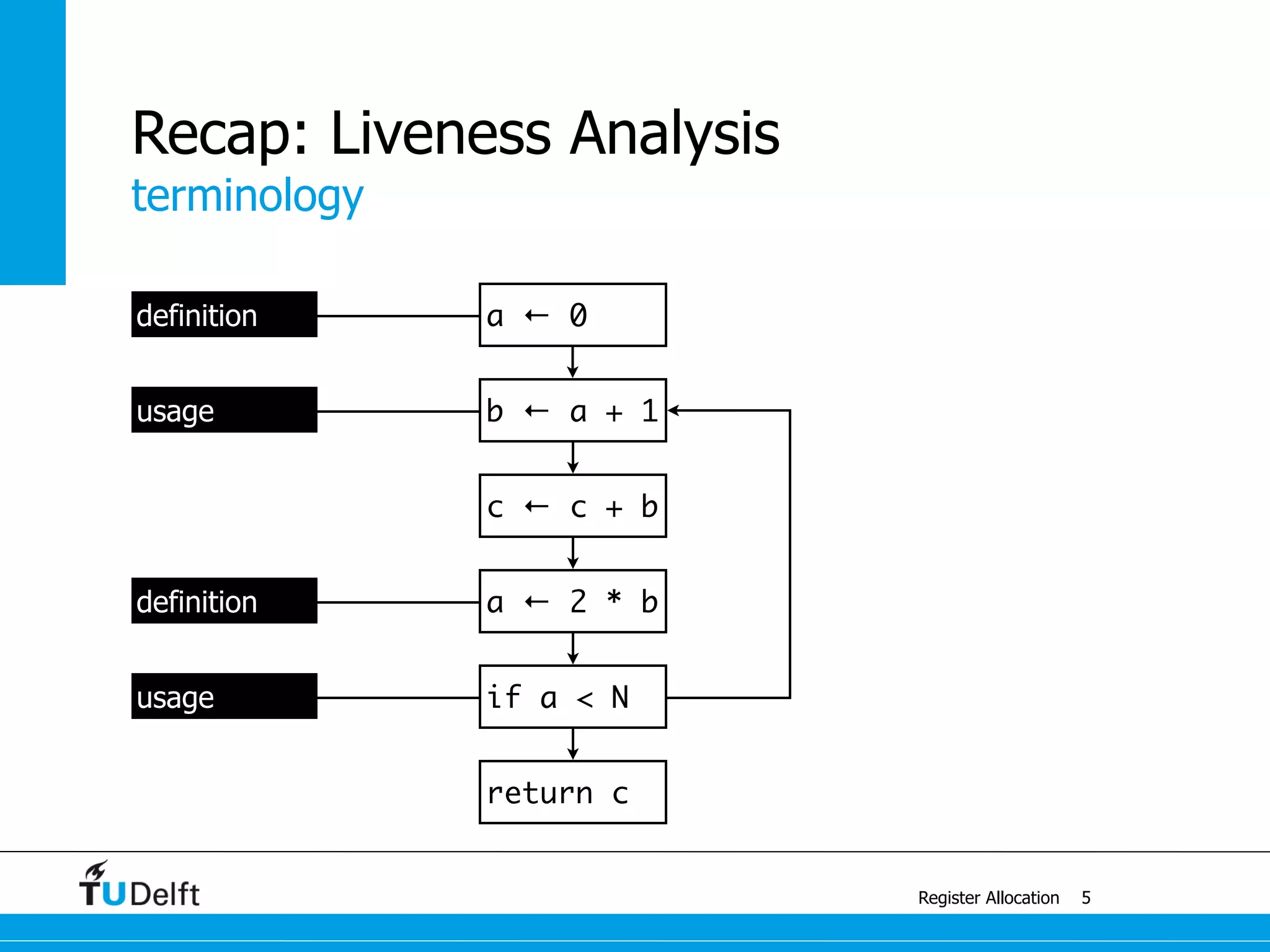
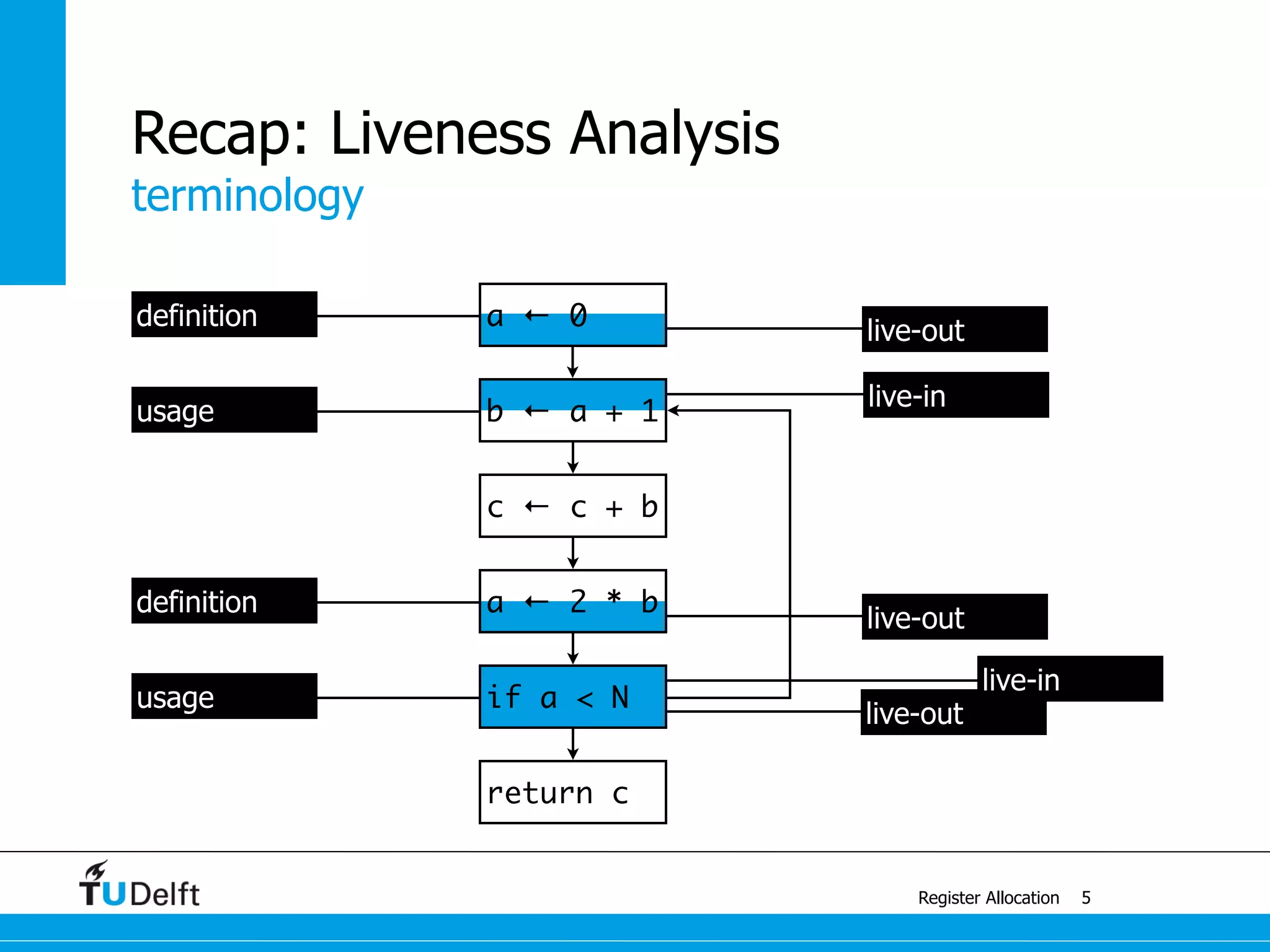
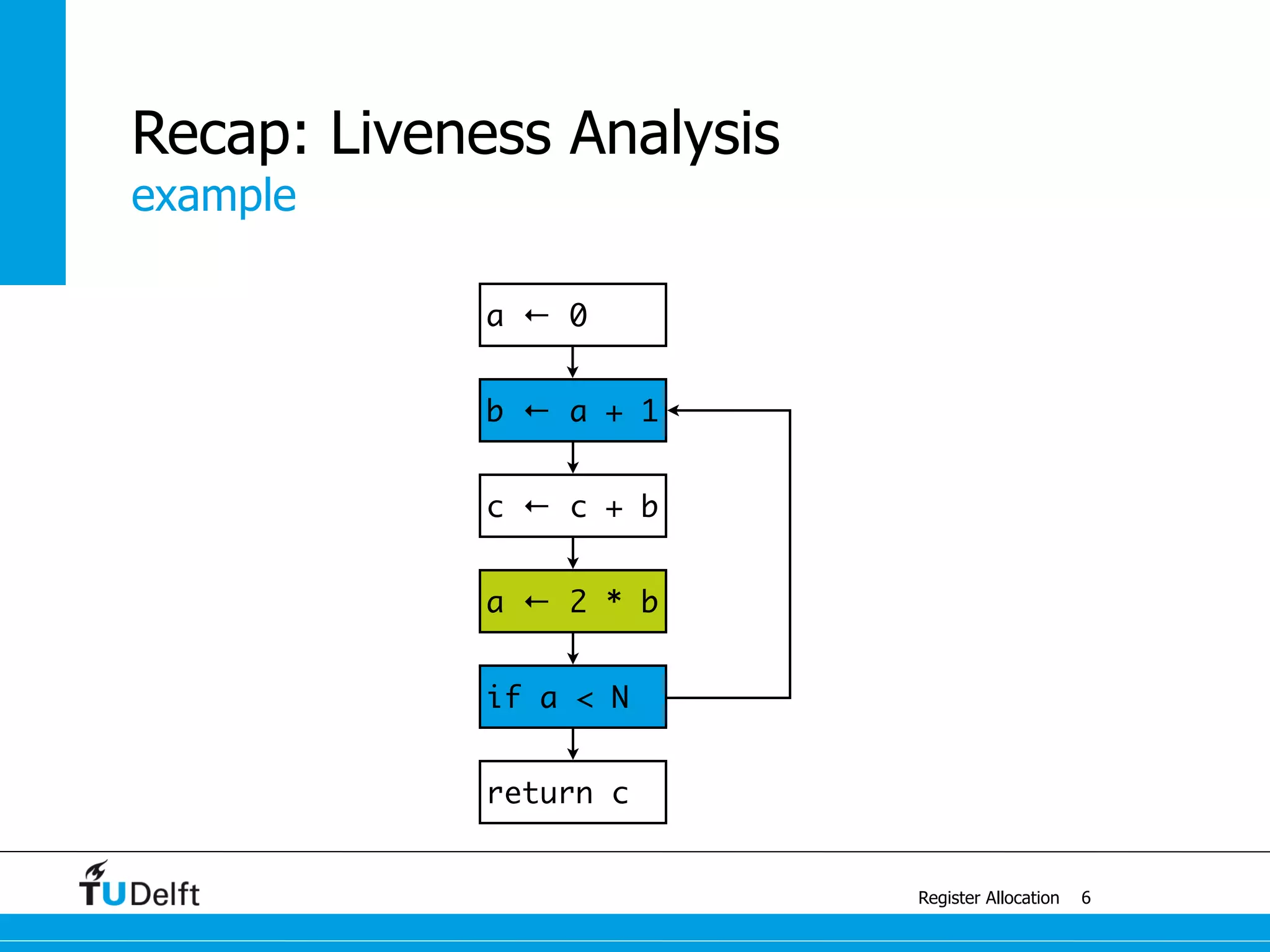
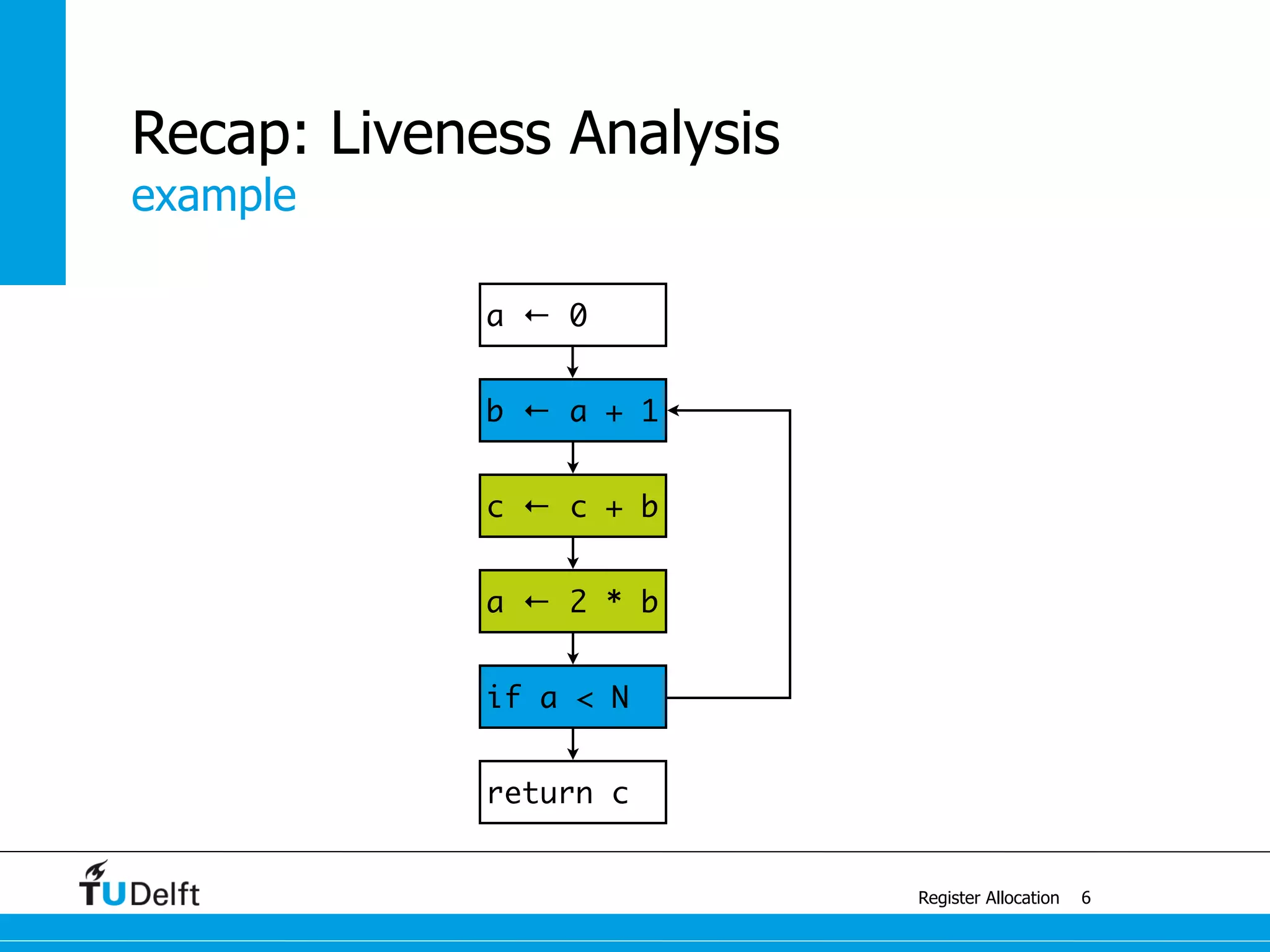
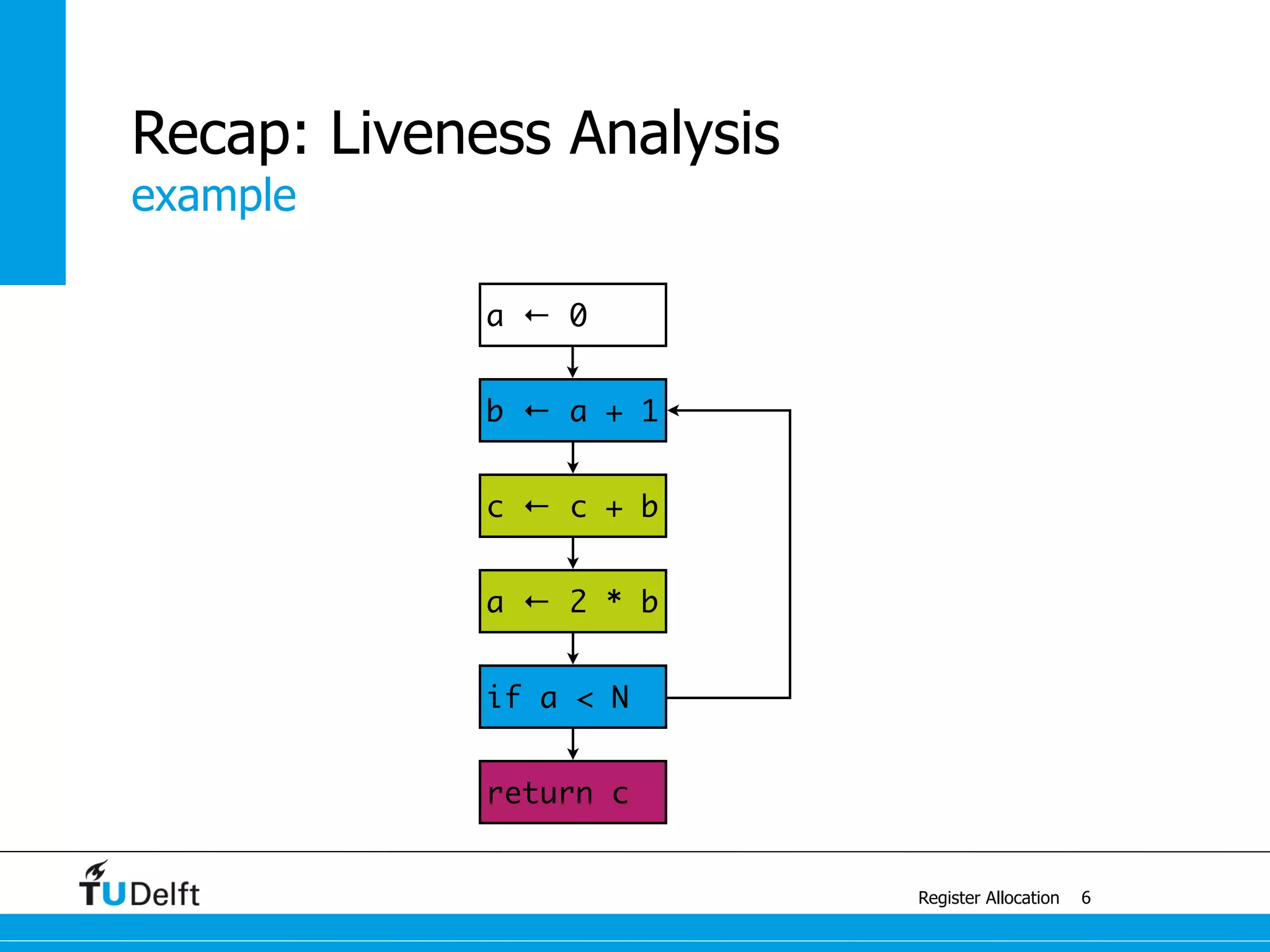
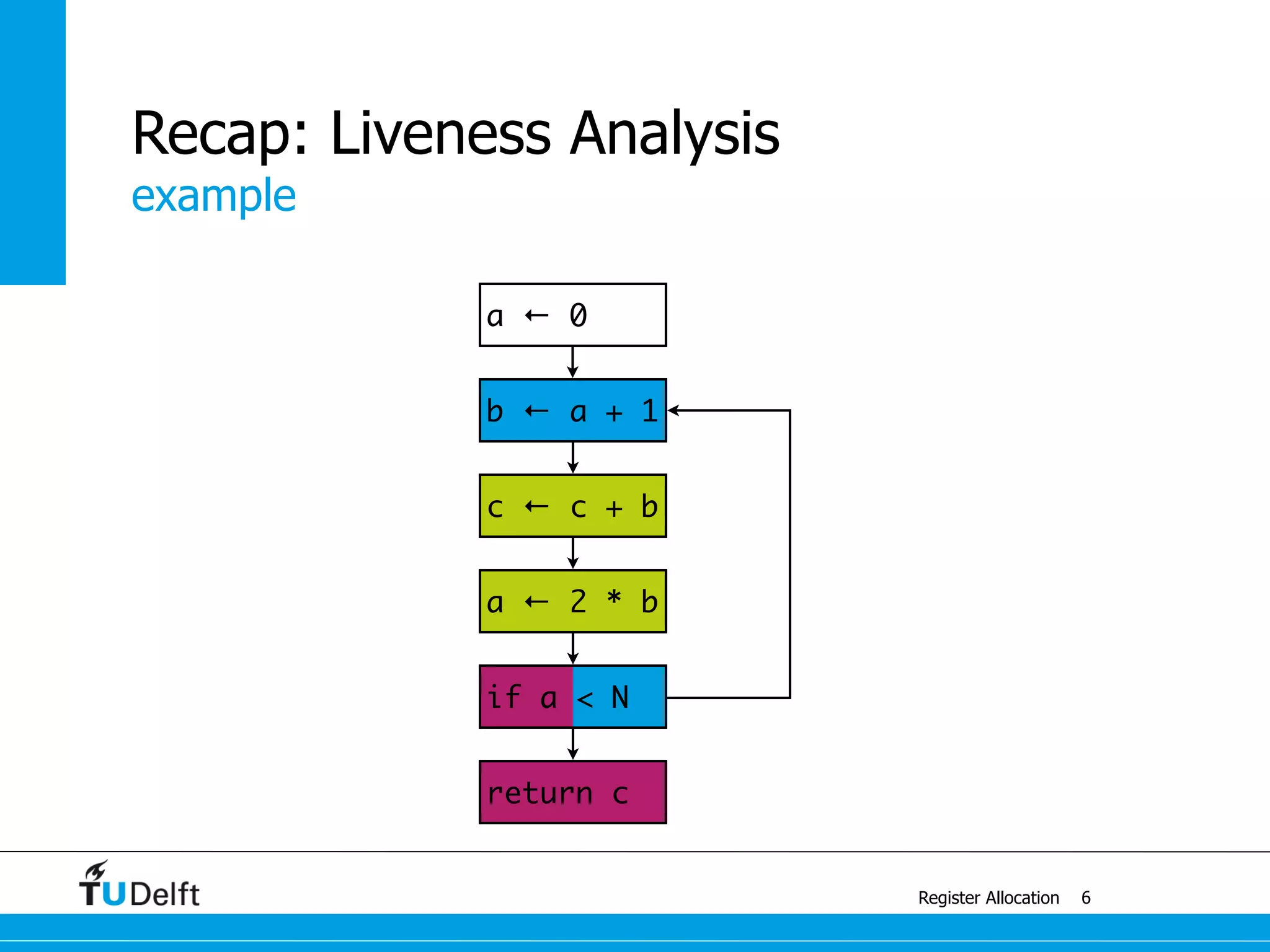
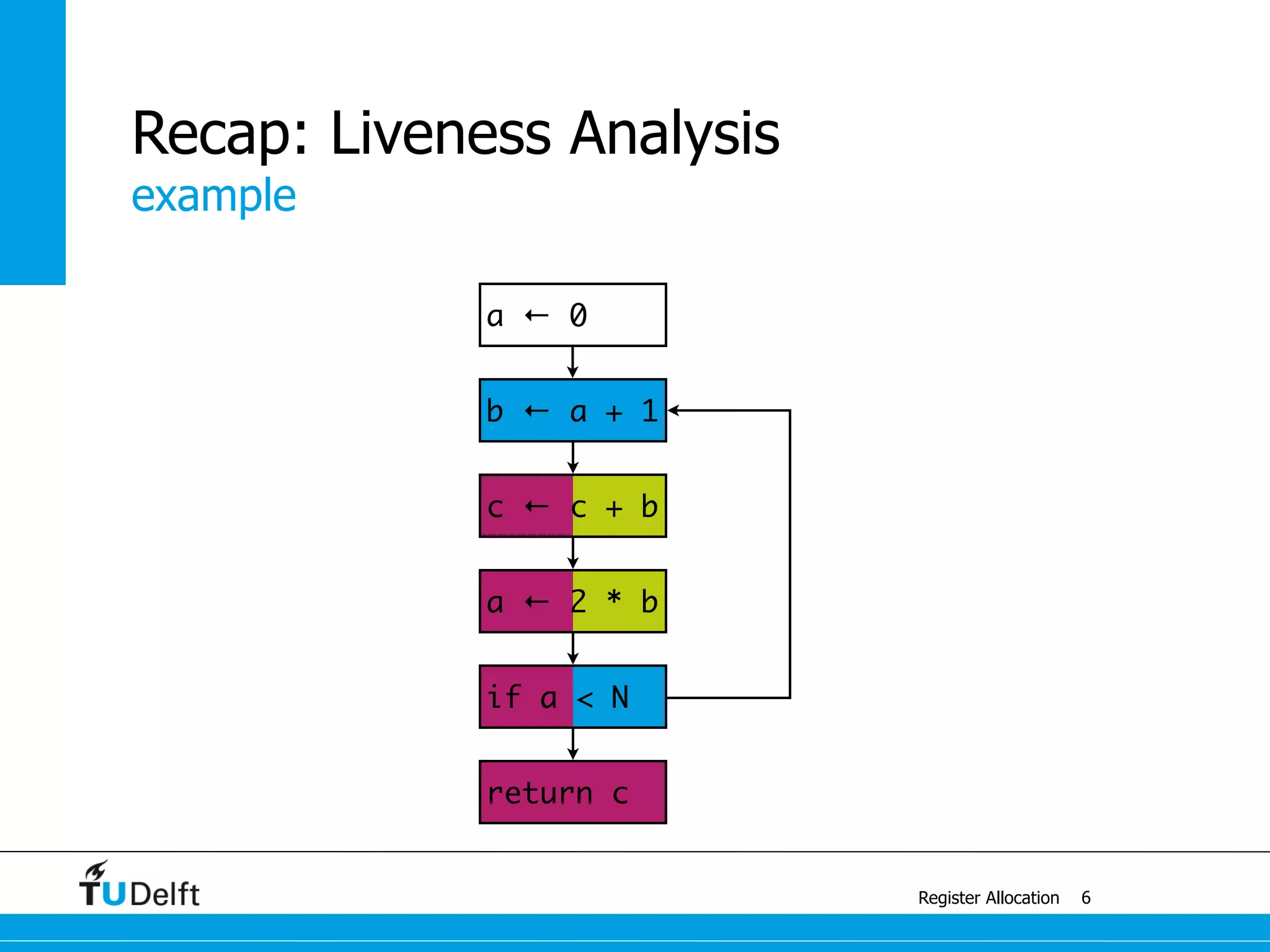
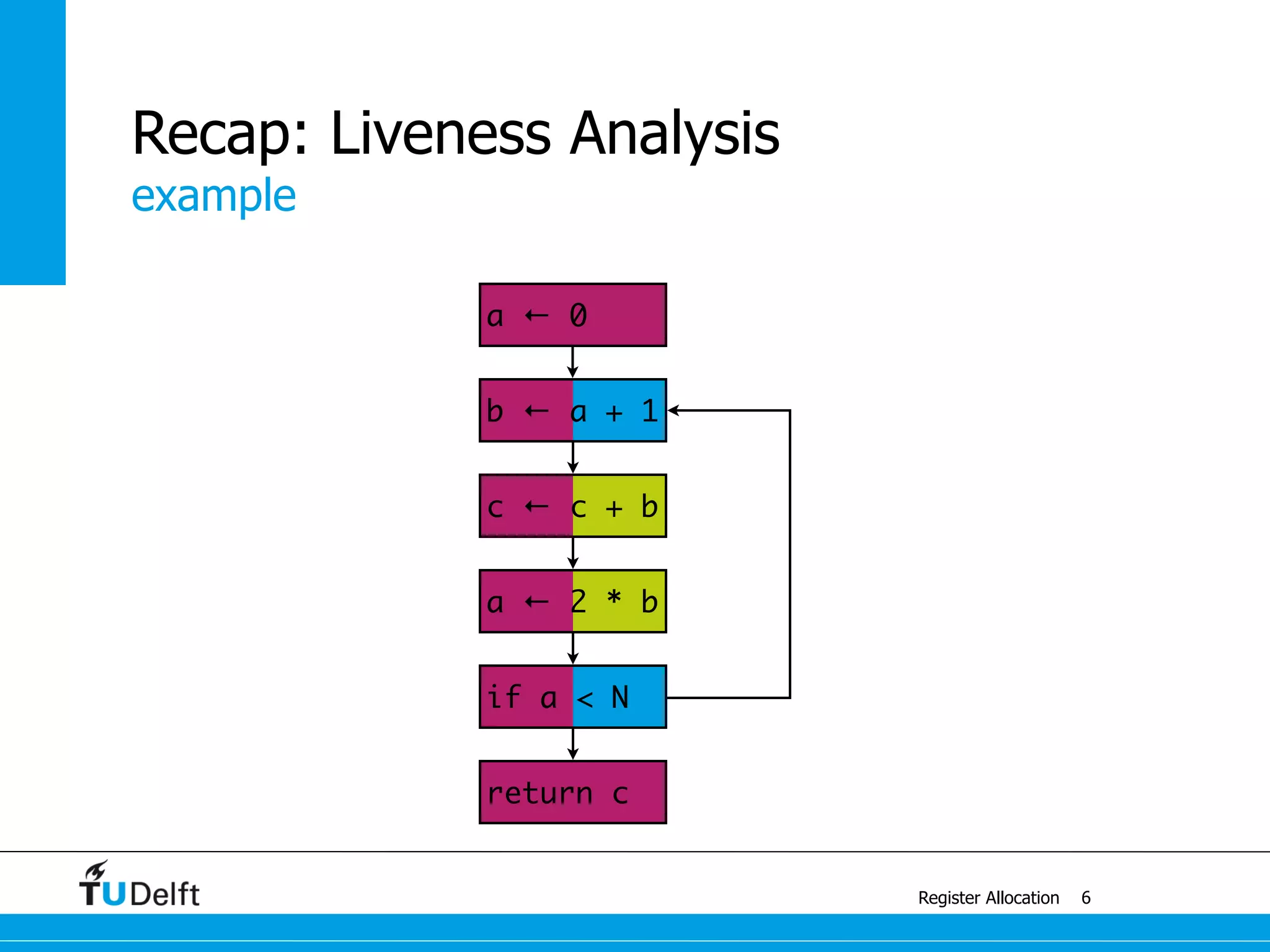
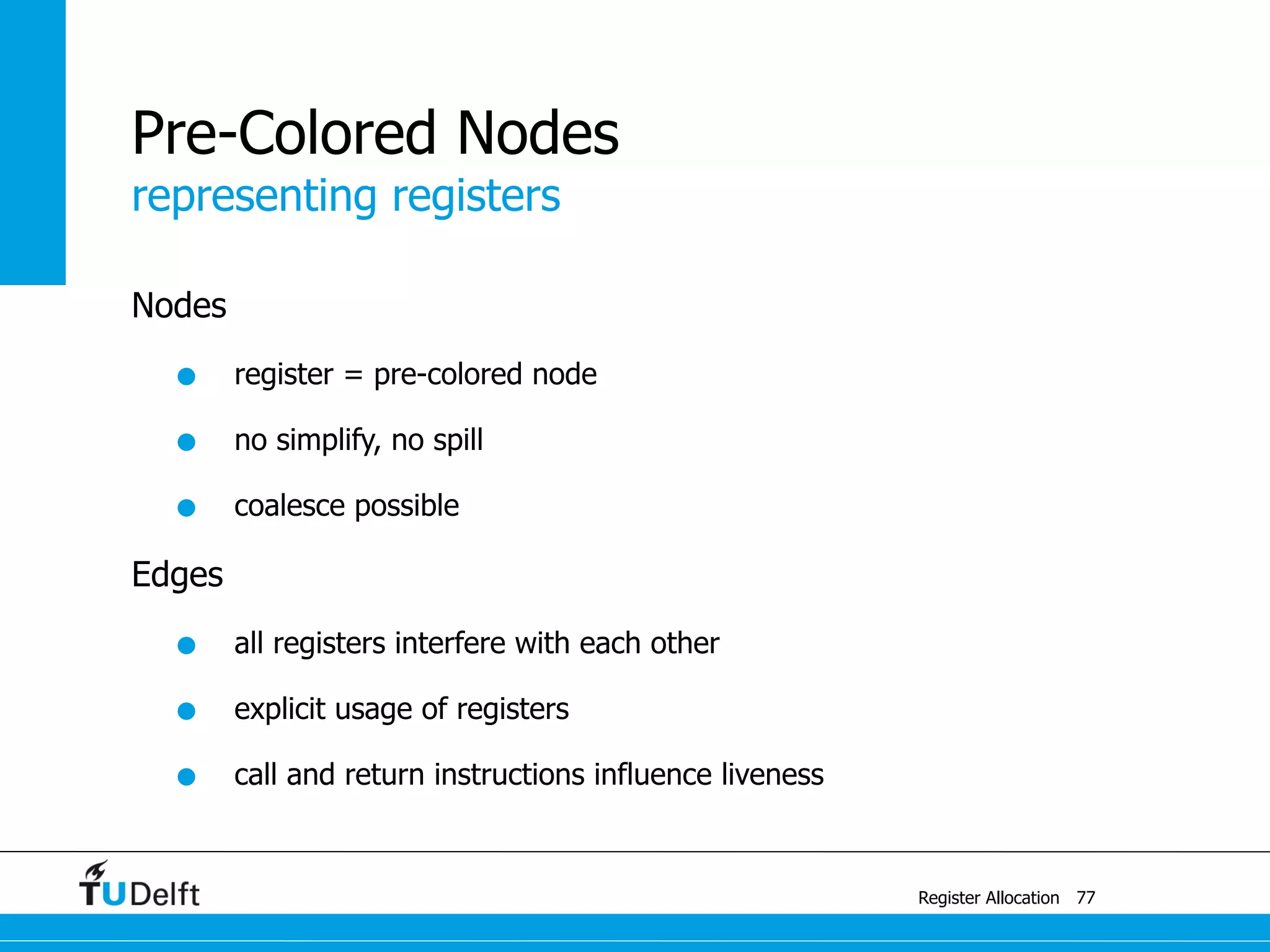
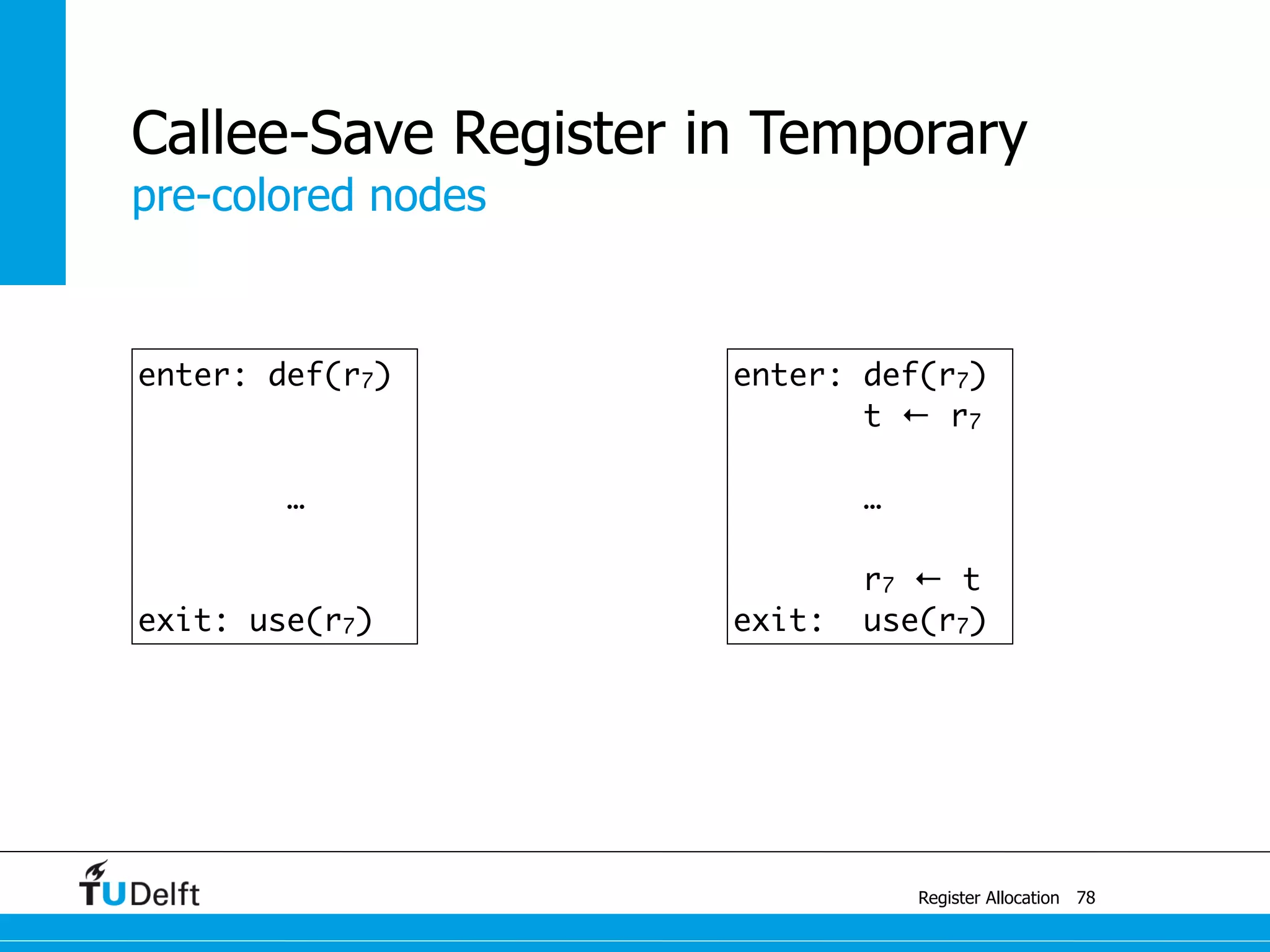
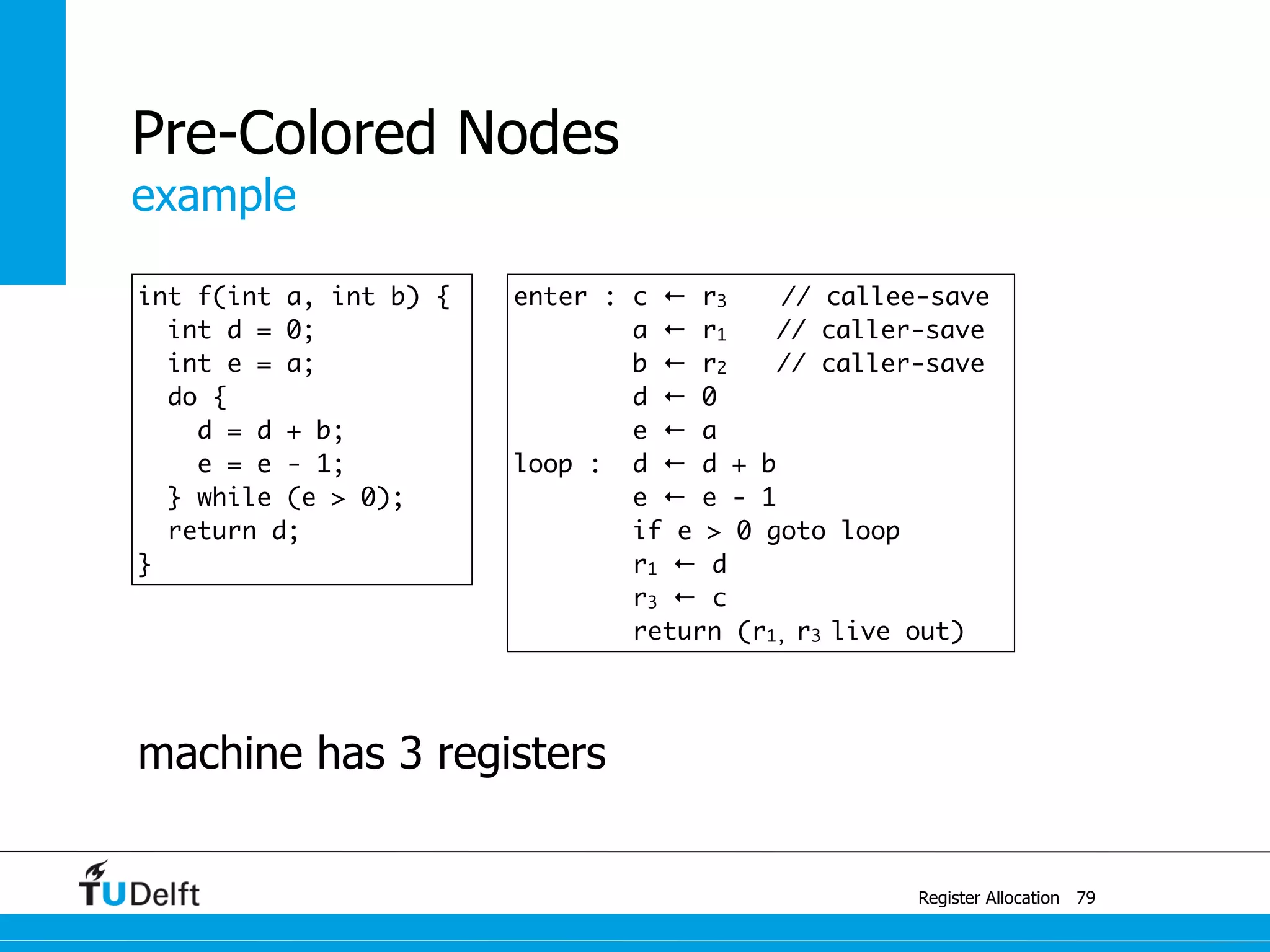
Register Allocation
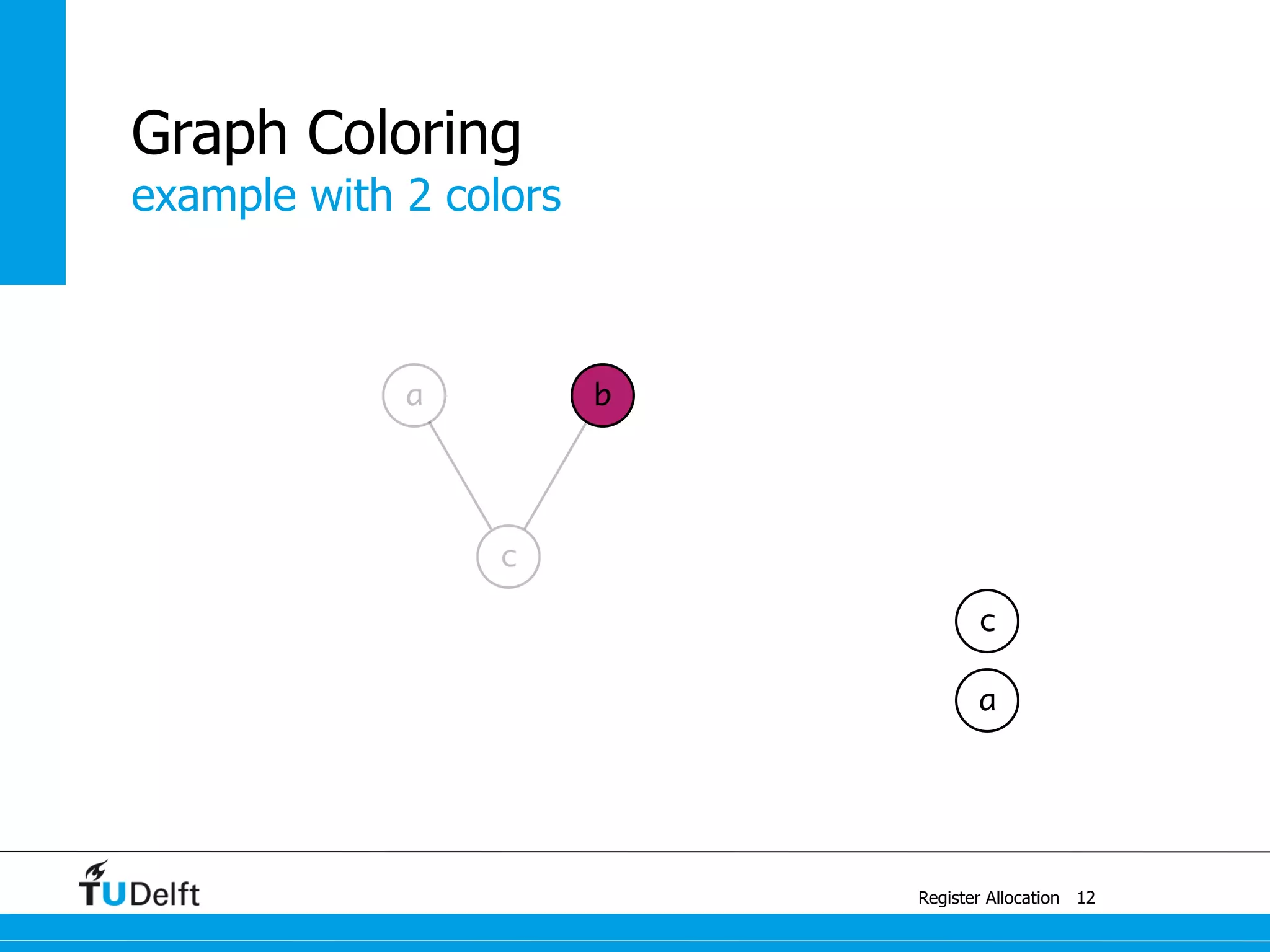
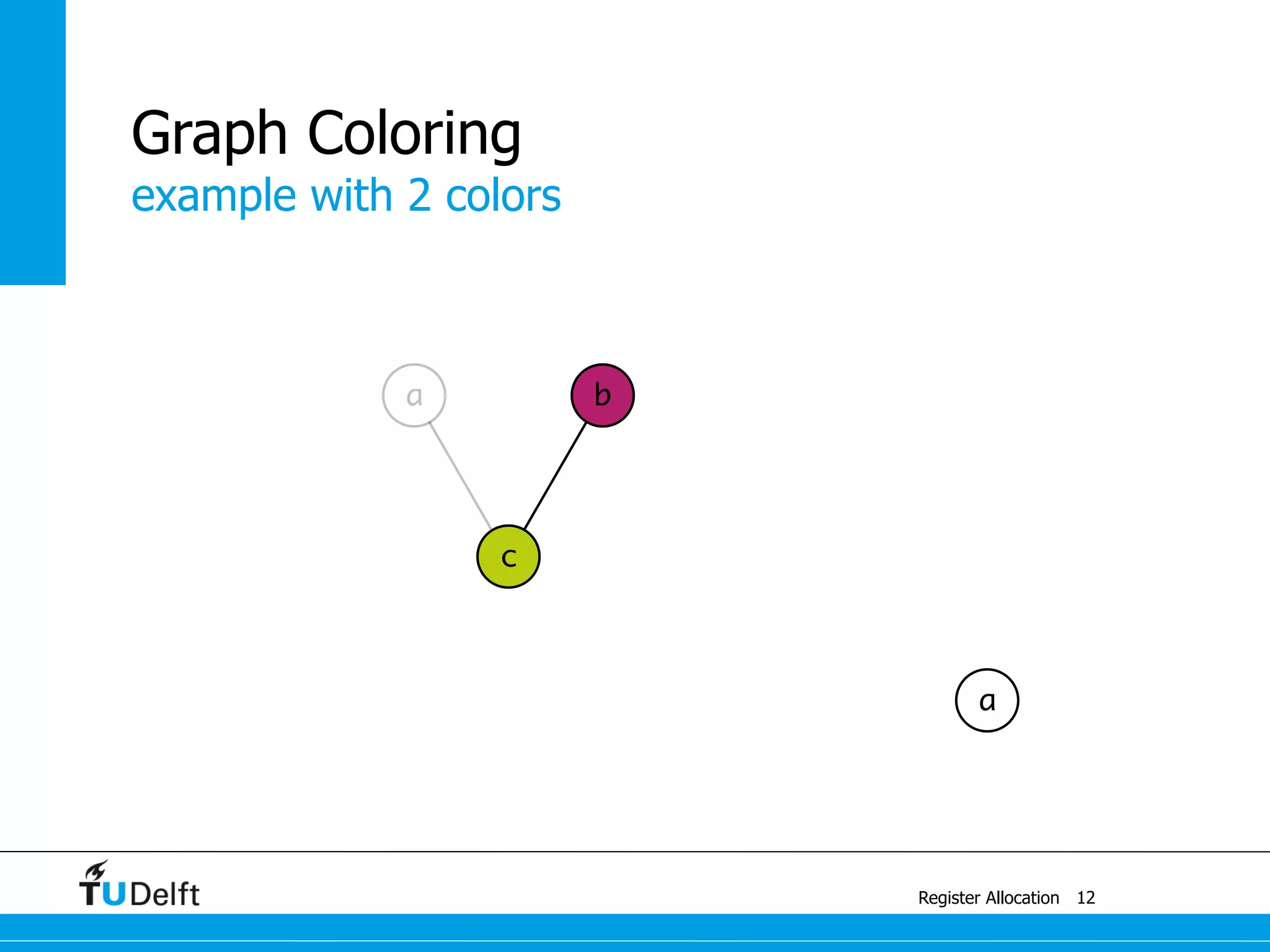
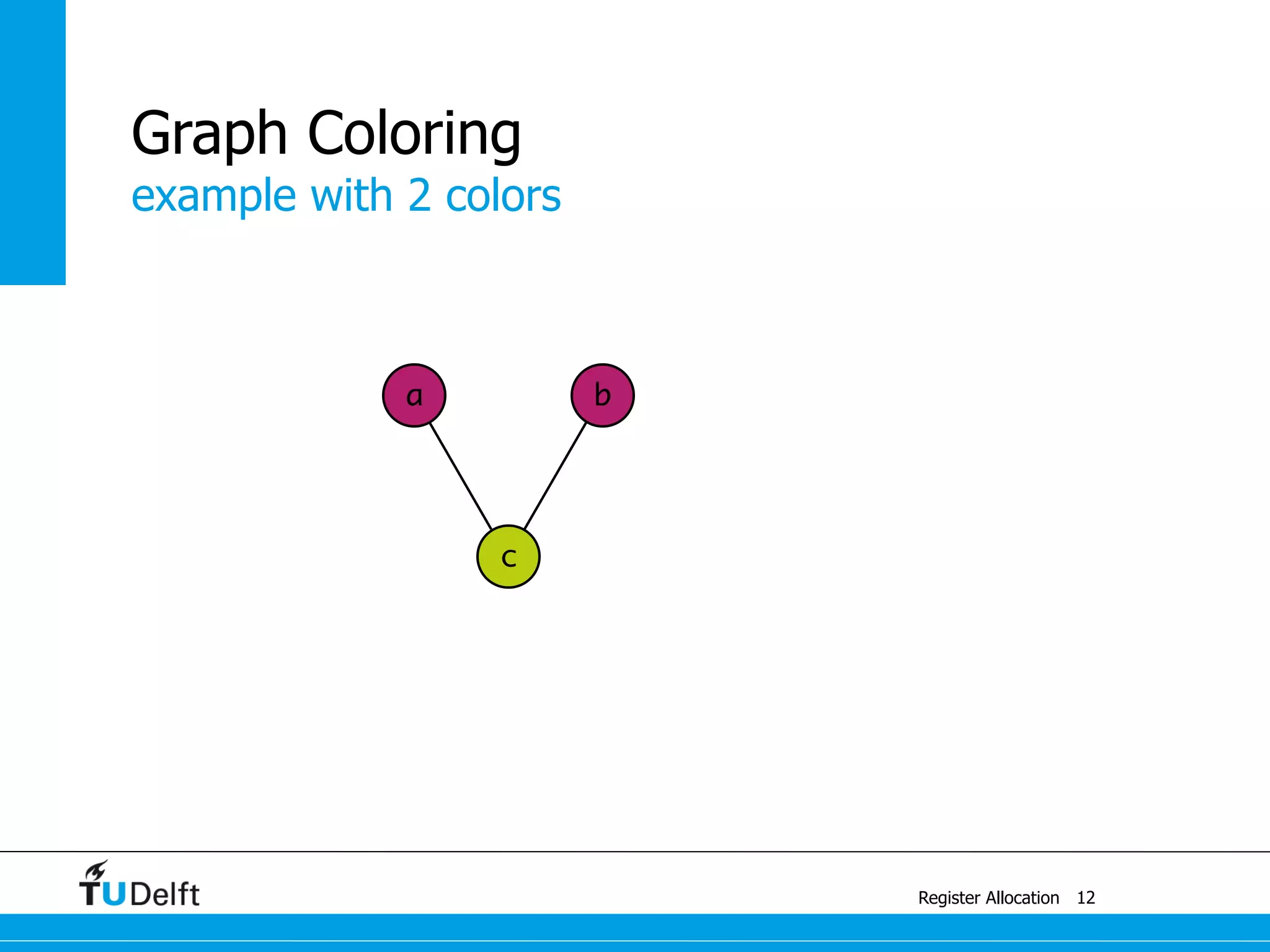
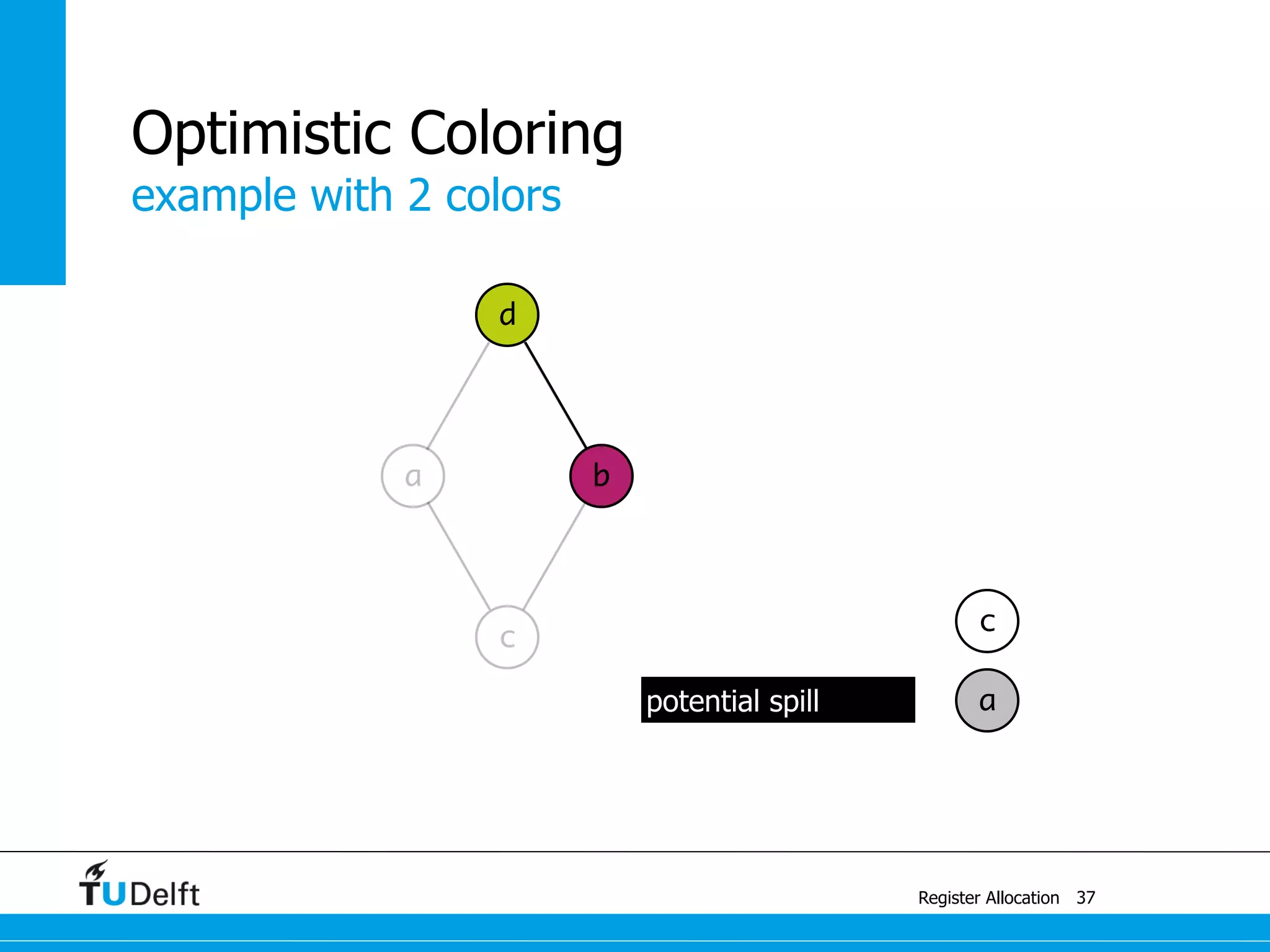
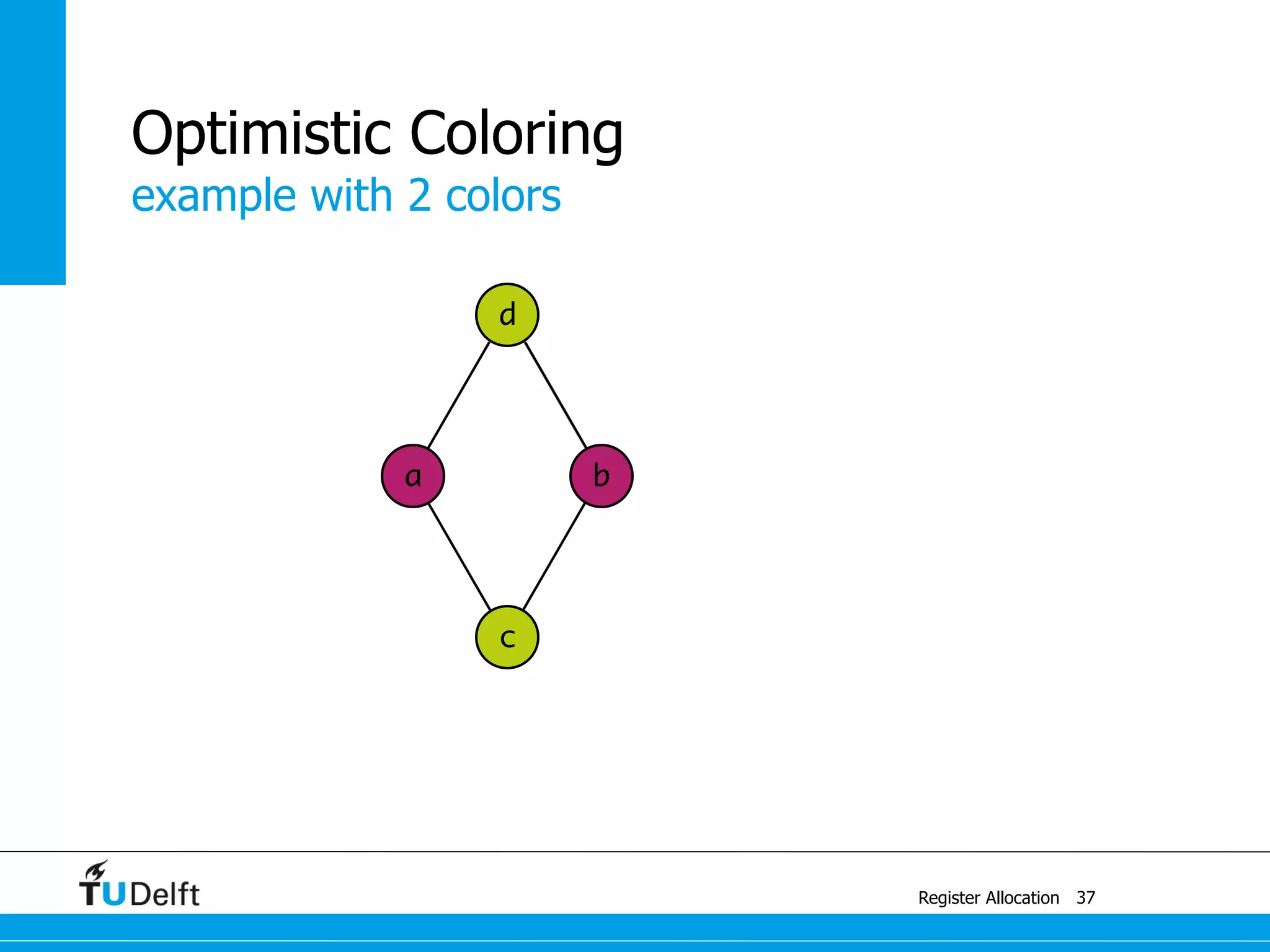
Allocate Minimal Number of Registers
2
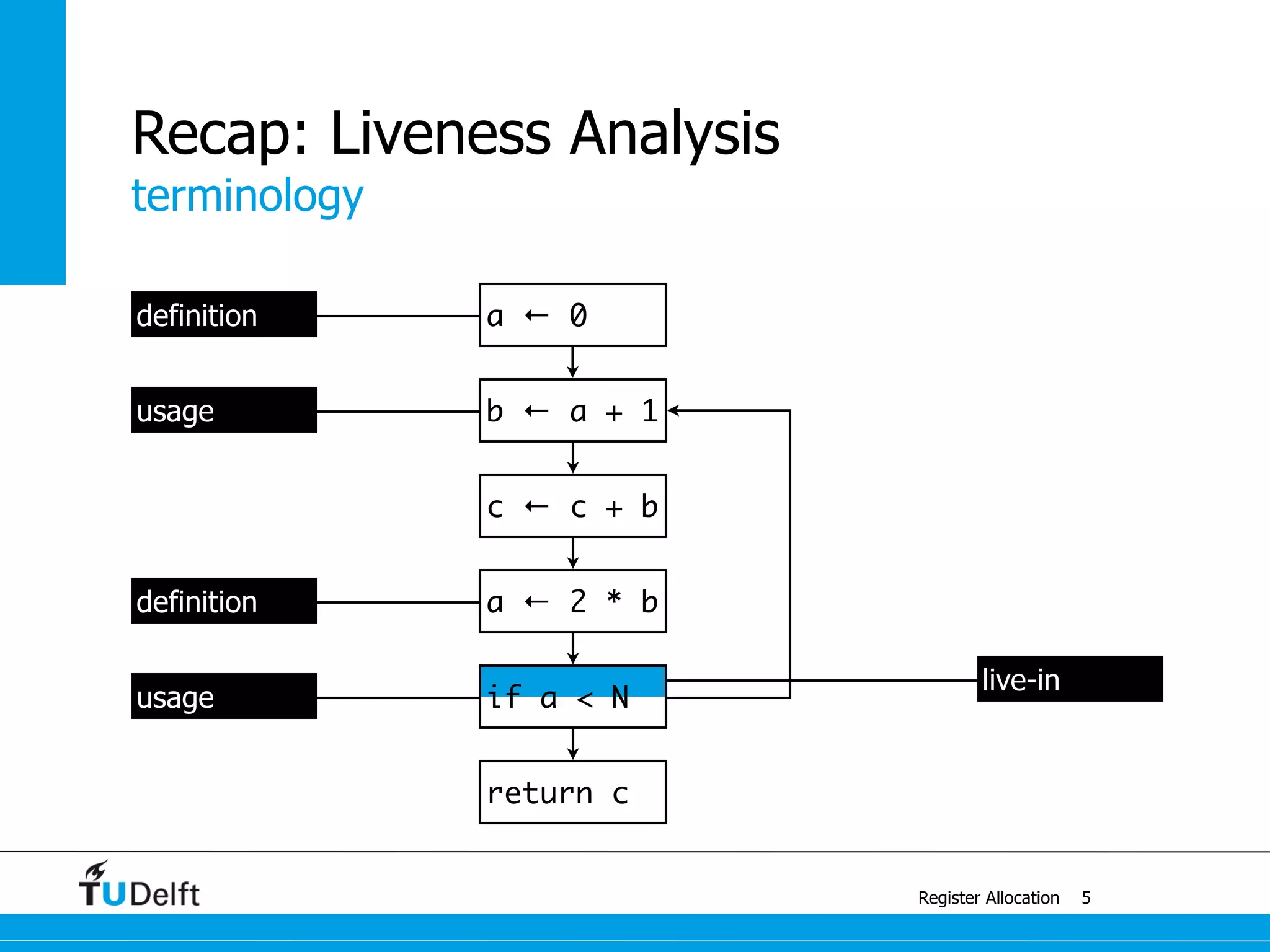
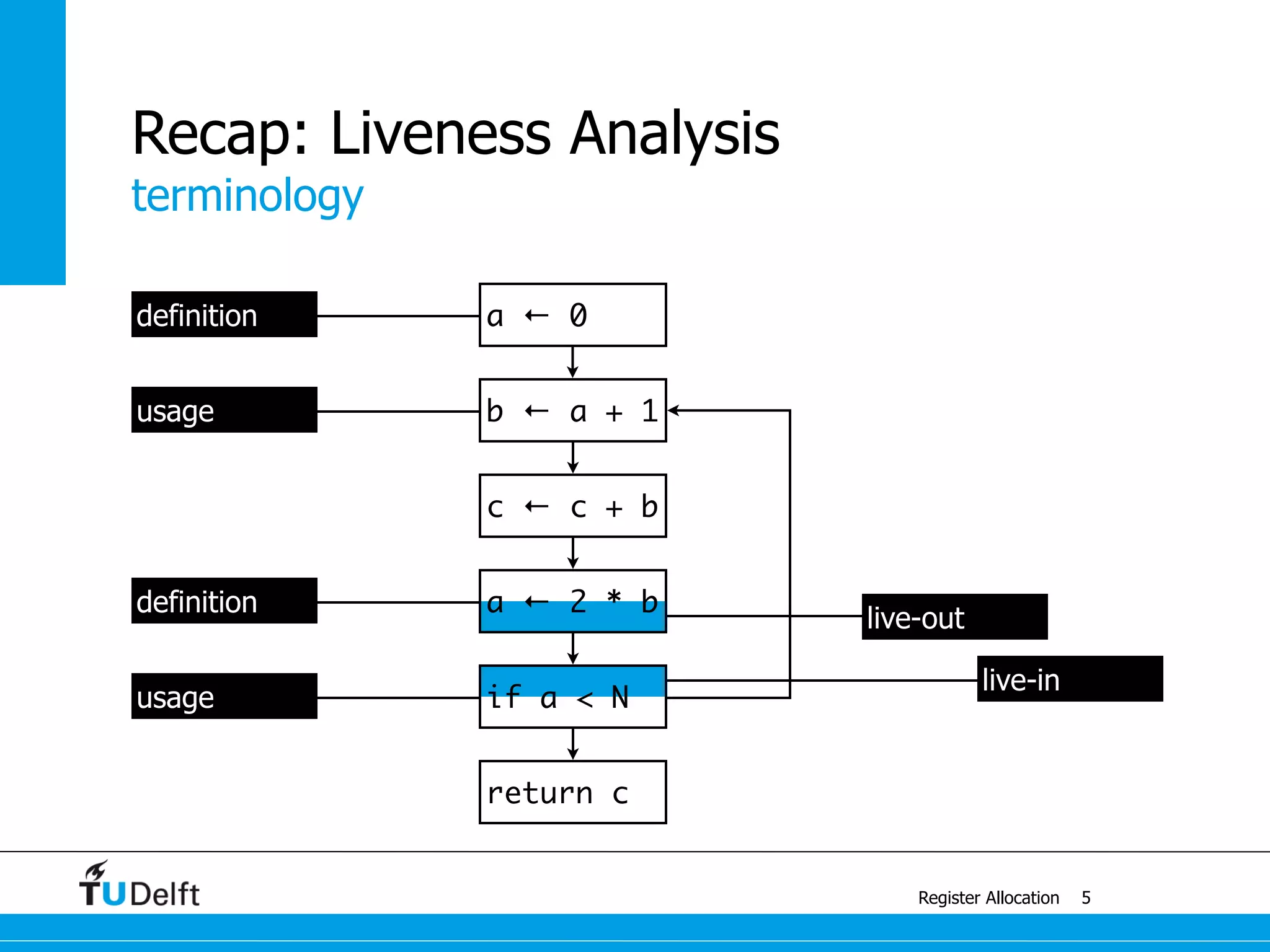
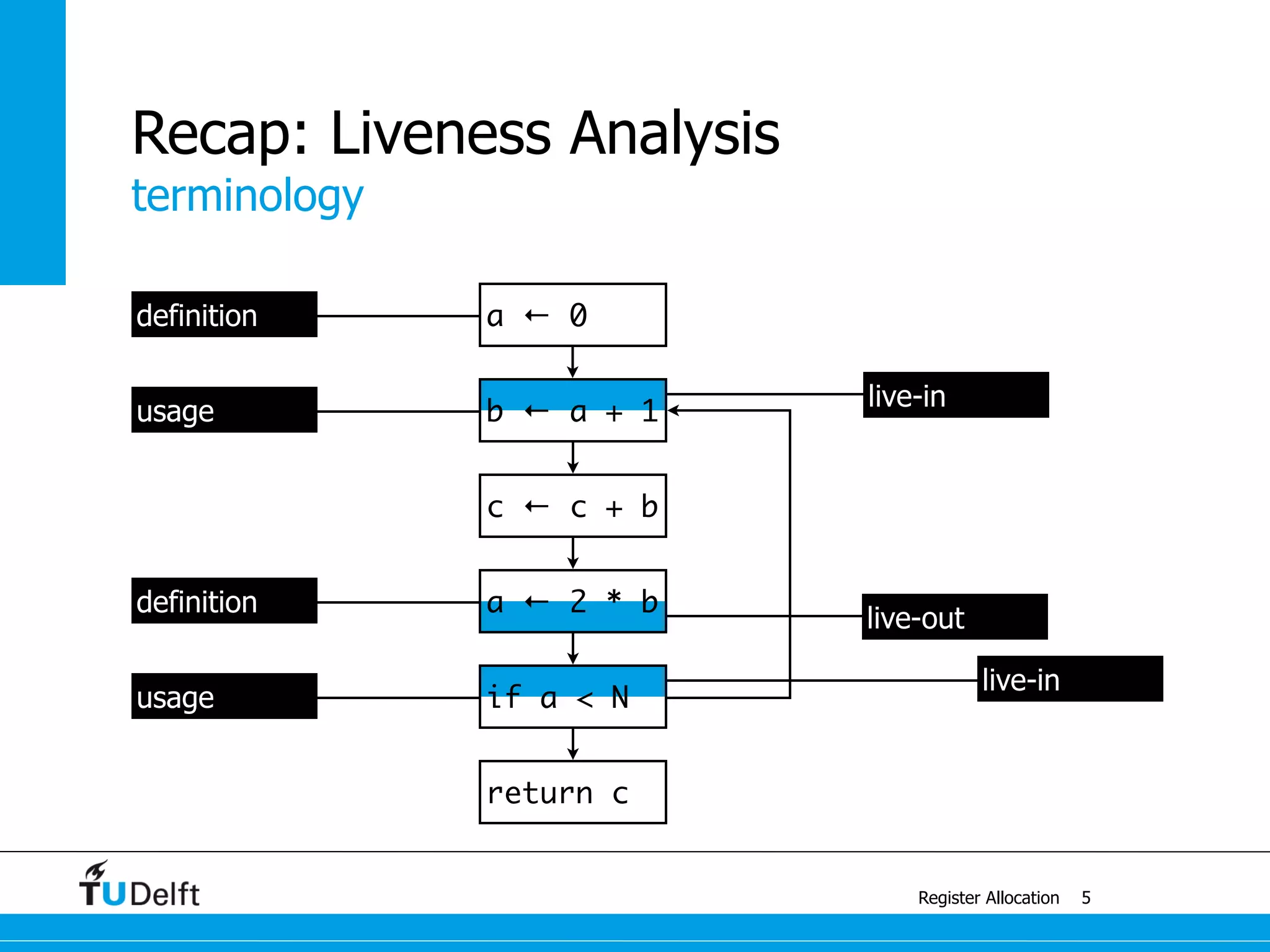
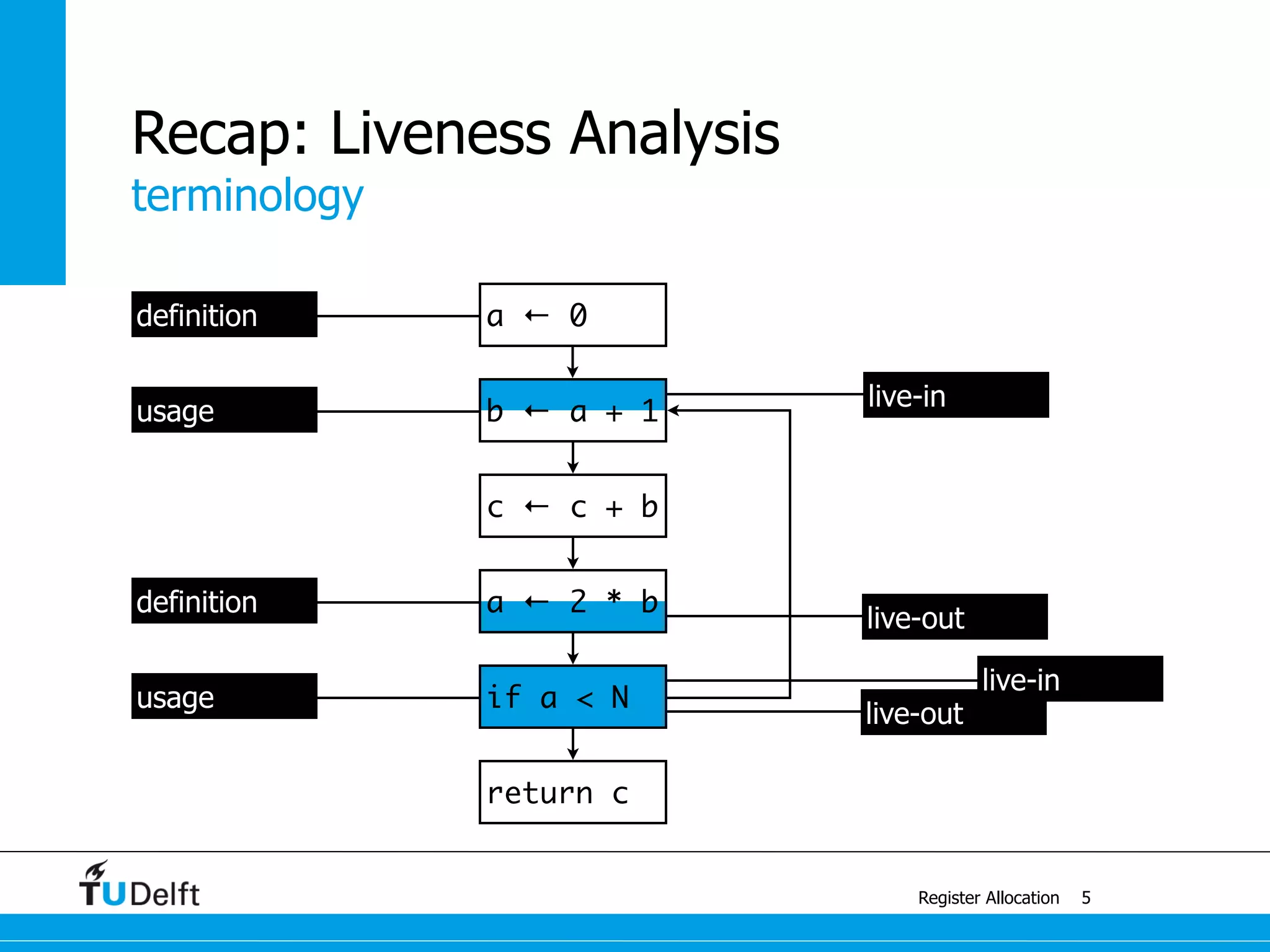
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-2-2048.jpg)

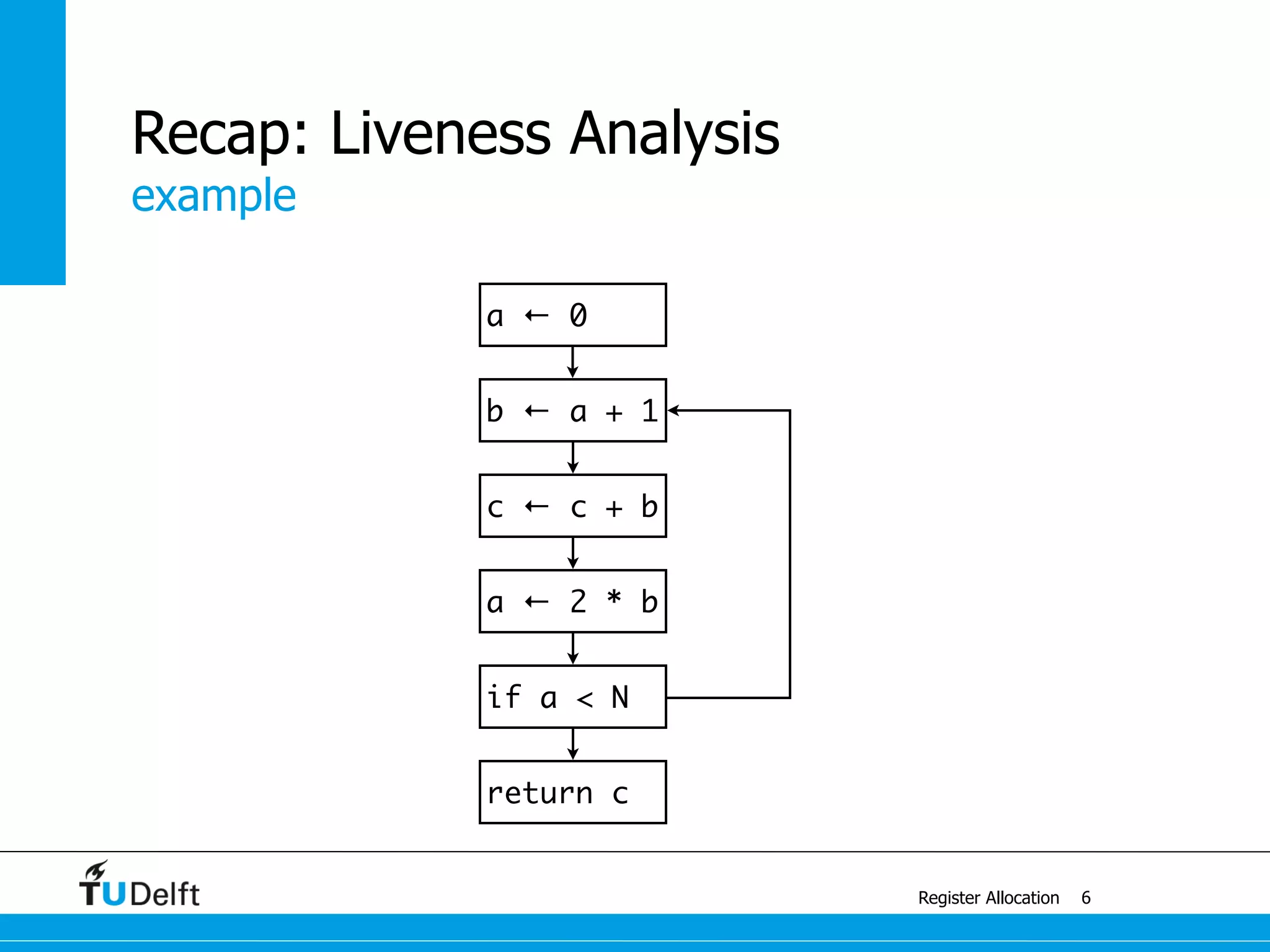
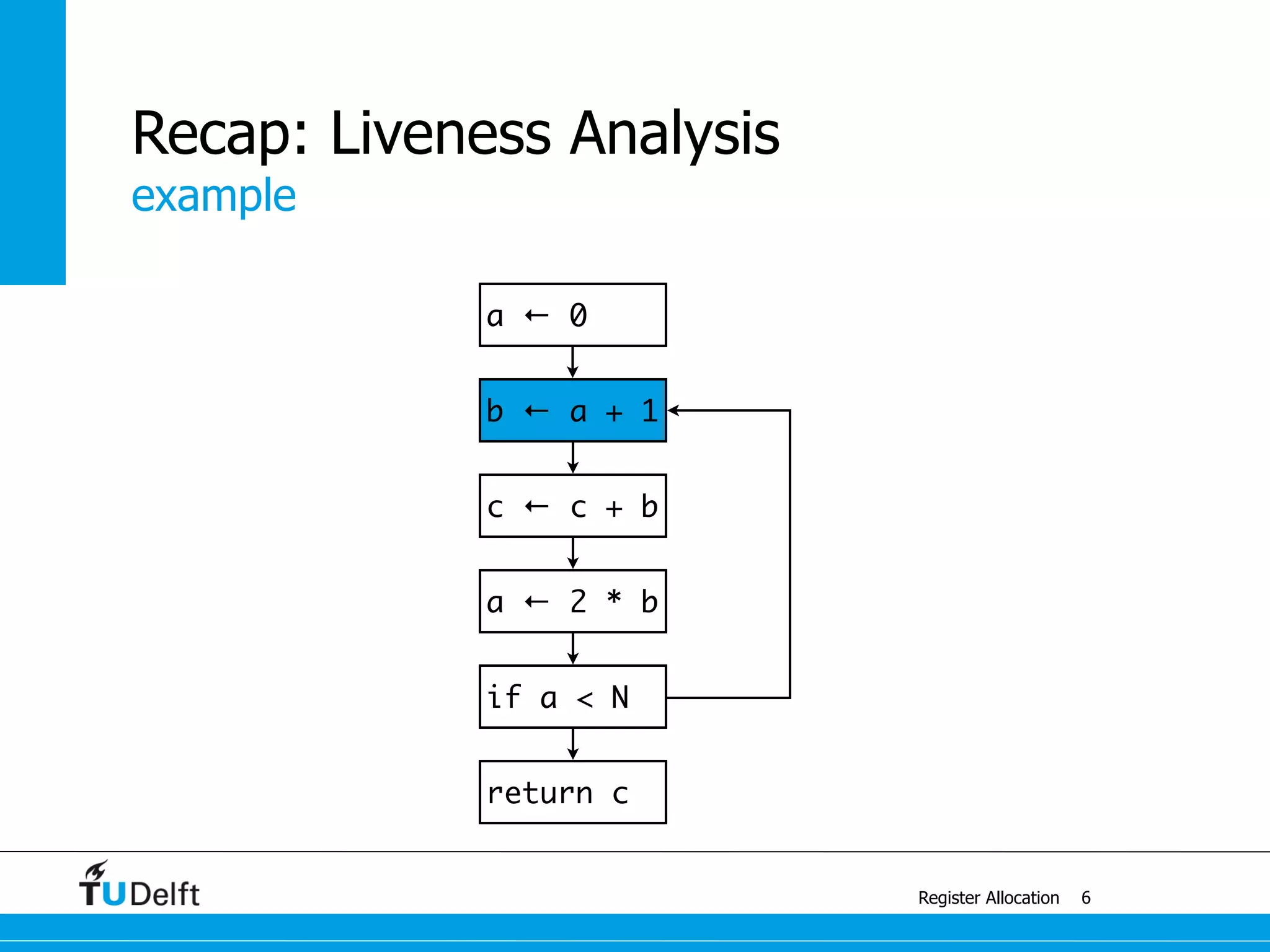
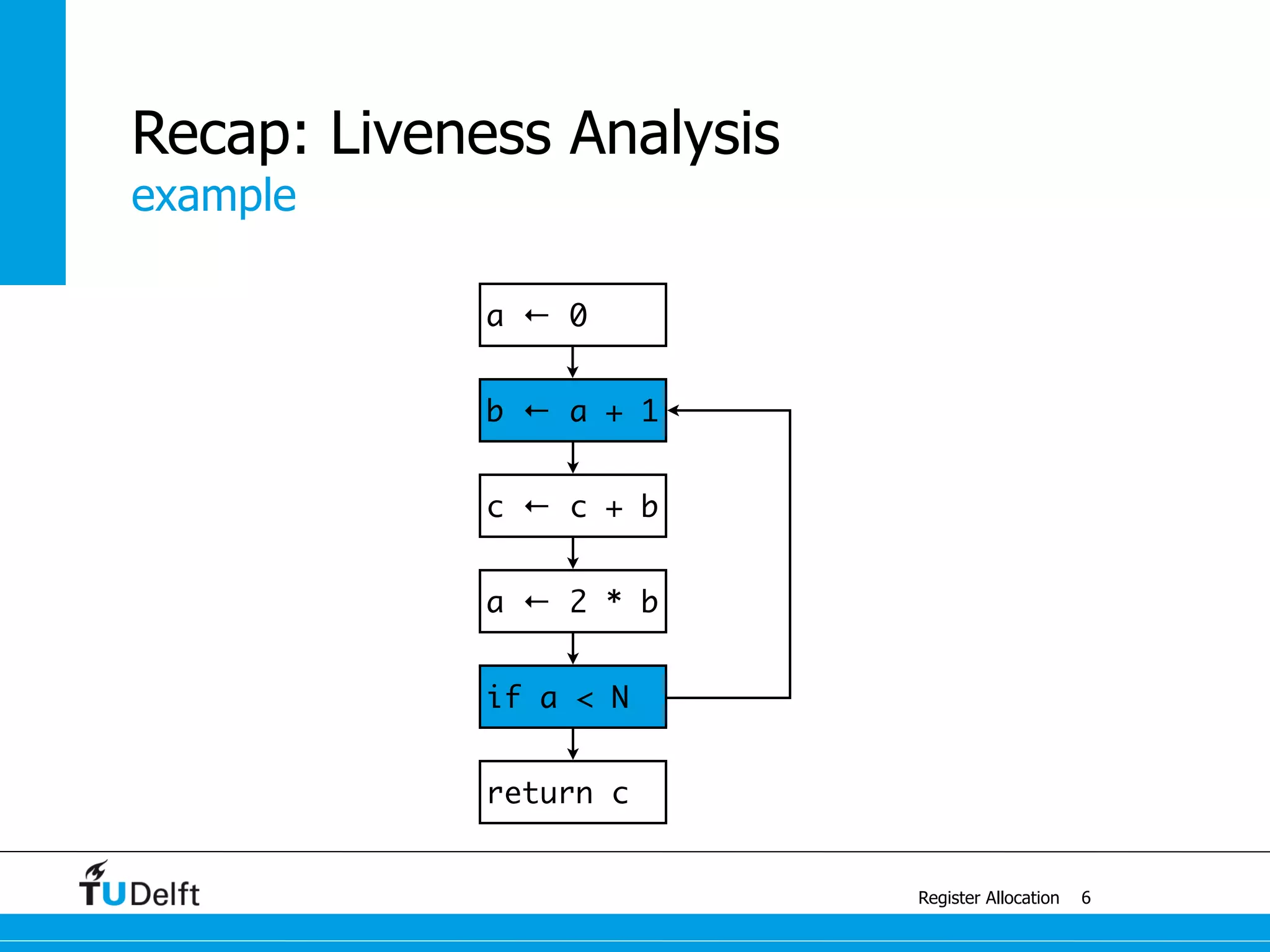


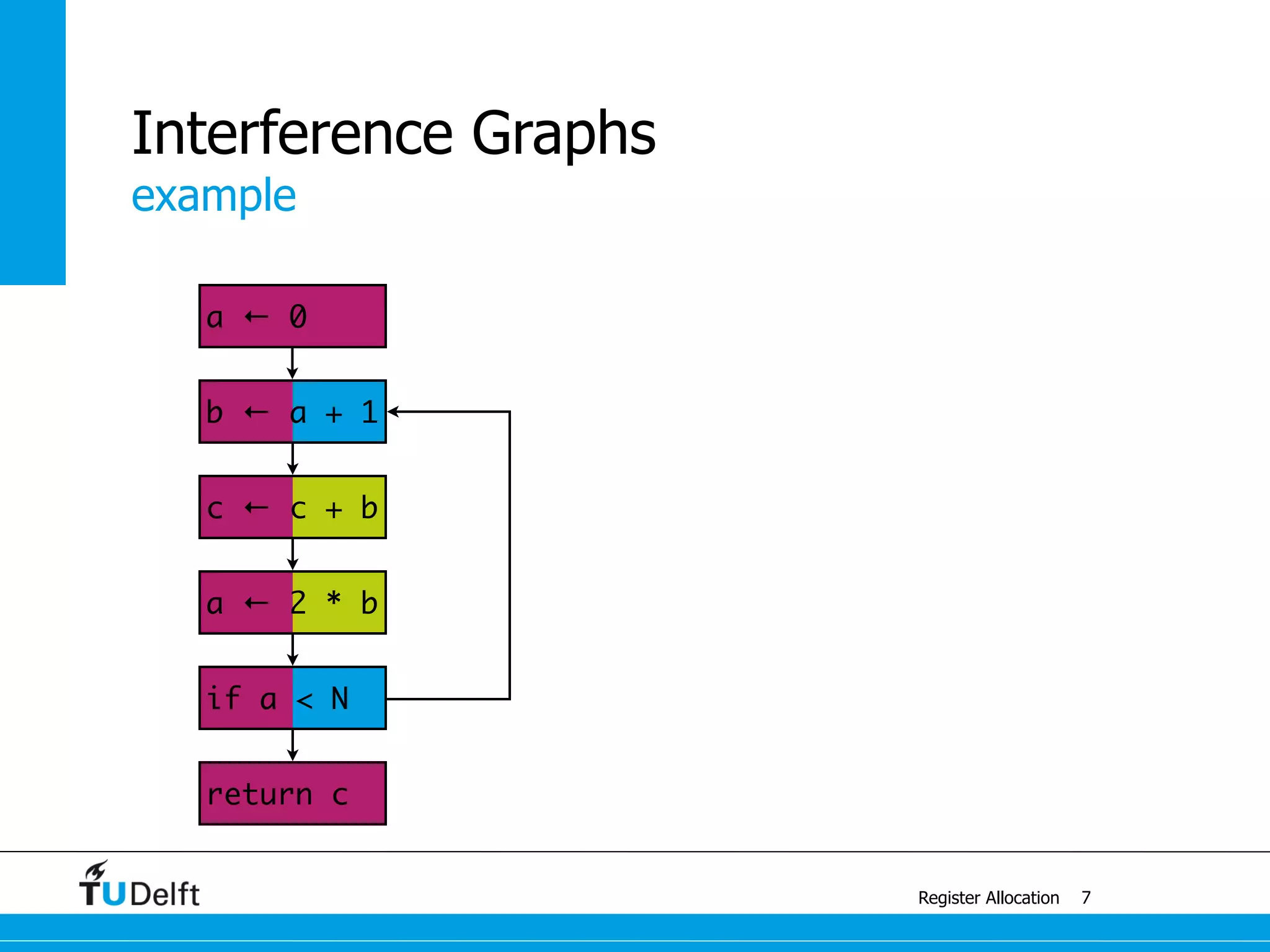
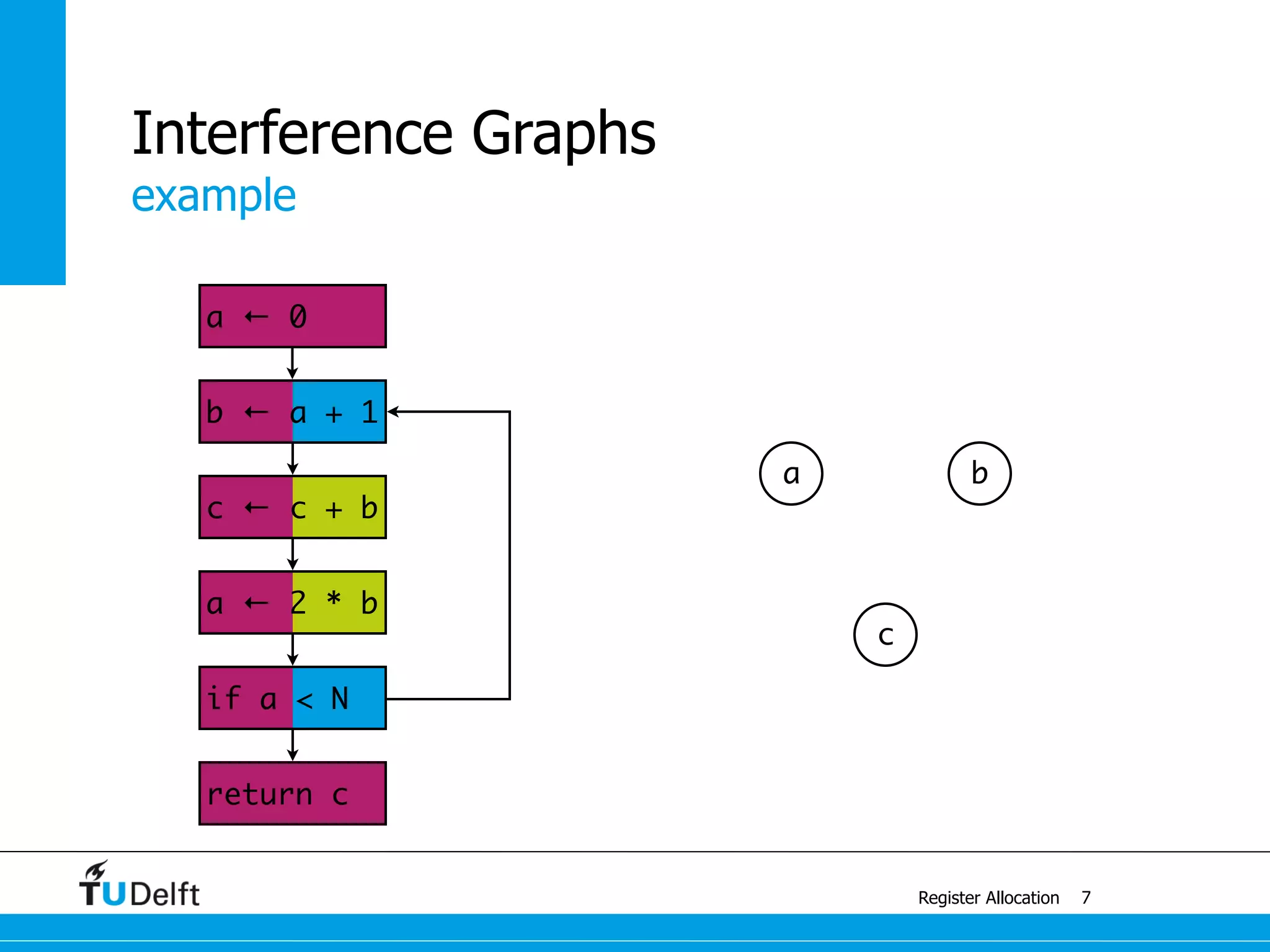








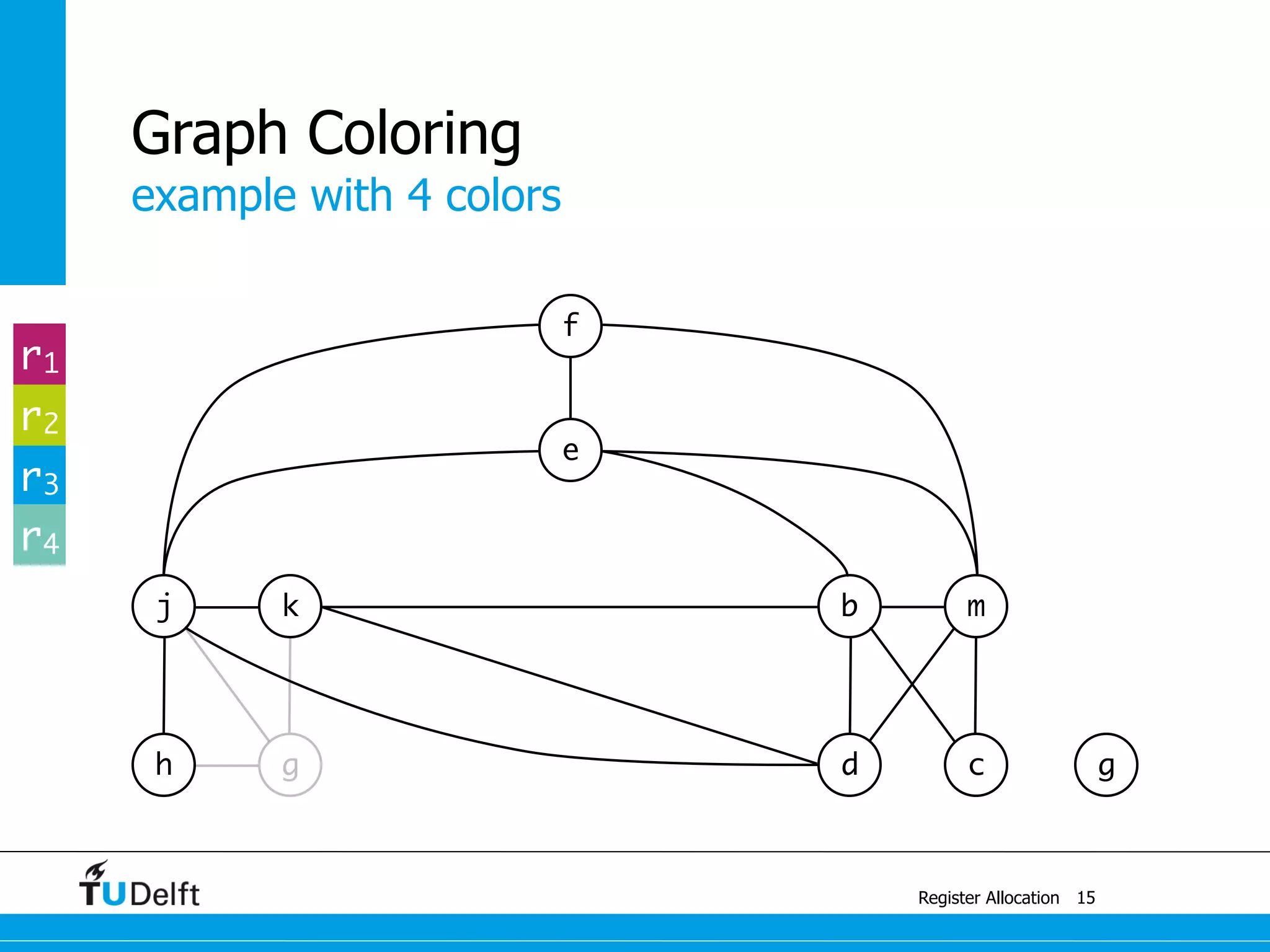
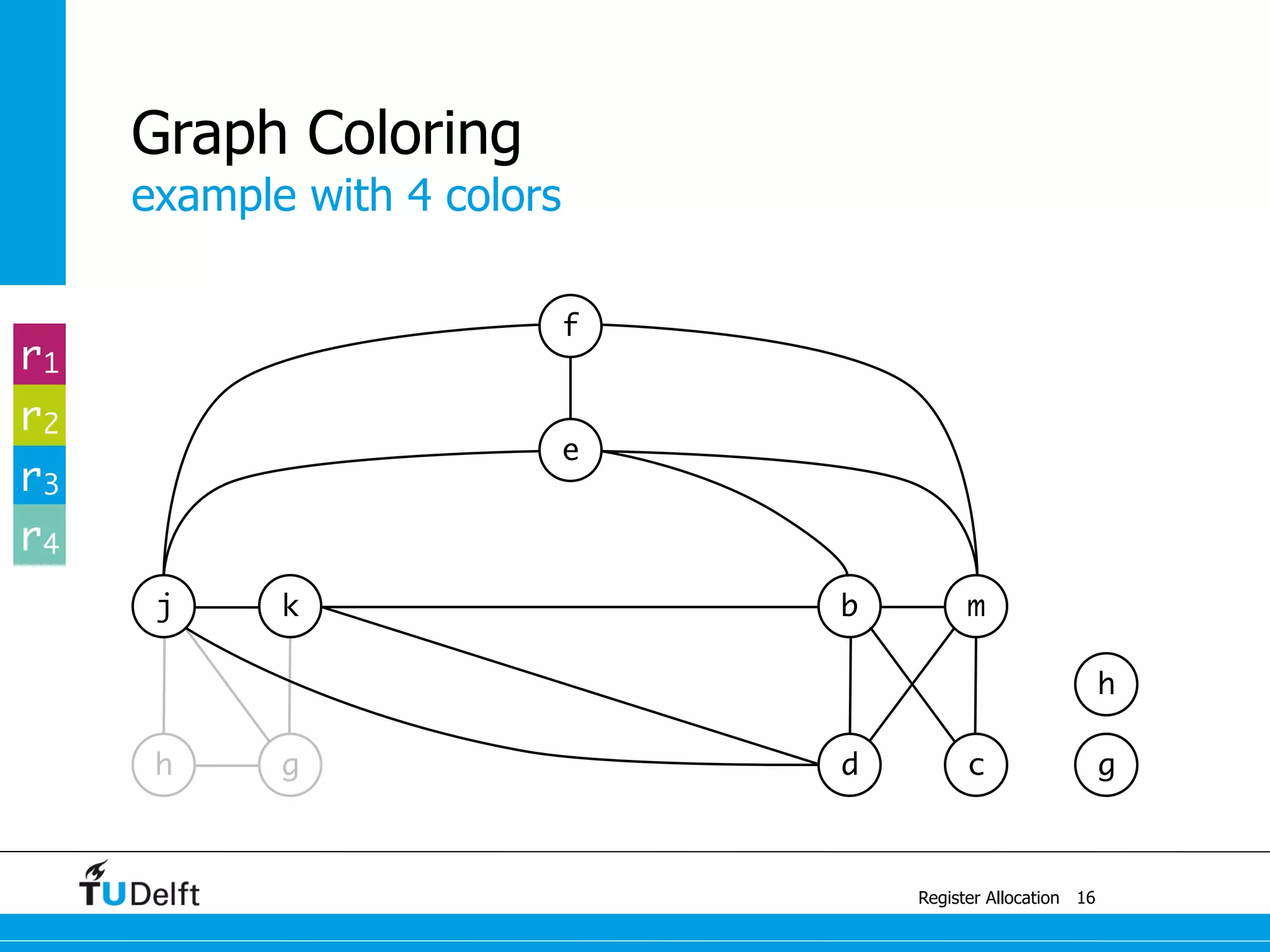
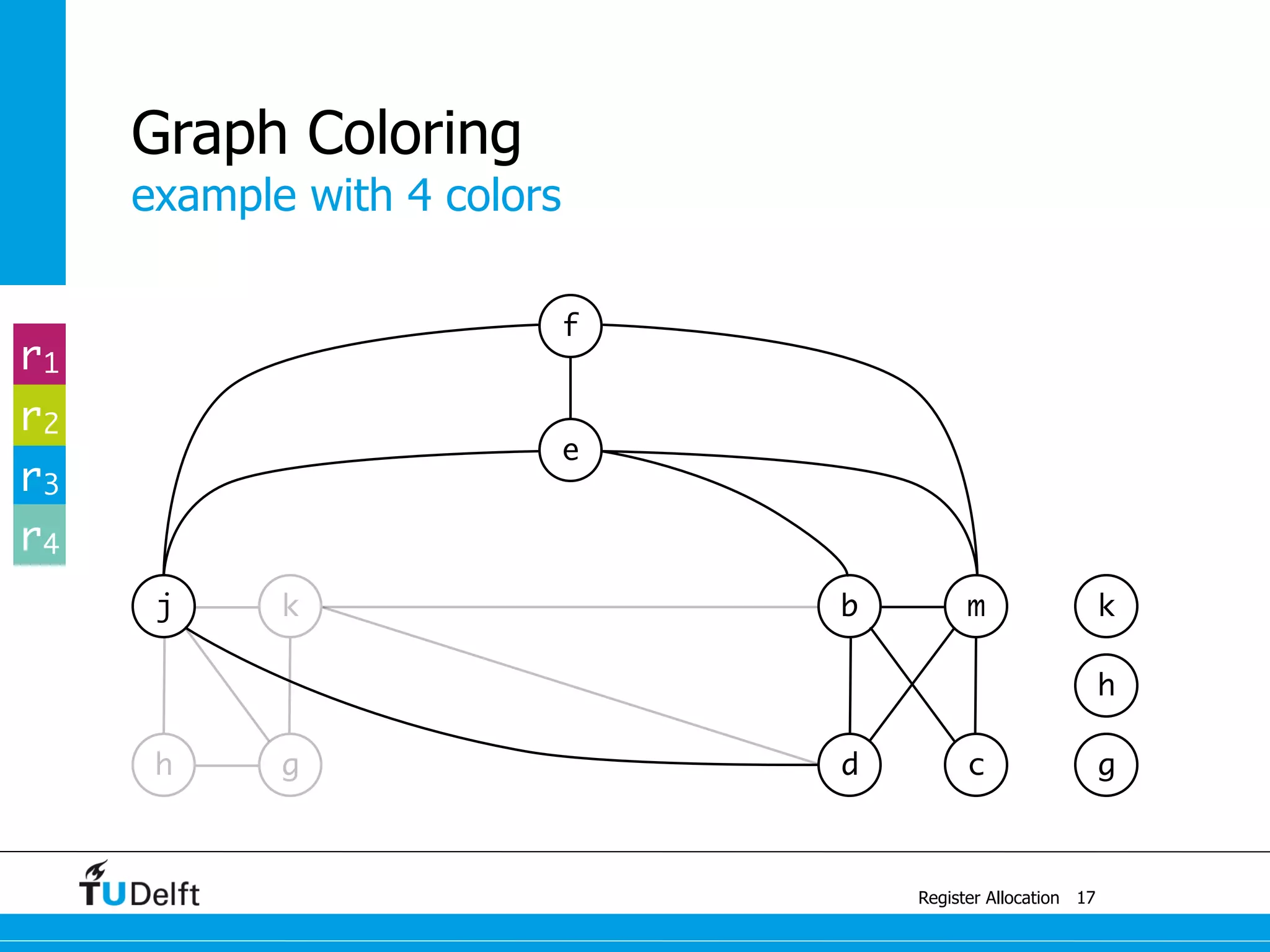
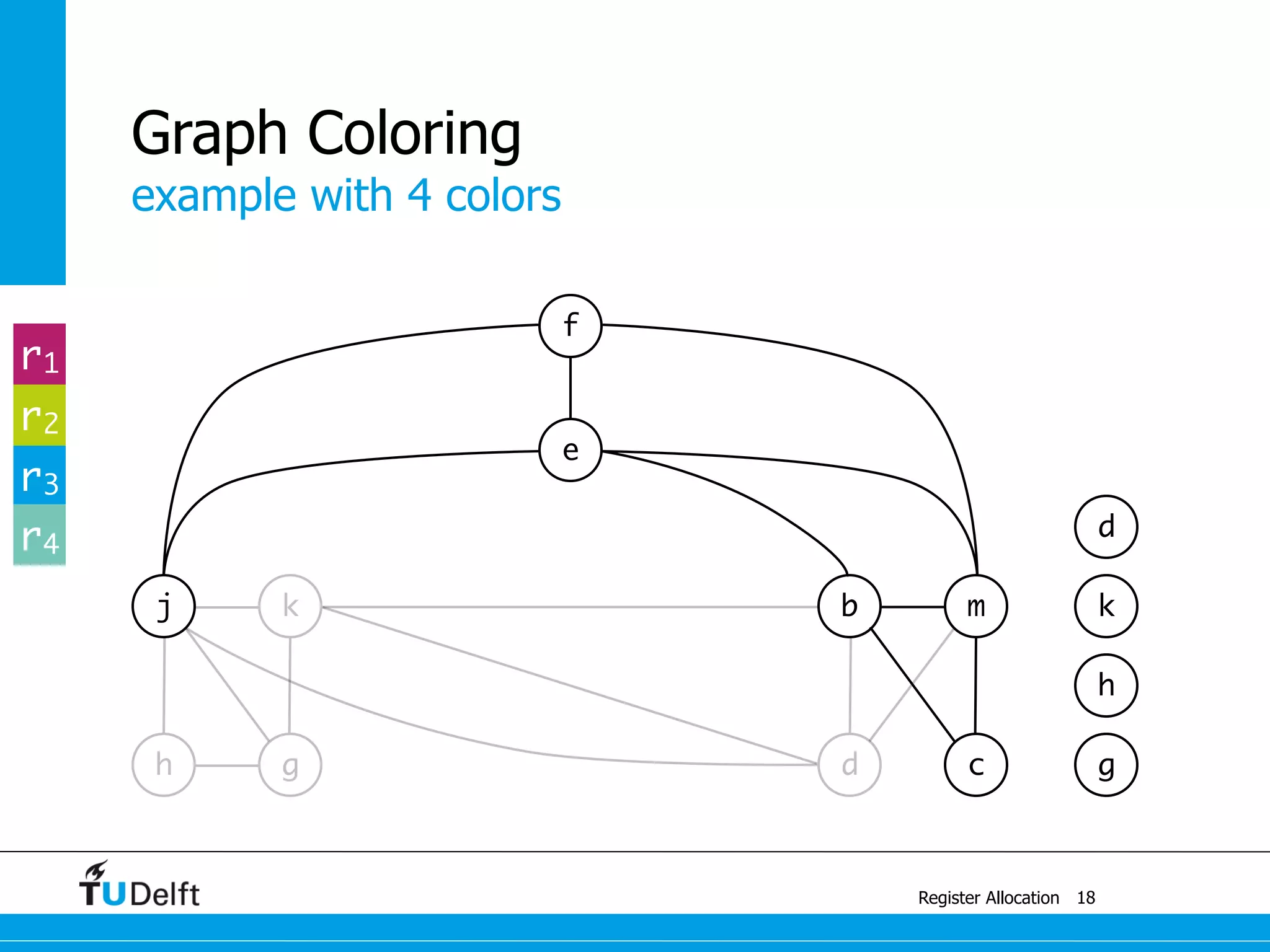
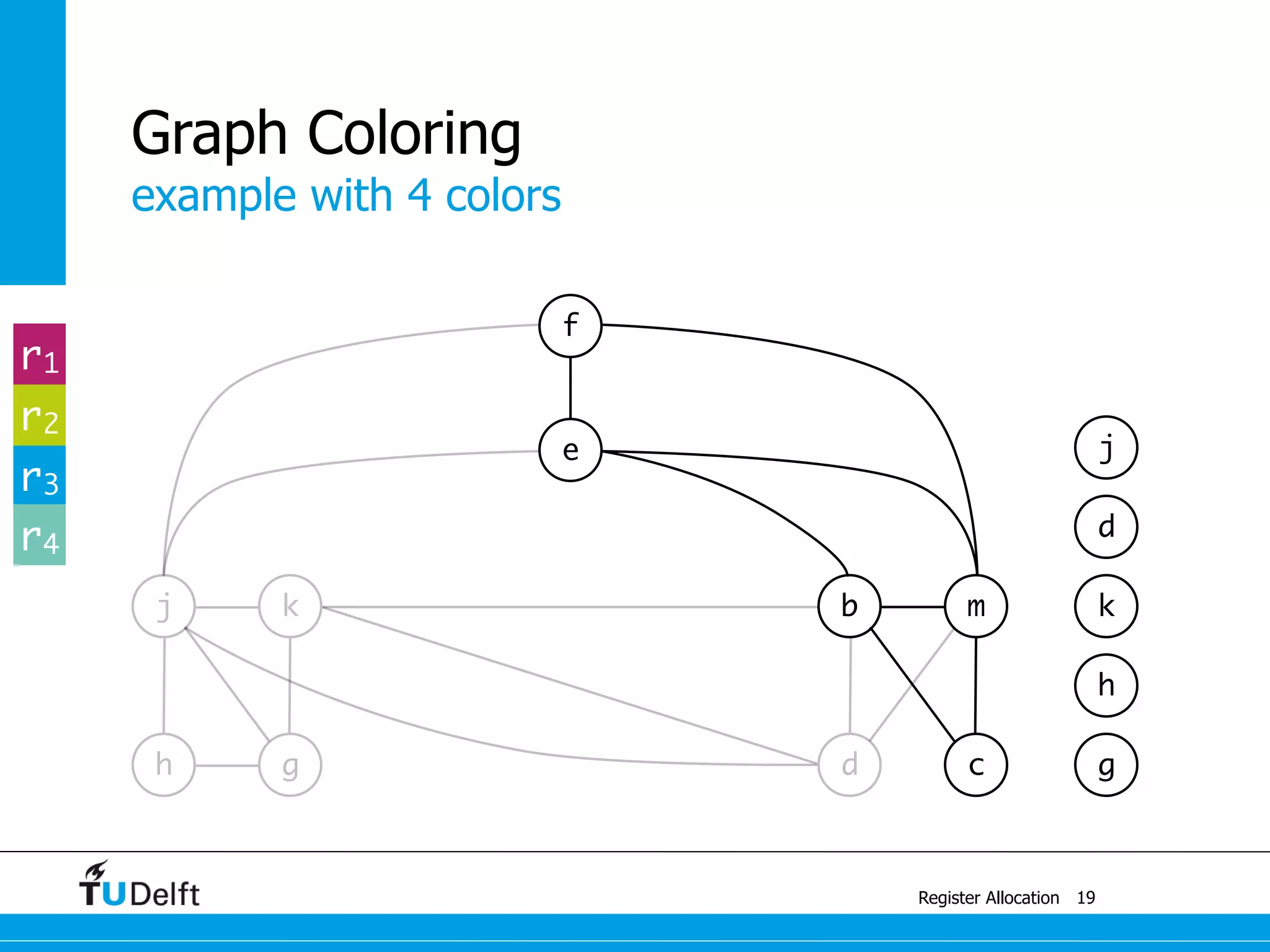
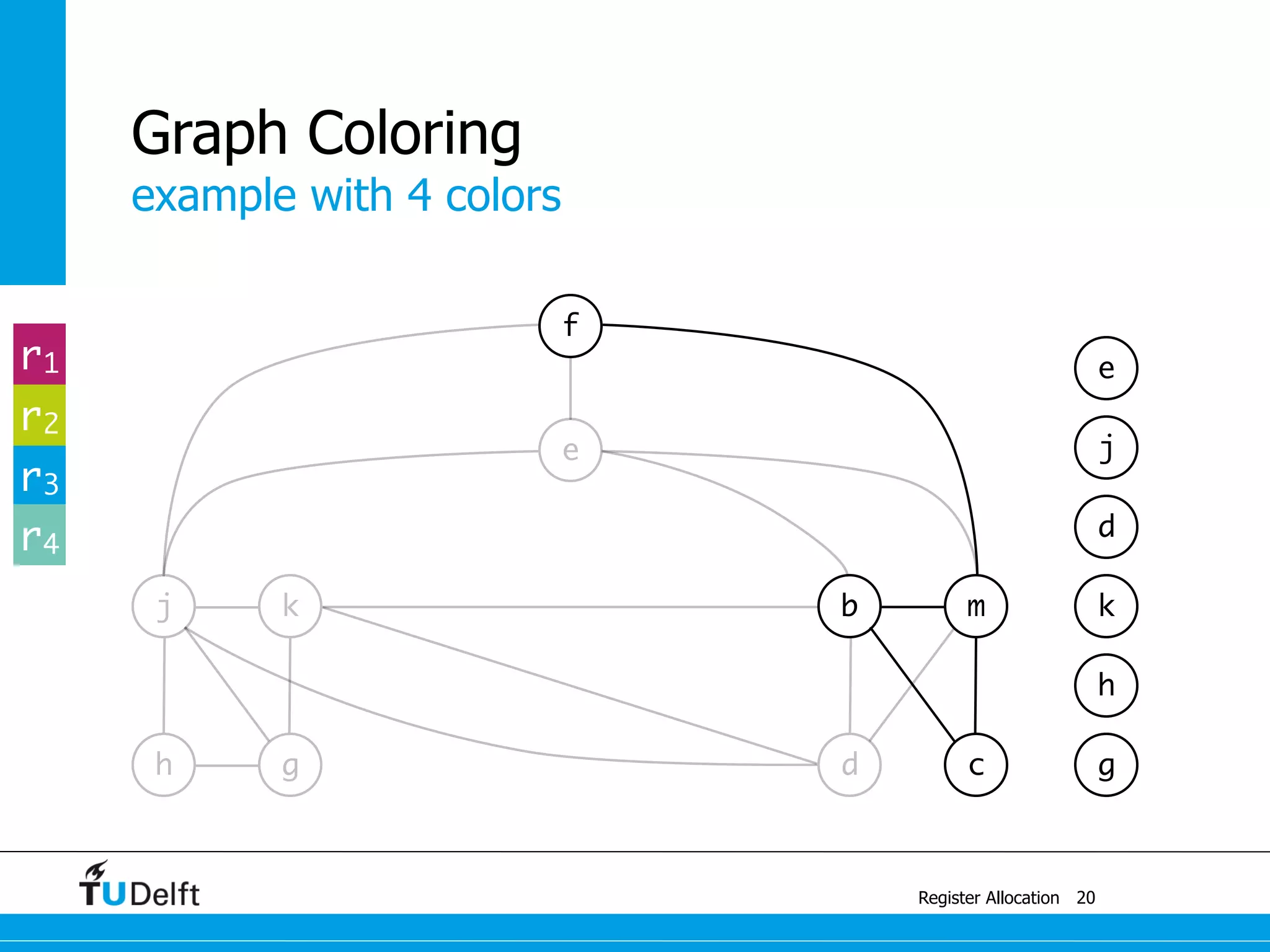
![example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
13
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-46-2048.jpg)
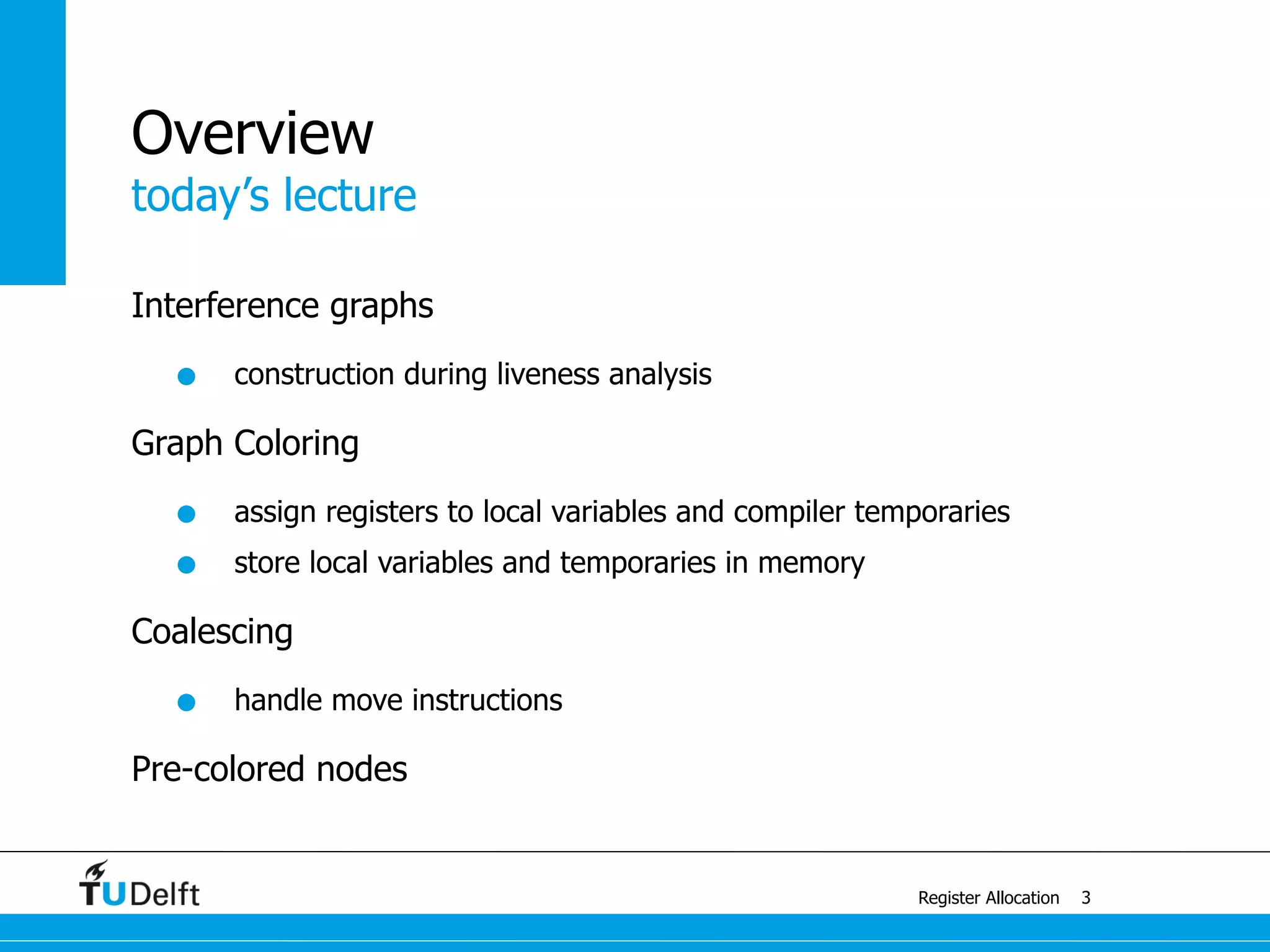
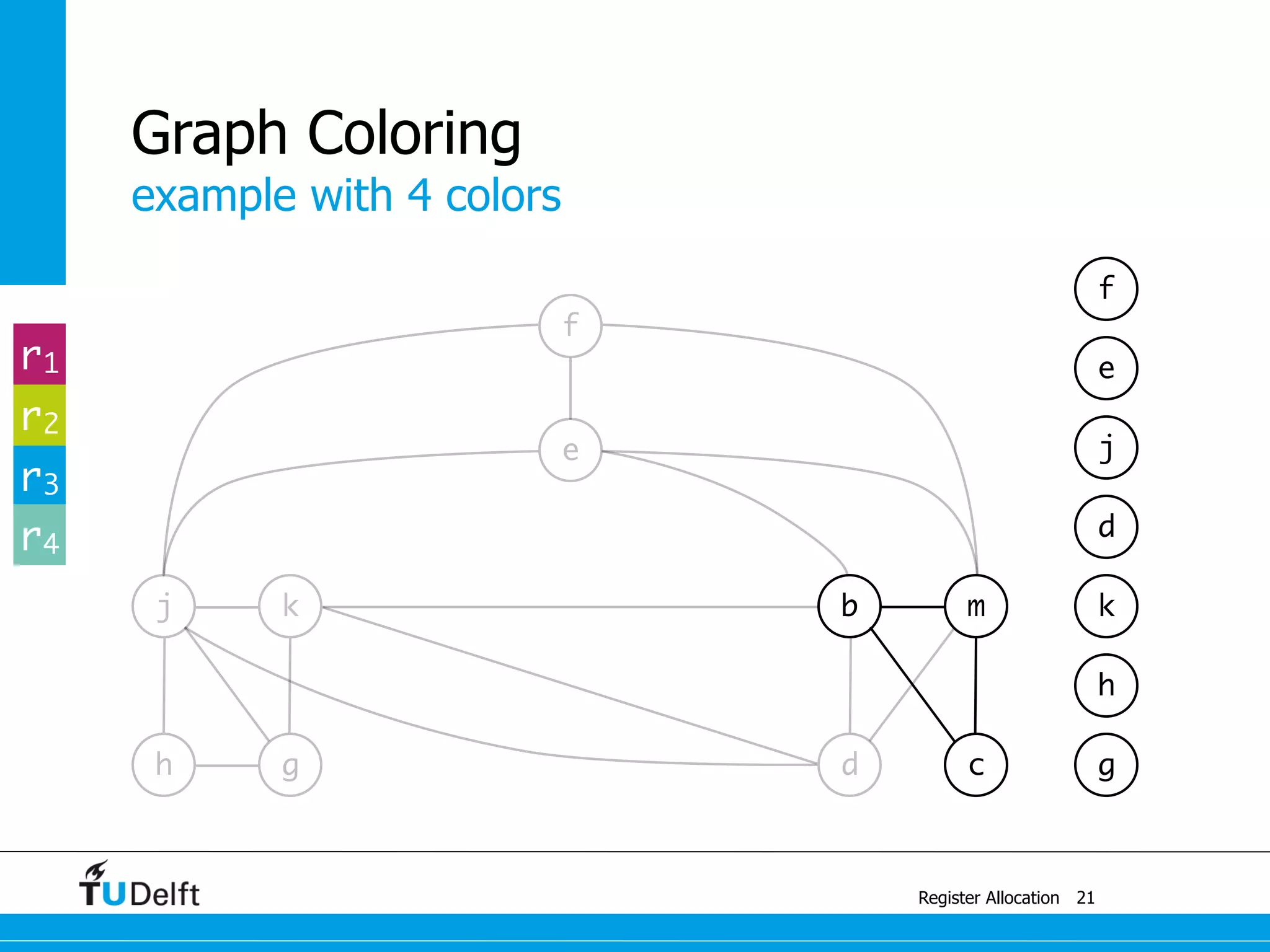
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
14
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-47-2048.jpg)

![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
23
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
d
j
e
f
b
c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-56-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
24
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
d
j
e
f
b
c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-57-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
25
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
d
j
e
f
b
c
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
r1 := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := r1 + 4
j := b
live out: d k j
r1
r2
r3
r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-58-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
26
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
d
j
e
f
b
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
r1 := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
r2 := e + 8
d := r2
k := r1 + 4
j := b
live out: d k j
r1
r2
r3
r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-59-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
27
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
d
j
e
f
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
r1 := mem[j + 16]
r3 := mem[f]
r2 := e + 8
d := r2
k := r1 + 4
j := r3
live out: d k j
r1
r2
r3
r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-60-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
28
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
d
j
e
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
r3 := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
r1 := mem[j + 16]
r3 := mem[r3]
r2 := e + 8
d := r2
k := r1 + 4
j := r3
live out: d k j
r1
r2
r3
r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-61-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
29
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
d
j
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
r3 := g * h
r4 := mem[j + 8]
r1 := mem[j + 16]
r3 := mem[r3]
r2 := r4 + 8
d := r2
k := r1 + 4
j := r3
live out: d k j
r1
r2
r3
r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-62-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
30
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
d
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k r2
g := mem[r2 + 12]
h := k - 1
r3 := g * h
r4 := mem[r2 + 8]
r1 := mem[r2 + 16]
r3 := mem[r3]
r2 := r4 + 8
d := r2
k := r1 + 4
r2 := r3
live out: d k r2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-63-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
31
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k r2
g := mem[r2 + 12]
h := k - 1
r3 := g * h
r4 := mem[r2 + 8]
r1 := mem[r2 + 16]
r3 := mem[r3]
r2 := r4 + 8
r4 := r2
k := r1 + 4
r2 := r3
live out: r4 k r2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-64-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
32
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: r1 r2
g := mem[r2 + 12]
h := r1 - 1
r3 := g * h
r4 := mem[r2 + 8]
r1 := mem[r2 + 16]
r3 := mem[r3]
r2 := r4 + 8
r4 := r2
r1 := r1 + 4
r2 := r3
live out: r4 r1 r2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-65-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
33
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: r1 r2
g := mem[r2 + 12]
r3 := r1 - 1
r3 := g * r3
r4 := mem[r2 + 8]
r1 := mem[r2 + 16]
r3 := mem[r3]
r2 := r4 + 8
r4 := r2
r1 := r1 + 4
r2 := r3
live out: r4 r1 r2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-66-2048.jpg)
![j k
example with 4 colors
Register Allocation
Graph Coloring
34
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: r1 r2
r4 := mem[r2 + 12]
r3 := r1 - 1
r3 := r4 * r3
r4 := mem[r2 + 8]
r1 := mem[r2 + 16]
r3 := mem[r3]
r2 := r4 + 8
r4 := r2
r1 := r1 + 4
r2 := r3
live out: r4 r1 r2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-67-2048.jpg)


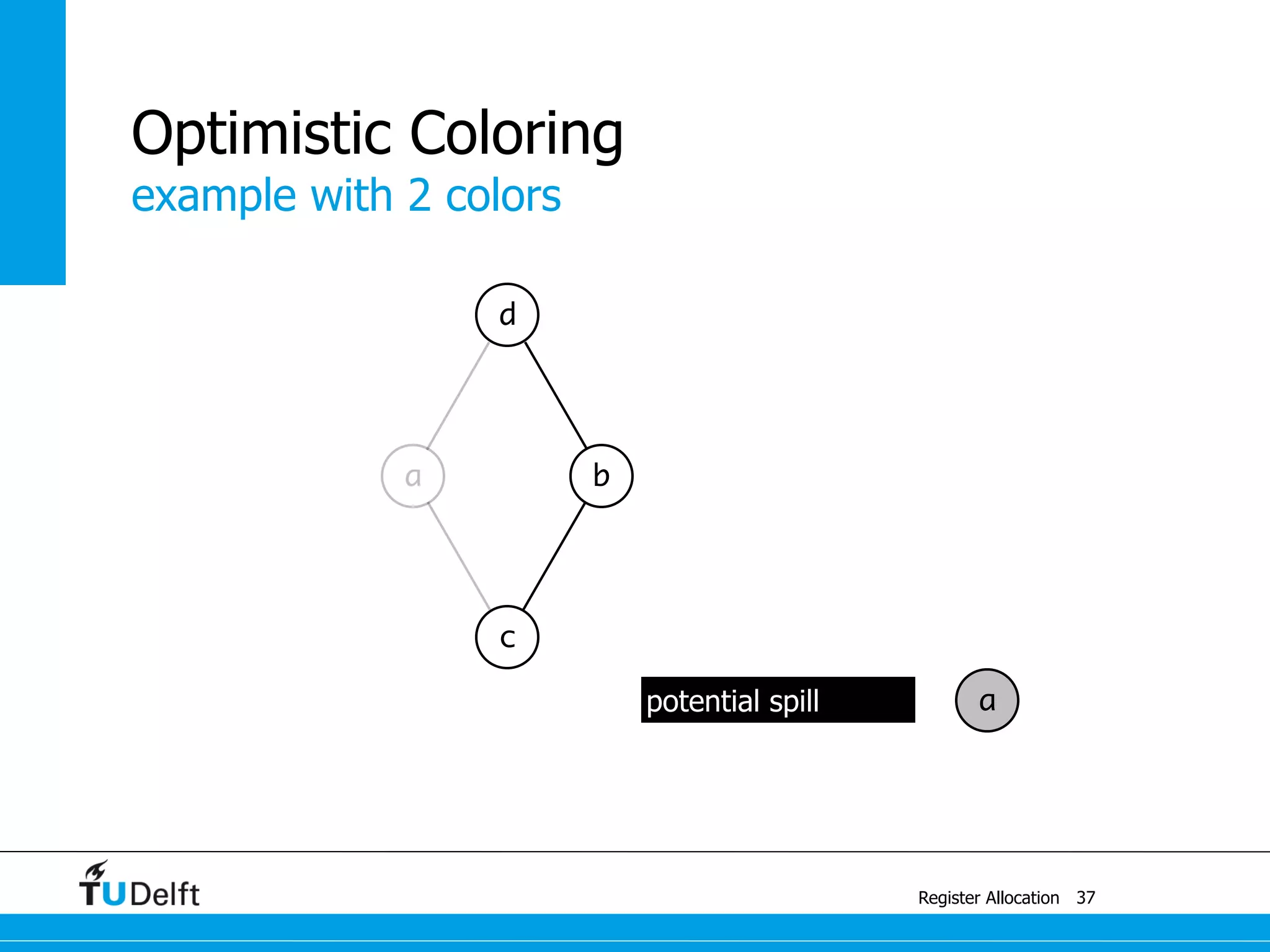
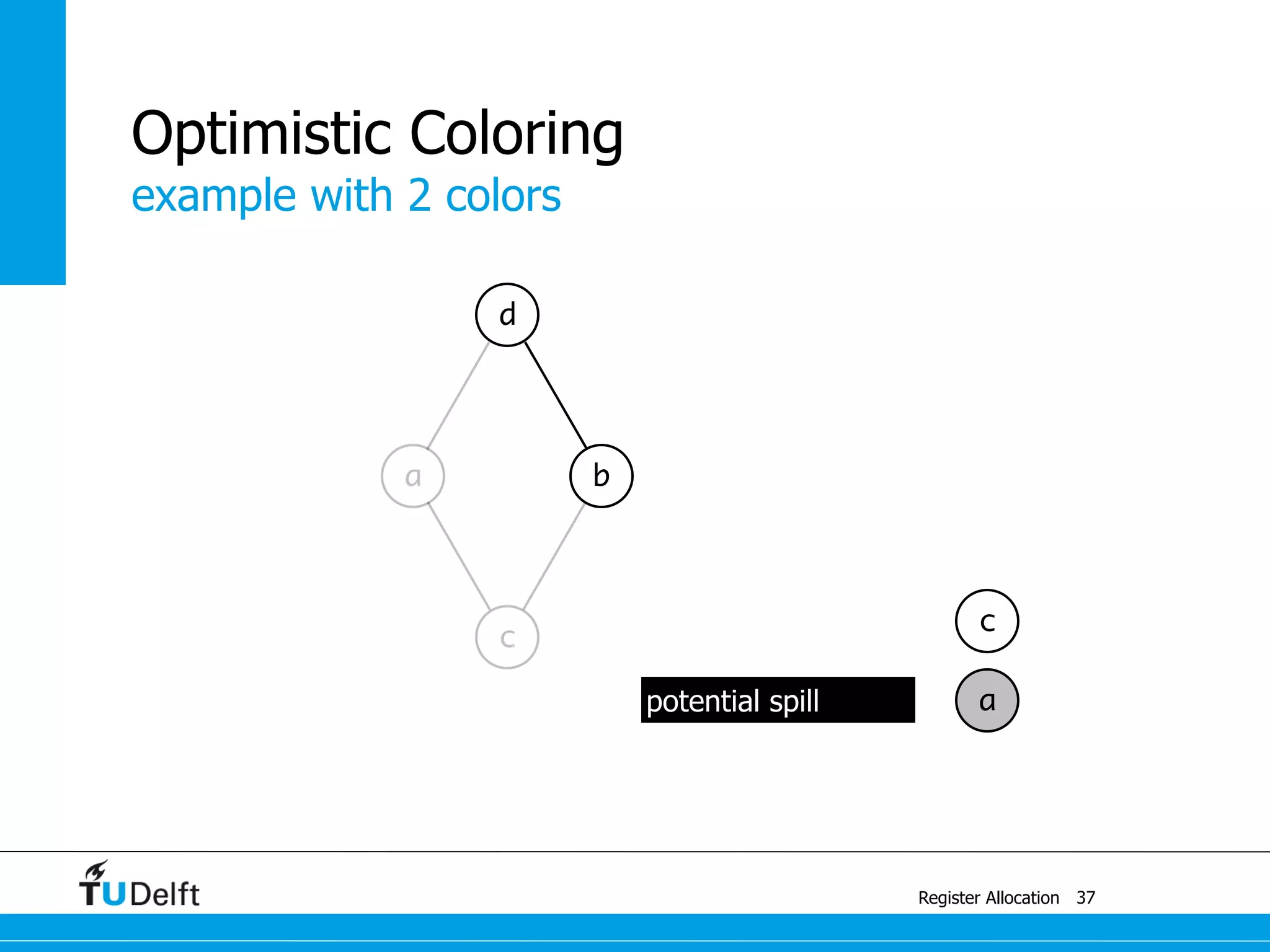
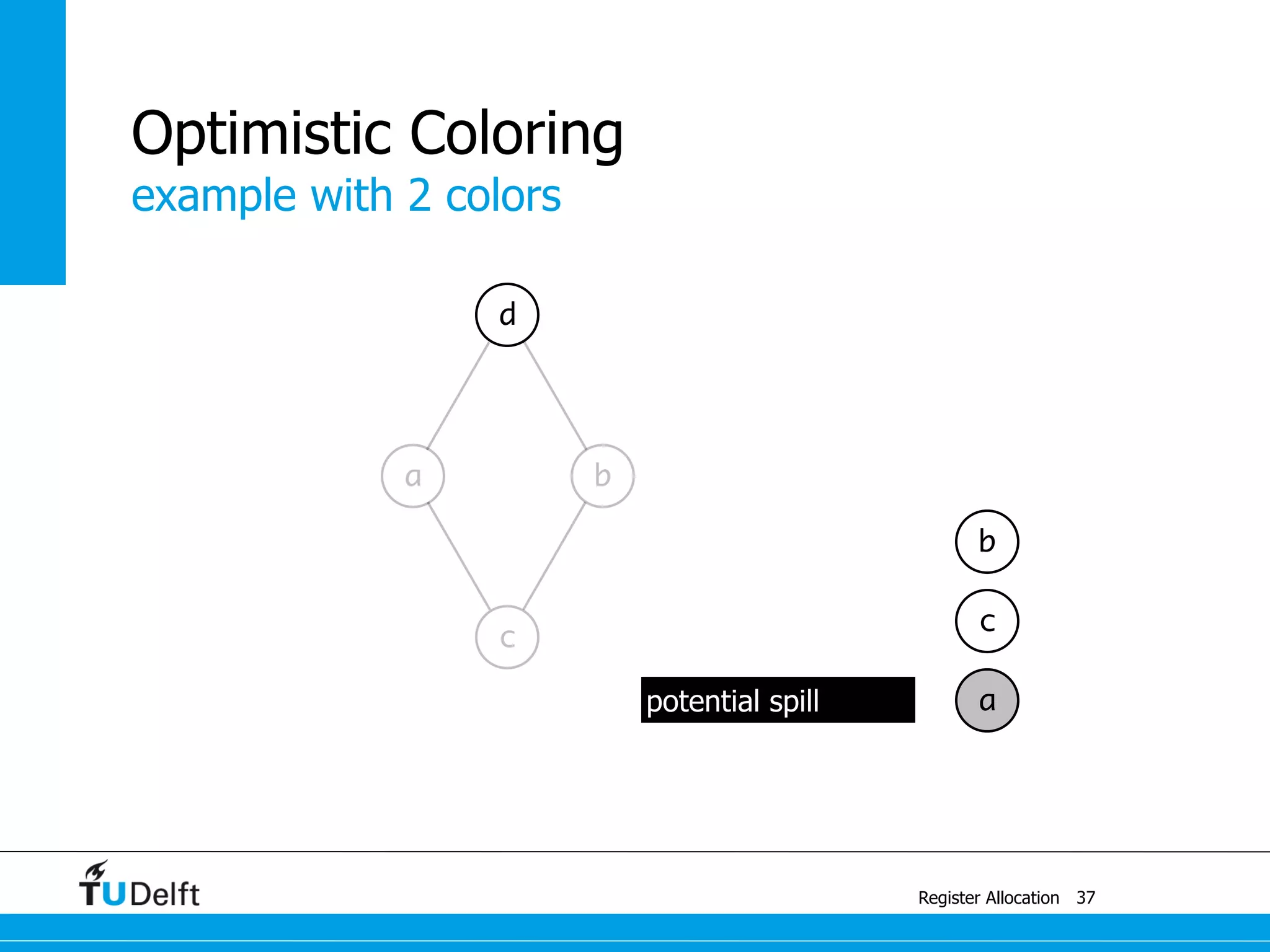
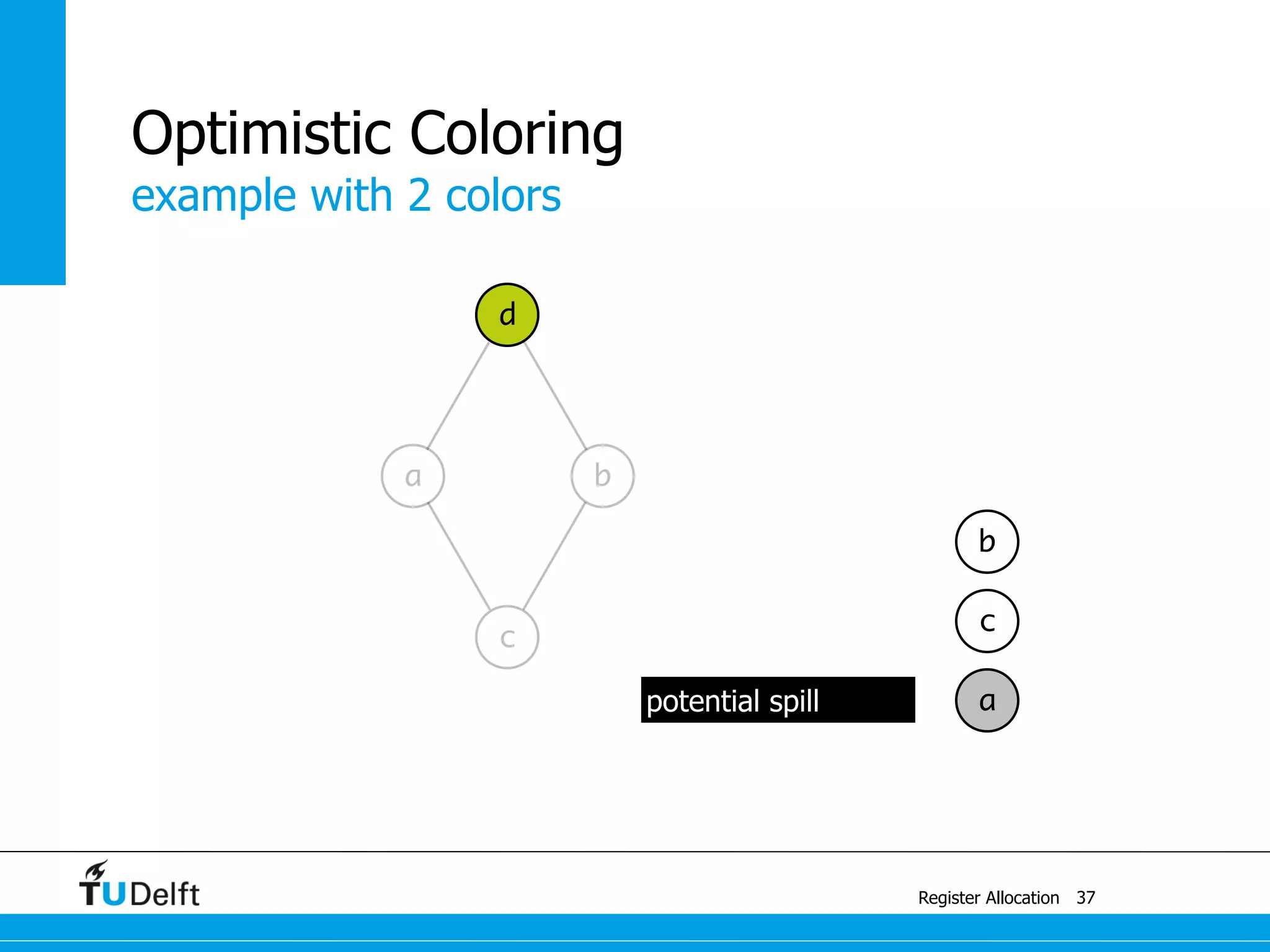


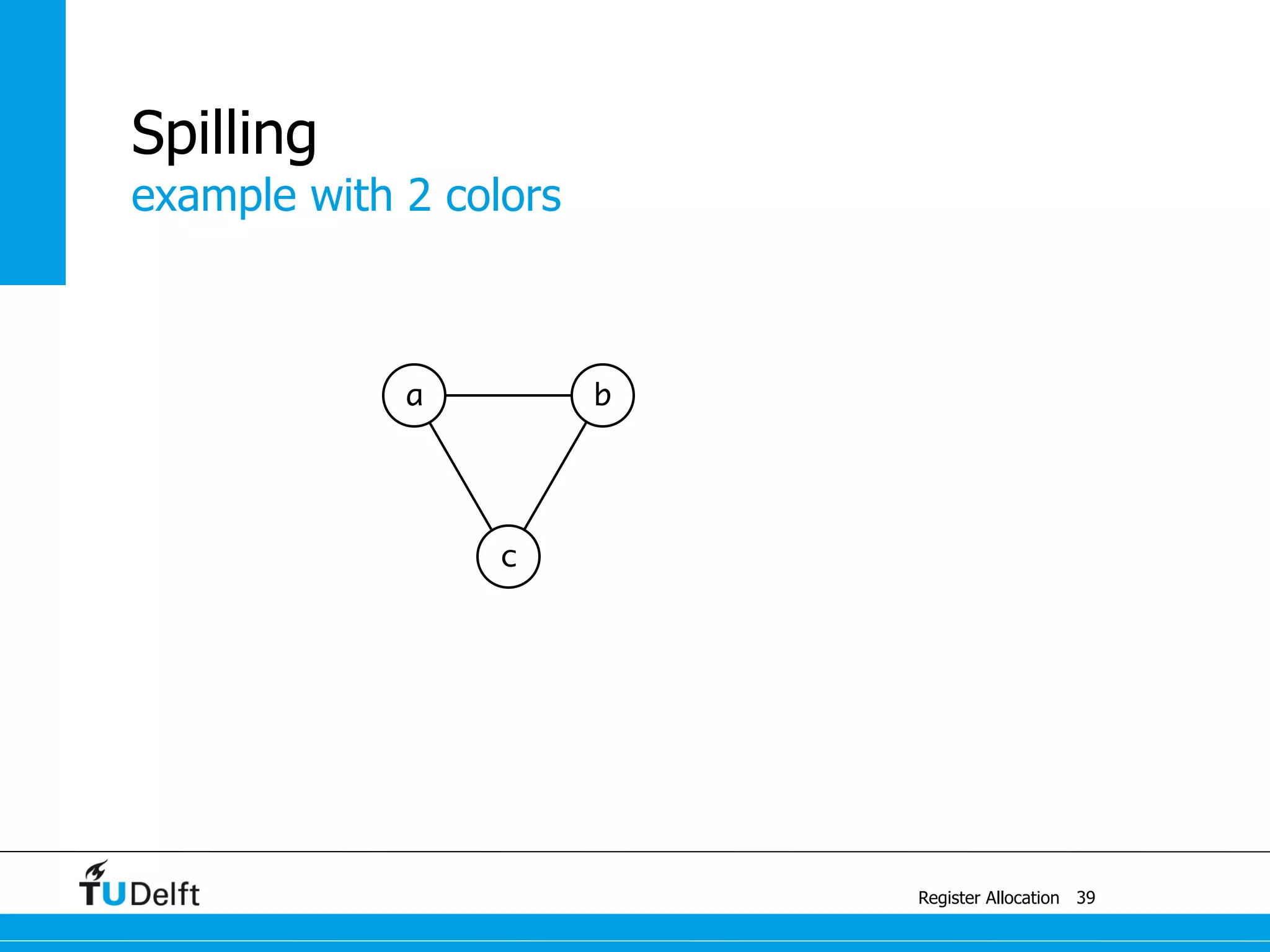
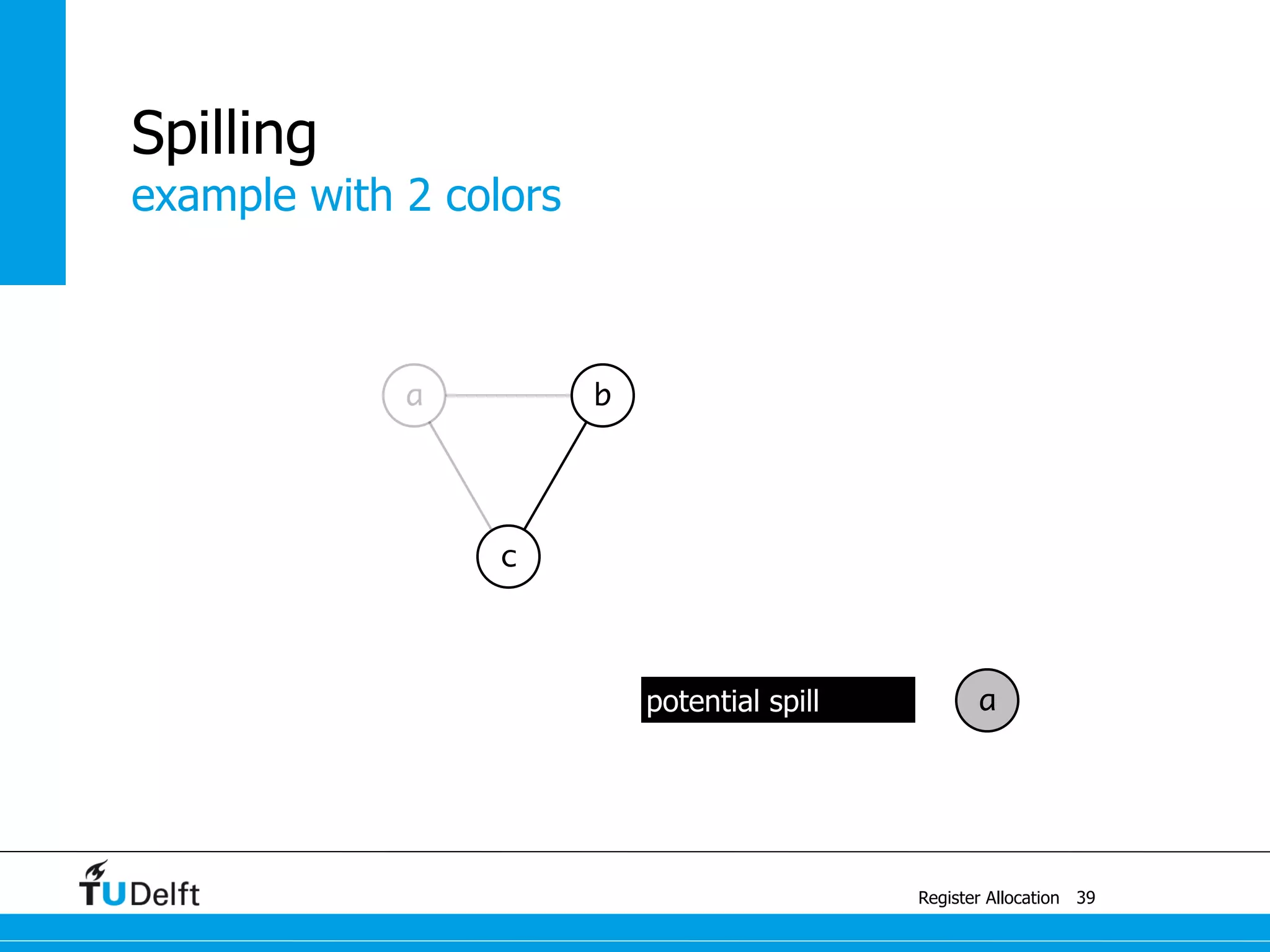
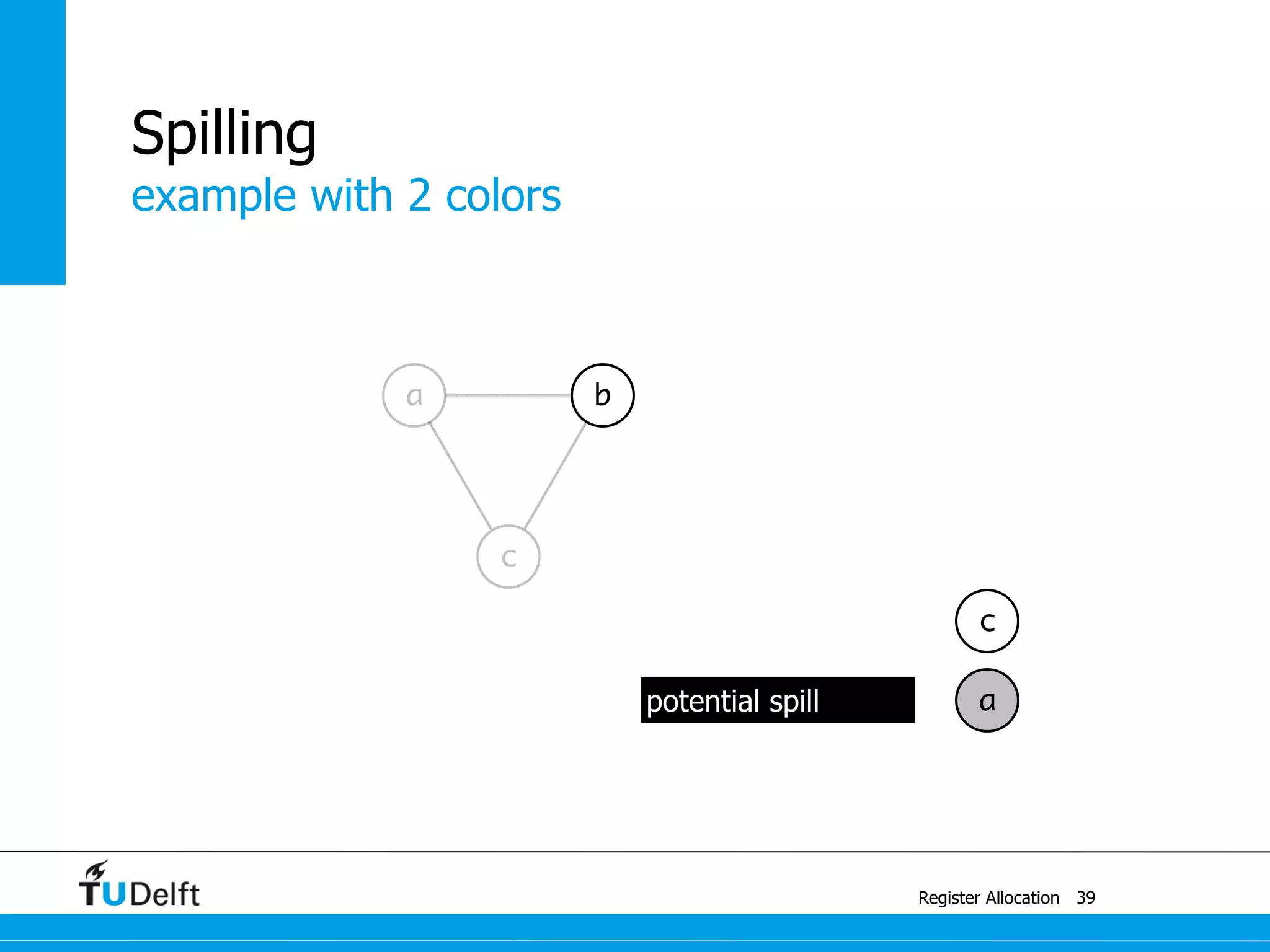
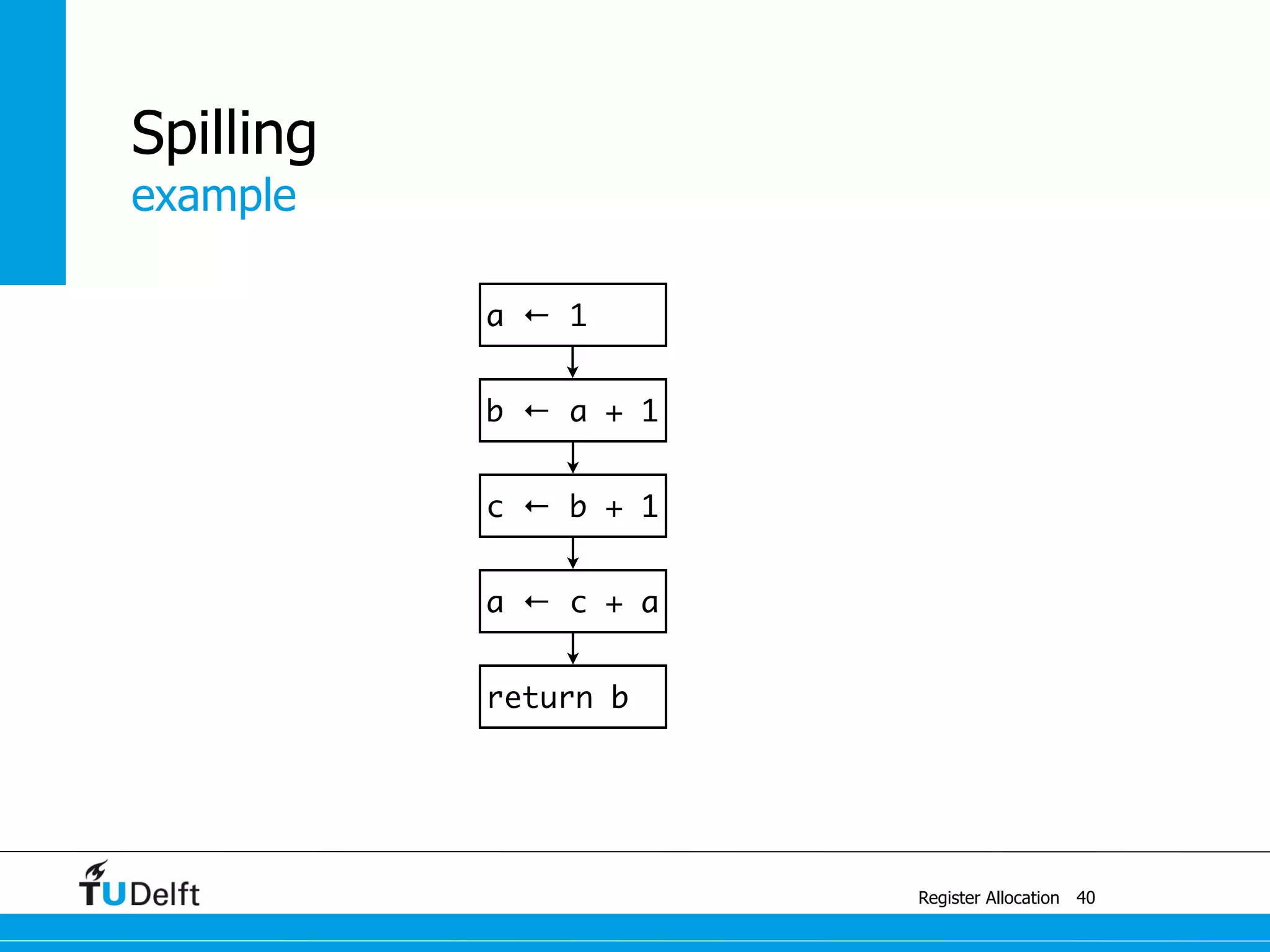
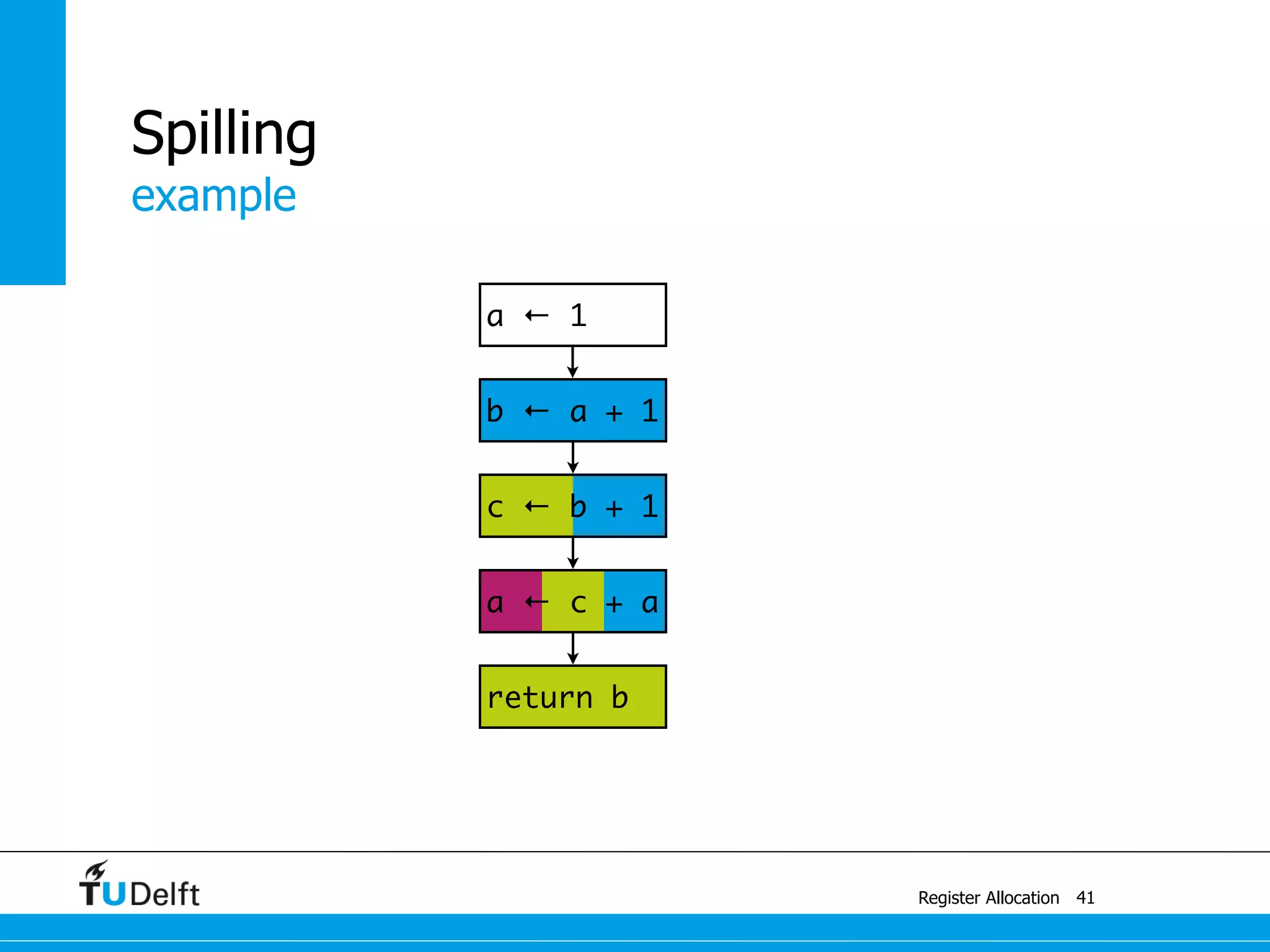
![a1 ← 1
M[42] ← a1
example
Register Allocation
Spilling
41
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-88-2048.jpg)
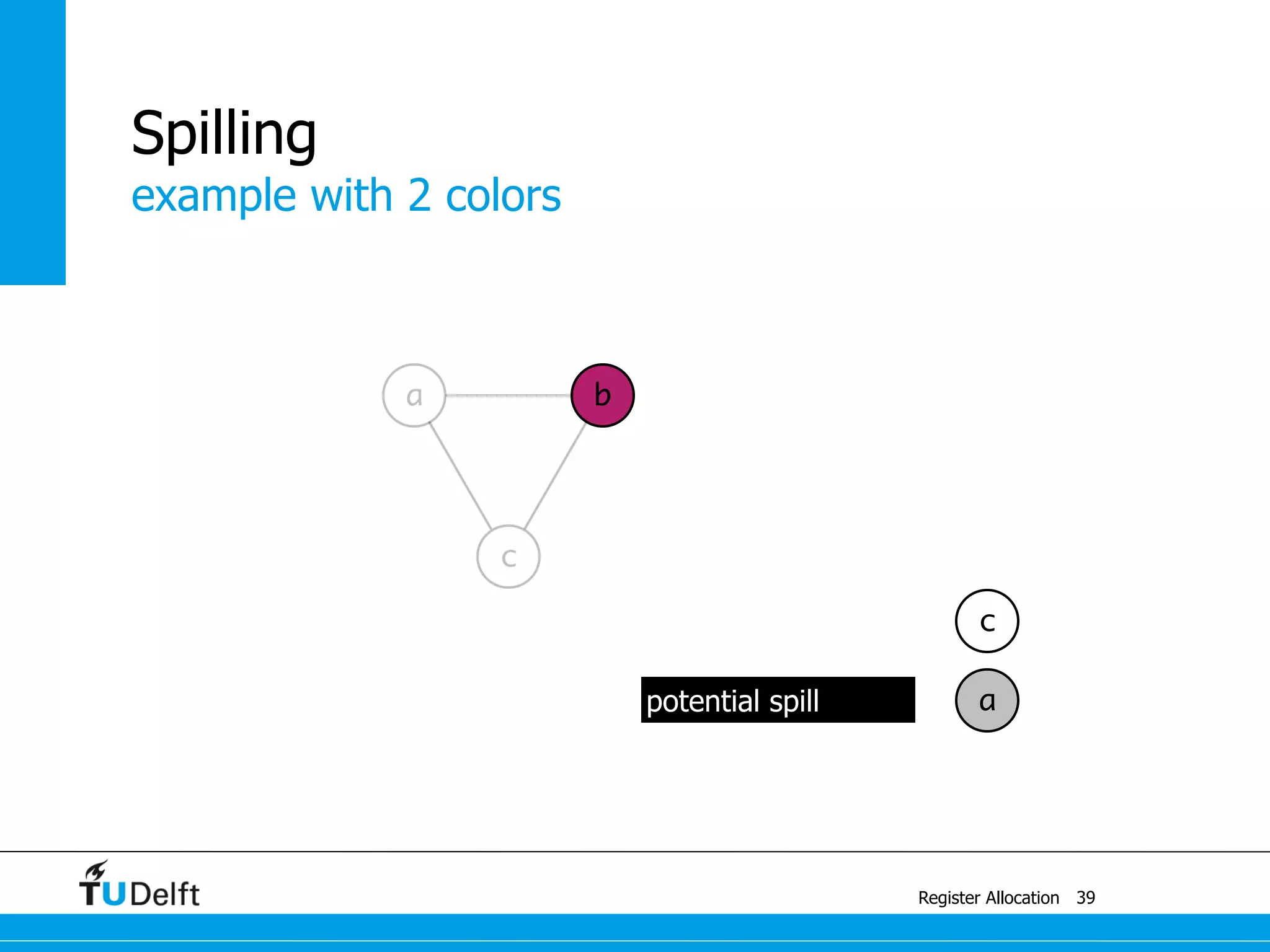
![a1 ← 1
M[42] ← a1
b ← a2 + 1
a2 ← M[42]
example
Register Allocation
Spilling
41
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-89-2048.jpg)
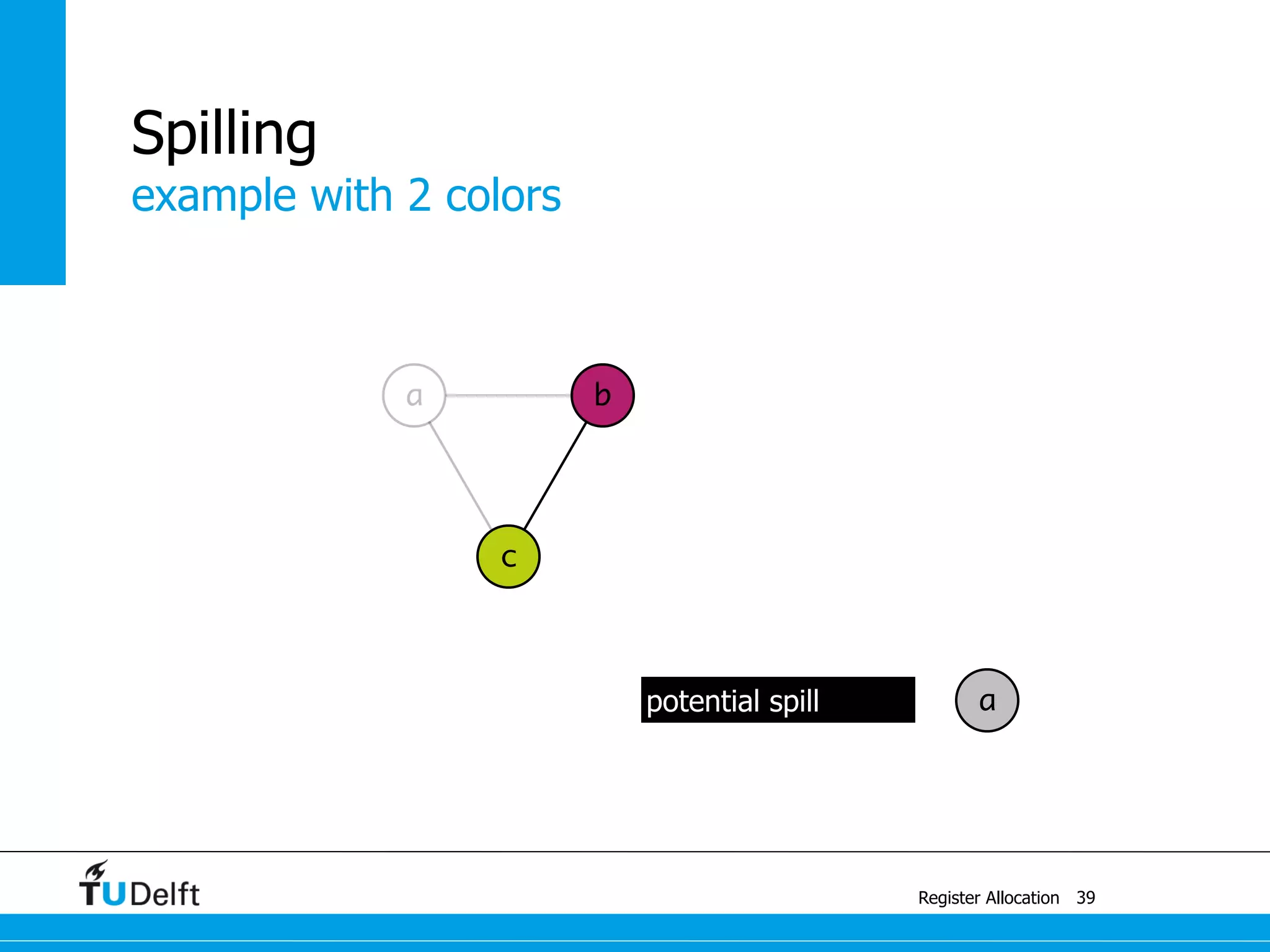
![a1 ← 1
M[42] ← a1
b ← a2 + 1
a2 ← M[42]
a4 ← c + a3
M[42] ← a4
a3 ← M[42]
example
Register Allocation
Spilling
41
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-90-2048.jpg)
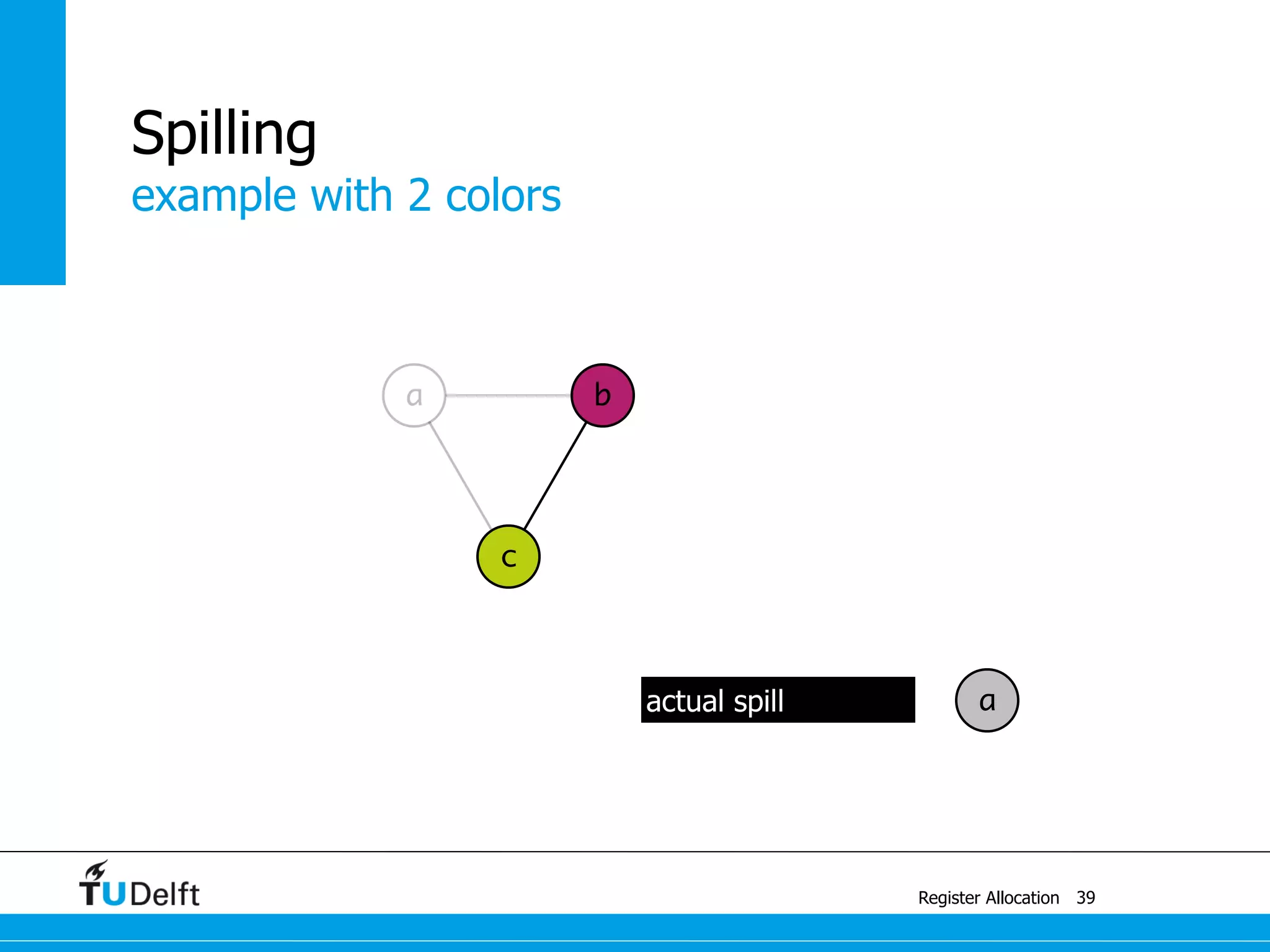
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
42
a4 ← c + a3
M[42] ← a4
a3 ← M[42]
a1 ← 1
M[42] ← a1
b ← a2 + 1
a2 ← M[42]
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-91-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
42
a4 ← c + a3
M[42] ← a4
a3 ← M[42]
a1 ← 1
M[42] ← a1
b ← a2 + 1
a2 ← M[42]
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-92-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
42
a4 ← c + a3
M[42] ← a4
a3 ← M[42]
a1 ← 1
M[42] ← a1
b ← a2 + 1
a2 ← M[42]
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-93-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
42
a4 ← c + a3
M[42] ← a4
a3 ← M[42]
a1 ← 1
M[42] ← a1
b ← a2 + 1
a2 ← M[42]
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-94-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
42
a4 ← c + a3
M[42] ← a4
a3 ← M[42]
a1 ← 1
M[42] ← a1
b ← a2 + 1
a2 ← M[42]
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-95-2048.jpg)
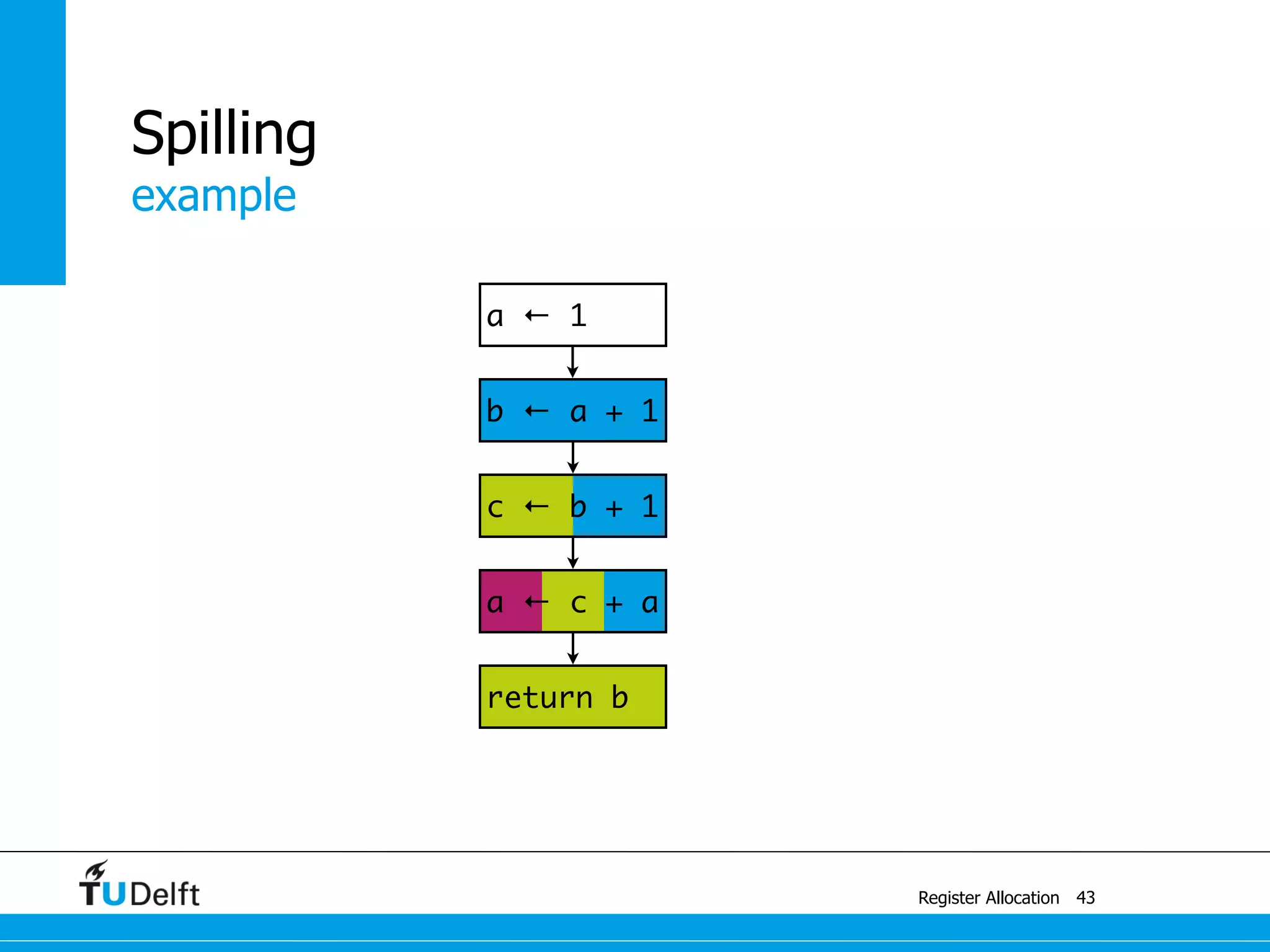
![b2 ← M[42]
c ← b2 + 1
example
Register Allocation
Spilling
43
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-97-2048.jpg)
![b2 ← M[42]
c ← b2 + 1
M[42] ← b1
b1 ← a + 1
example
Register Allocation
Spilling
43
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-98-2048.jpg)
![return b3
b3 ← M[42]
b2 ← M[42]
c ← b2 + 1
M[42] ← b1
b1 ← a + 1
example
Register Allocation
Spilling
43
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-99-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
44
return b3
b3 ← M[42]
b2 ← M[42]
c ← b2 + 1
M[42] ← b1
b1 ← a + 1
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-100-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
44
return b3
b3 ← M[42]
b2 ← M[42]
c ← b2 + 1
M[42] ← b1
b1 ← a + 1
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-101-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
44
return b3
b3 ← M[42]
b2 ← M[42]
c ← b2 + 1
M[42] ← b1
b1 ← a + 1
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-102-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
44
return b3
b3 ← M[42]
b2 ← M[42]
c ← b2 + 1
M[42] ← b1
b1 ← a + 1
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-103-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Spilling
44
return b3
b3 ← M[42]
b2 ← M[42]
c ← b2 + 1
M[42] ← b1
b1 ← a + 1
a ← c + a
c ← b + 1
b ← a + 1
a ← 1
return b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-104-2048.jpg)

![coalescing
Register Allocation
Eliminating Move Instructions
46
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-106-2048.jpg)
![coalescing
Register Allocation
Eliminating Move Instructions
47
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-107-2048.jpg)
![Register Allocation
Coalescing
48
coalesce |ˌkəʊəˈlɛs|
verb [no object]
come together to form one mass or whole: the puddles had coalesced
into shallow streams.
• [with object] combine (elements) in a mass or whole: his idea served to
coalesce all that happened into one connected whole.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-108-2048.jpg)
![j k
example
Register Allocation
Recap: Graph Coloring
49
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-109-2048.jpg)
![j k
example
Register Allocation
Recap: Graph Coloring
49
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-110-2048.jpg)
![j k
example
Register Allocation
Recap: Graph Coloring
49
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-111-2048.jpg)
![j k
better solution
Register Allocation
Coalescing
50
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-112-2048.jpg)
![j k
better solution
Register Allocation
Coalescing
50
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-113-2048.jpg)
![j k
better solution
Register Allocation
Coalescing
50
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-114-2048.jpg)
![jb k
coalescing nodes
Register Allocation
Coalescing
51
m
e
f
h g cd
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-115-2048.jpg)


![j k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
54
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-118-2048.jpg)
![j k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
55
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-119-2048.jpg)
![j k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
56
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-120-2048.jpg)
![j k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
57
g
b m
e
f
h g d c
h
k
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-121-2048.jpg)
![j k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
58
g
b m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-122-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
59
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-123-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
60
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-124-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
61
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
jb
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-125-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
62
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
jb
fr1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-126-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
63
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
jb
f
m
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
e := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := e + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-127-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
64
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
jb
f
m
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
r1 := mem[j + 8]
m := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := r1 + 8
d := c
k := m + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-128-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
65
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
jb
fr1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
f := g * h
r1 := mem[j + 8]
r2 := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[f]
c := r1 + 8
d := c
k := r2 + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-129-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
66
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
jb
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k j
g := mem[j + 12]
h := k - 1
r3 := g * h
r1 := mem[j + 8]
r2 := mem[j + 16]
b := mem[r3]
c := r1 + 8
d := c
k := r2 + 4
j := b
live out: d k j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-130-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
67
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
cd
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k r4
g := mem[r4 + 12]
h := k - 1
r3 := g * h
r1 := mem[r4 + 8]
r2 := mem[r4 + 16]
b := mem[r3]
c := r1 + 8
d := c
k := r2 + 4
r4 := r4
live out: d k r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-131-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
68
g
m
e
f
h g
h
k
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: k r4
g := mem[r4 + 12]
h := k - 1
r3 := g * h
r1 := mem[r4 + 8]
r2 := mem[r4 + 16]
b := mem[r3]
r1 := r1 + 8
r1 := r1
k := r2 + 4
r4 := r4
live out: r1 k r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-132-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
69
g
m
e
f
h g
h
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: r2 r4
g := mem[r4 + 12]
h := r2 - 1
r3 := g * h
r1 := mem[r4 + 8]
r2 := mem[r4 + 16]
b := mem[r3]
r1 := r1 + 8
r1 := r1
k := r2 + 4
r4 := r4
live out: r1 r2 r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-133-2048.jpg)
![cd
jb k
example
Register Allocation
Coalescing
70
g
m
e
f
h g
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: r2 r4
g := mem[r4 + 12]
r2 := r2 - 1
r3 := g * r2
r1 := mem[r4 + 8]
r2 := mem[r4 + 16]
b := mem[r3]
r1 := r1 + 8
r1 := r1
k := r2 + 4
r4 := r4
live out: r1 r2 r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-134-2048.jpg)
![jb k
coalescing nodes
Register Allocation
Coalescing
71
m
e
f
h g cd
r1
r2
r3
r4
live-in: r2 r4
r1 := mem[r4 + 12]
r2 := r2 - 1
r3 := r1 * r2
r1 := mem[r4 + 8]
r2 := mem[r4 + 16]
b := mem[r3]
r1 := r1 + 8
r1 := r1
k := r2 + 4
r4 := r4
live out: r1 r2 r4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-135-2048.jpg)

![CDECL
Register Allocation
Recap: Calling Conventions
Caller
• push parameters right-to-left on the stack
• clean-up stack after call
Callee
• save old BP
• initialise new BP
• save registers
• return result in AX
• restore registers
• restore BP
73
push 21
push 42
call _f
add ESP 8
push EBP
mov EBP ESP
mov EAX [EBP + 8]
mov EDX [EBP + 12]
add EAX EDX
pop EBP
ret](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-137-2048.jpg)
![STDCALL
Register Allocation
Recap: Calling Conventions
Caller
• push parameters right-to-left on the stack
Callee
• save old BP
• initialise new BP
• save registers
• return result in AX
• restore registers
• restore BP
74
push 21
push 42
call _f@8
push EBP
mov EBP ESP
mov EAX [EBP + 8]
mov EDX [EBP + 12]
add EAX EDX
pop EBP
ret 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-138-2048.jpg)
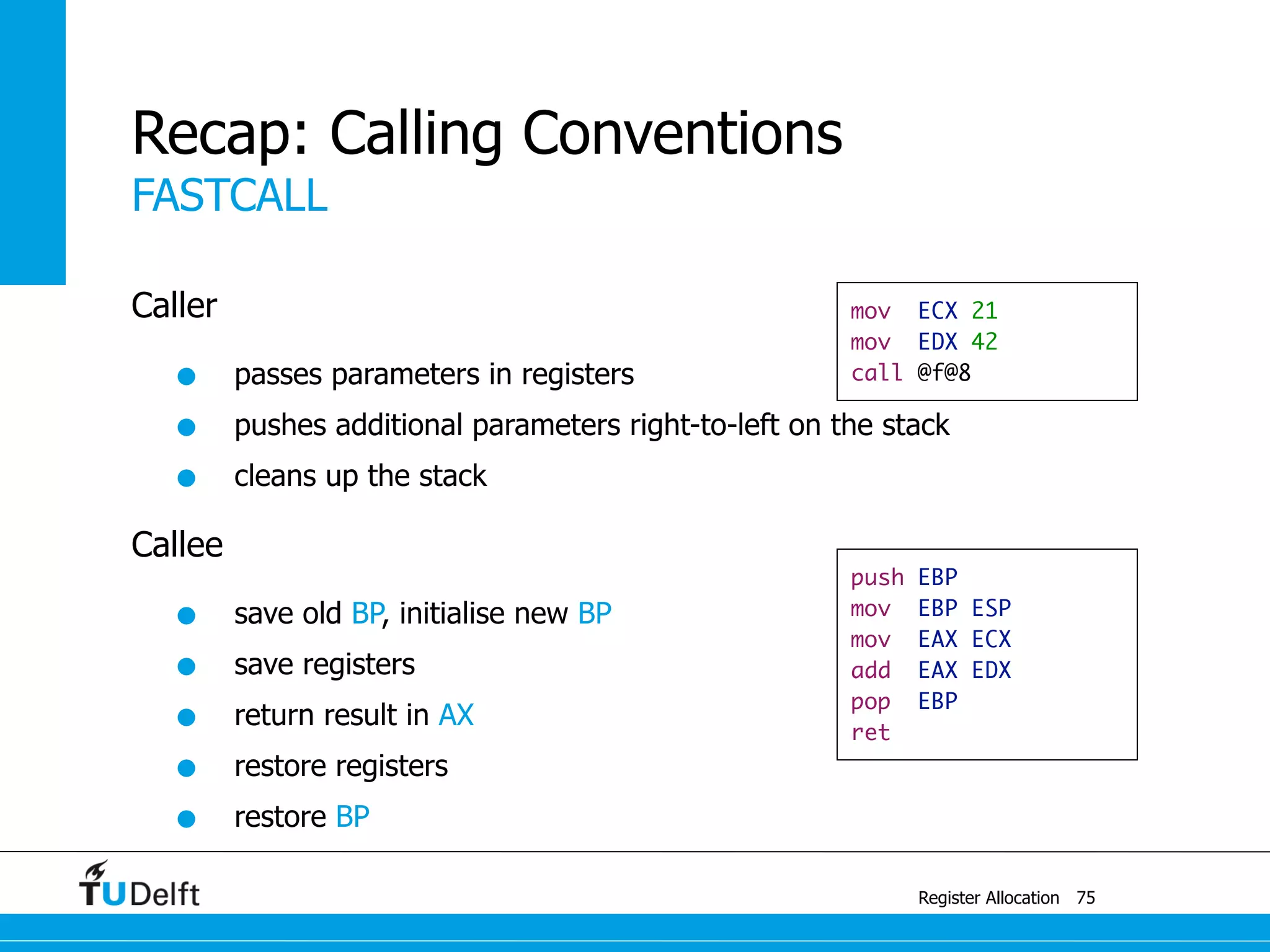





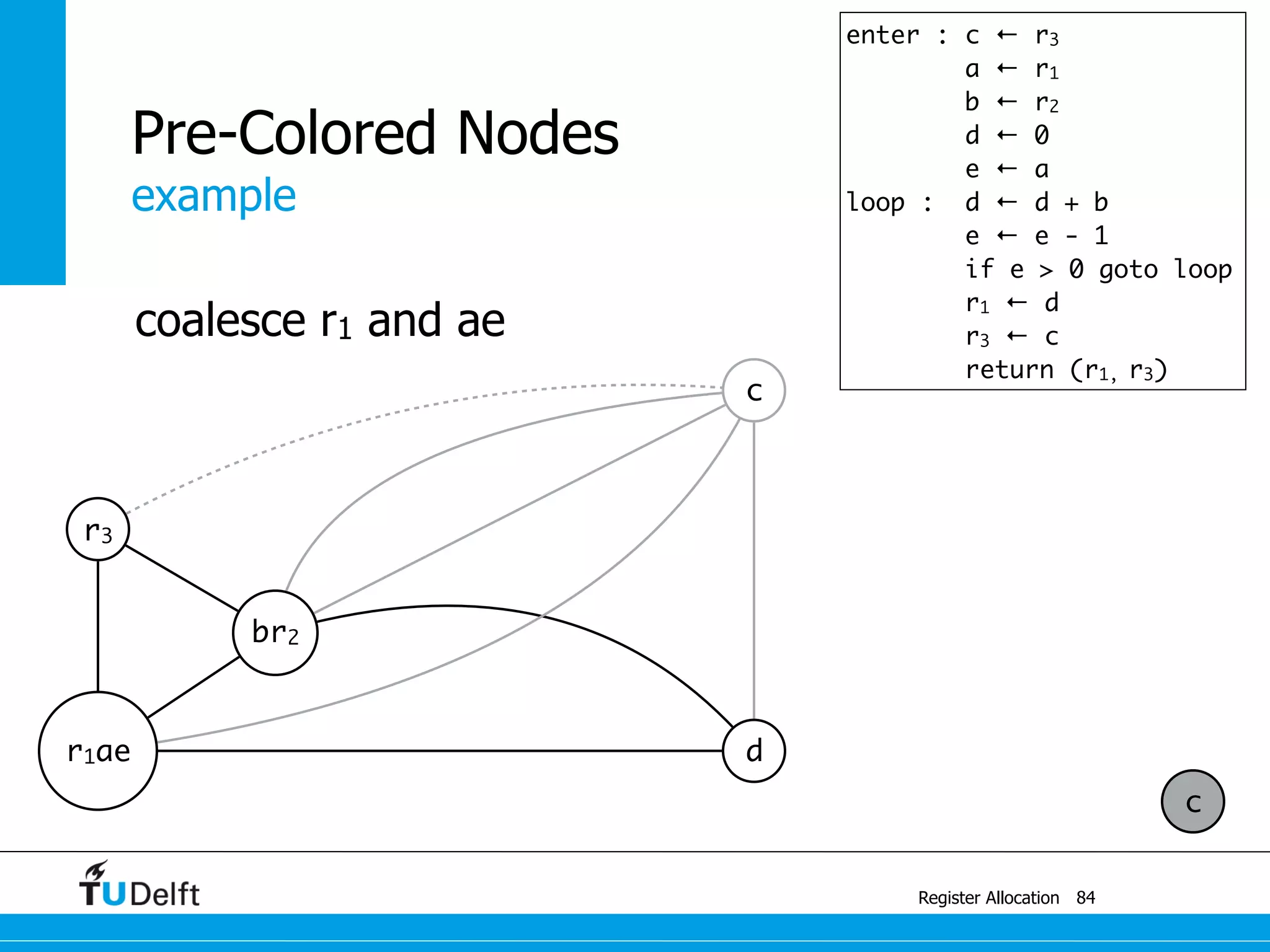
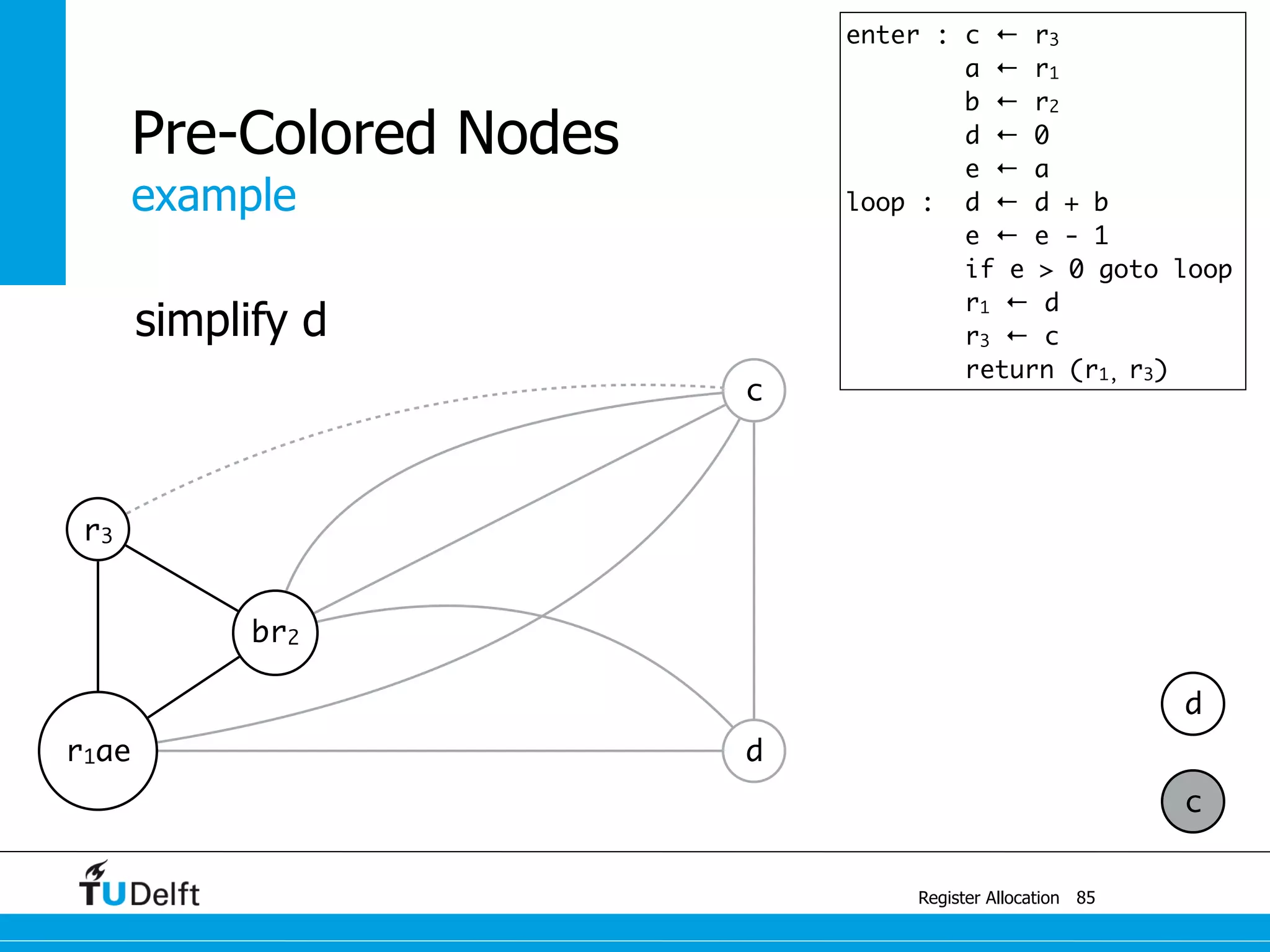
![example
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
87
r3
br2
r1ae r3
c
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
c
spill c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-151-2048.jpg)
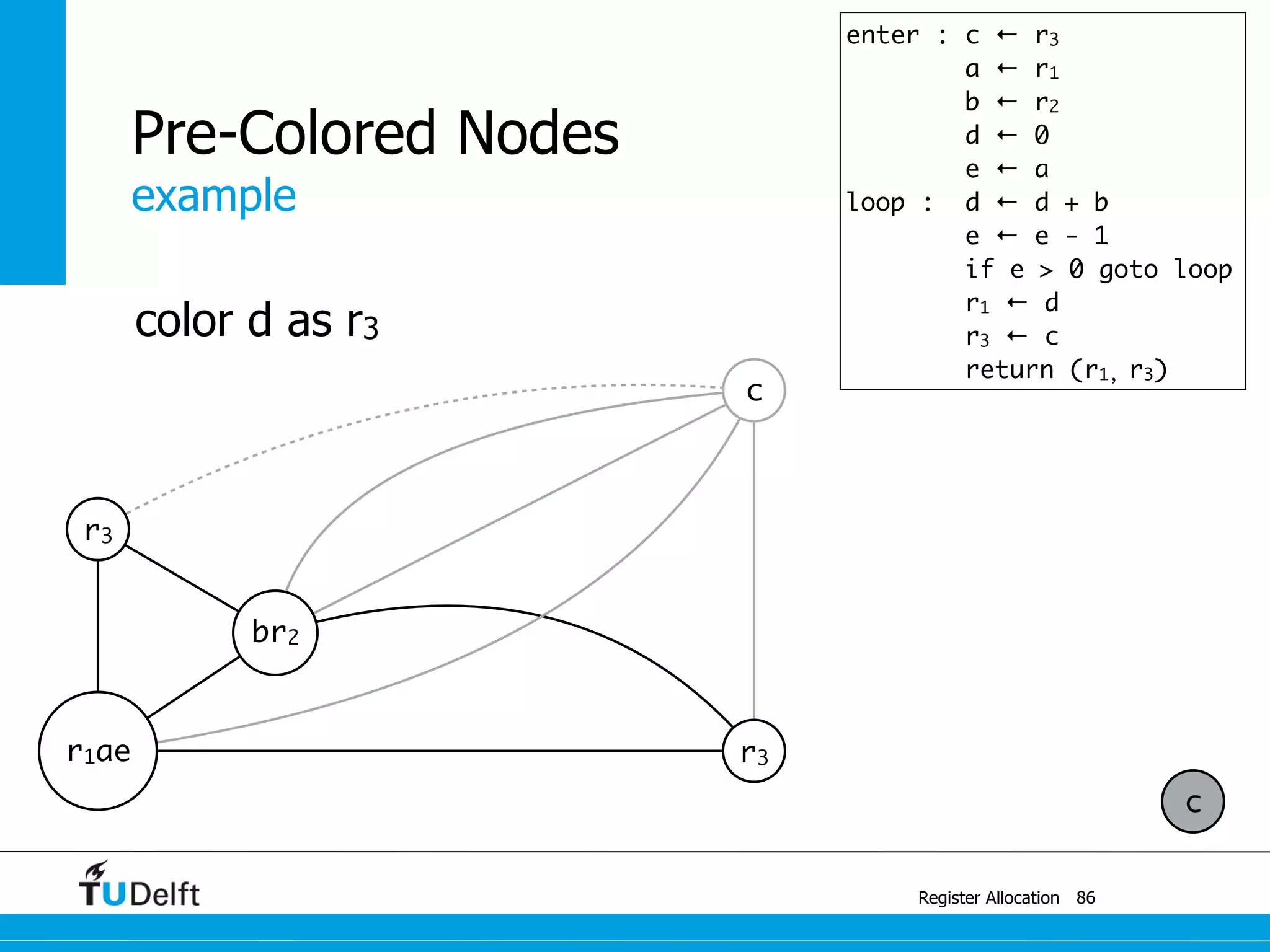
![example
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
88
r3
br2
r1ae r3
c
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
spill c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-152-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
89
r3
r2
b e
r1 a
d
c
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
start over](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-153-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
90
r3
r2
b e
r1 a
d
c
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-154-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
91
r3
r2
b e
r1 a
d
c1
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
c2
new graph](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-155-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
92
r3
r2
b e
r1 a
d
c1
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
c2
coalesce c1, c2, r3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-156-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
93
c1c2r3
r2
b e
r1 a
d
c1
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
c2
coalesce c1, c2, r3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-157-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
94
c1c2r3
r2
b e
r1 a
d
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
coalesce (b, r2) and (a, e)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-158-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
95
c1c2r3 br2
r1 ae
d
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
coalesce (ae, r1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-159-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
96
c1c2r3 br2
r1ae d
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
simplify d
d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-160-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
97
c1c2r3 br2
r1ae r3
enter : c1 ← r3
M[cloc] ← c1
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c2
c2 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
color d as r3
d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-161-2048.jpg)
![examples
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
98
c1c2r3 br2
r1ae r3
enter : r3 ← r3
M[cloc] ← r3
r1 ← r1
r2 ← r2
r3 ← 0
r1 ← r1
loop : r3 ← r3 + r2
r1 ← r1 - 1
if r1 > 0 goto loop
r1 ← r3
r3 ← r3
r3 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
apply register assigment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-162-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
99
enter : c ← r3
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c
return (r1, r3)
enter : r3 ← r3
M[cloc] ← r3
r1 ← r1
r2 ← r2
r3 ← 0
r1 ← r1
loop : r3 ← r3 + r2
r1 ← r1 - 1
if r1 > 0 goto loop
r1 ← r3
r3 ← r3
r3 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-163-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
100
enter : c ← r3
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c
return (r1, r3)
enter : r3 ← r3
M[cloc] ← r3
r1 ← r1
r2 ← r2
r3 ← 0
r1 ← r1
loop : r3 ← r3 + r2
r1 ← r1 - 1
if r1 > 0 goto loop
r1 ← r3
r3 ← r3
r3 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-164-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
101
enter : c ← r3
a ← r1
b ← r2
d ← 0
e ← a
loop : d ← d + b
e ← e - 1
if e > 0 goto loop
r1 ← d
r3 ← c
return (r1, r3)
enter : M[cloc] ← r3
r3 ← 0
loop : r3 ← r3 + r2
r1 ← r1 - 1
if r1 > 0 goto loop
r1 ← r3
r3 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-165-2048.jpg)
![example
Register Allocation
Pre-Colored Nodes
102
enter : M[cloc] ← r3
r3 ← 0
loop : r3 ← r3 + r2
r1 ← r1 - 1
if r1 > 0 goto loop
r3 ← M[cloc]
return (r1, r3)
int f(int a, int b) {
int d = 0;
int e = a;
do {
d = d + b;
e = e - 1;
} while (e > 0);
return d;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registerallocation-170116141822/75/Register-Allocation-166-2048.jpg)