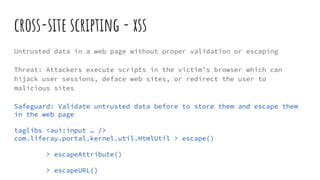
The document emphasizes the importance of security in Liferay Portal, detailing various web application security risks from the OWASP Top 10 and recommended safeguards. It covers strategies to mitigate vulnerabilities, such as updating software, using parameterized APIs, and implementing strong authentication measures. Additionally, it advises on the importance of logging, monitoring, and proper configuration to protect sensitive data from various attack vectors.