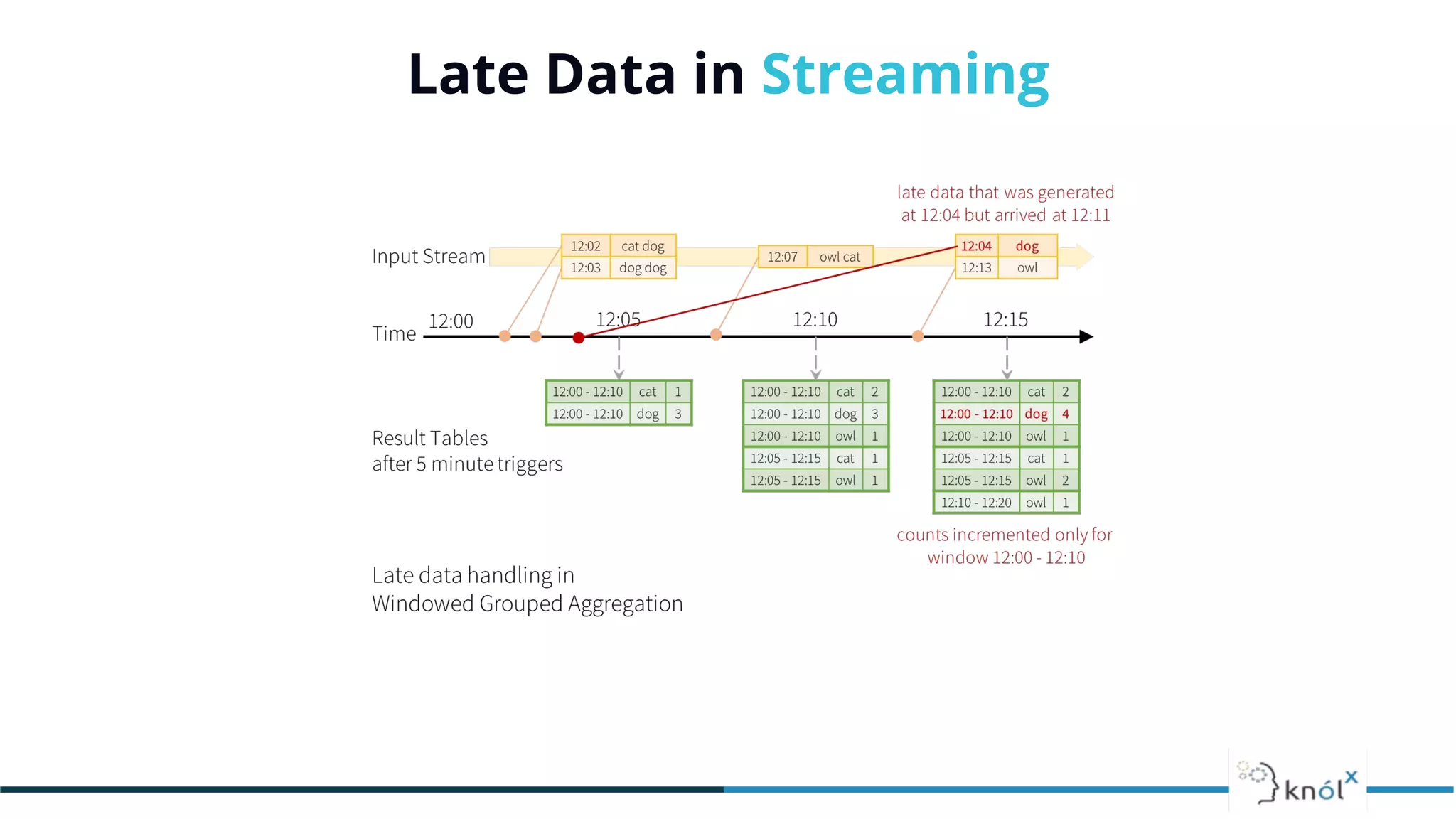
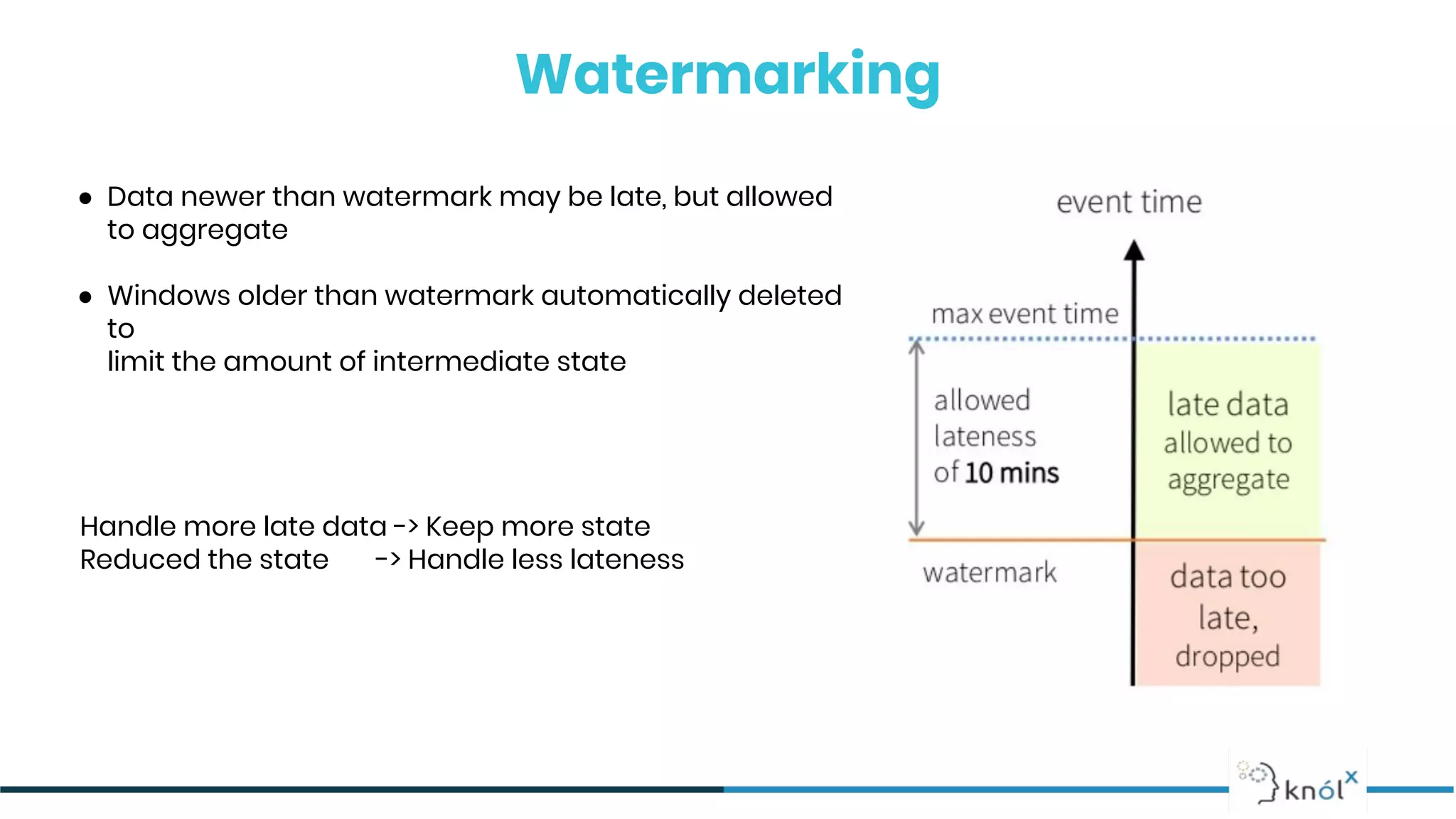
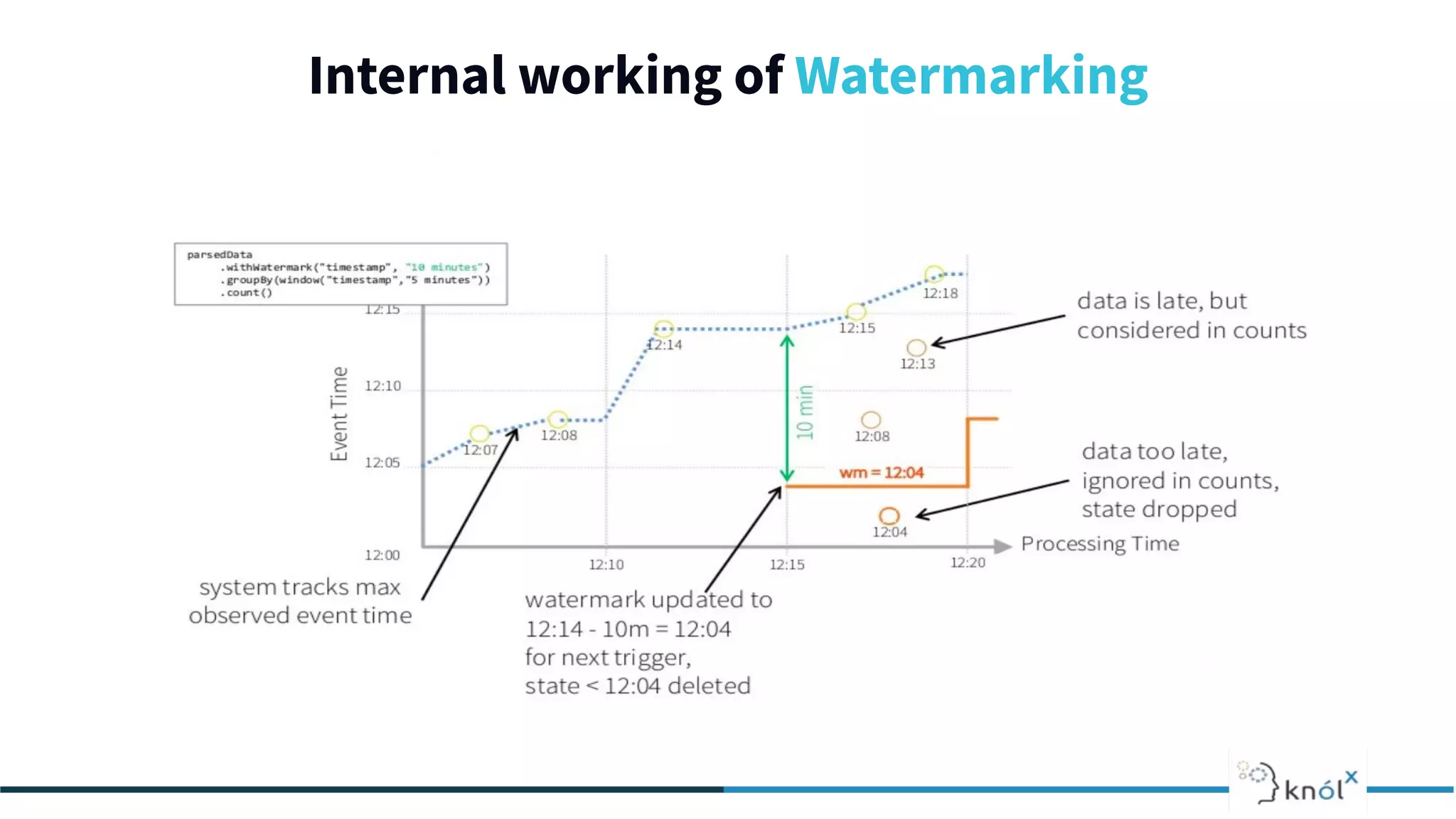
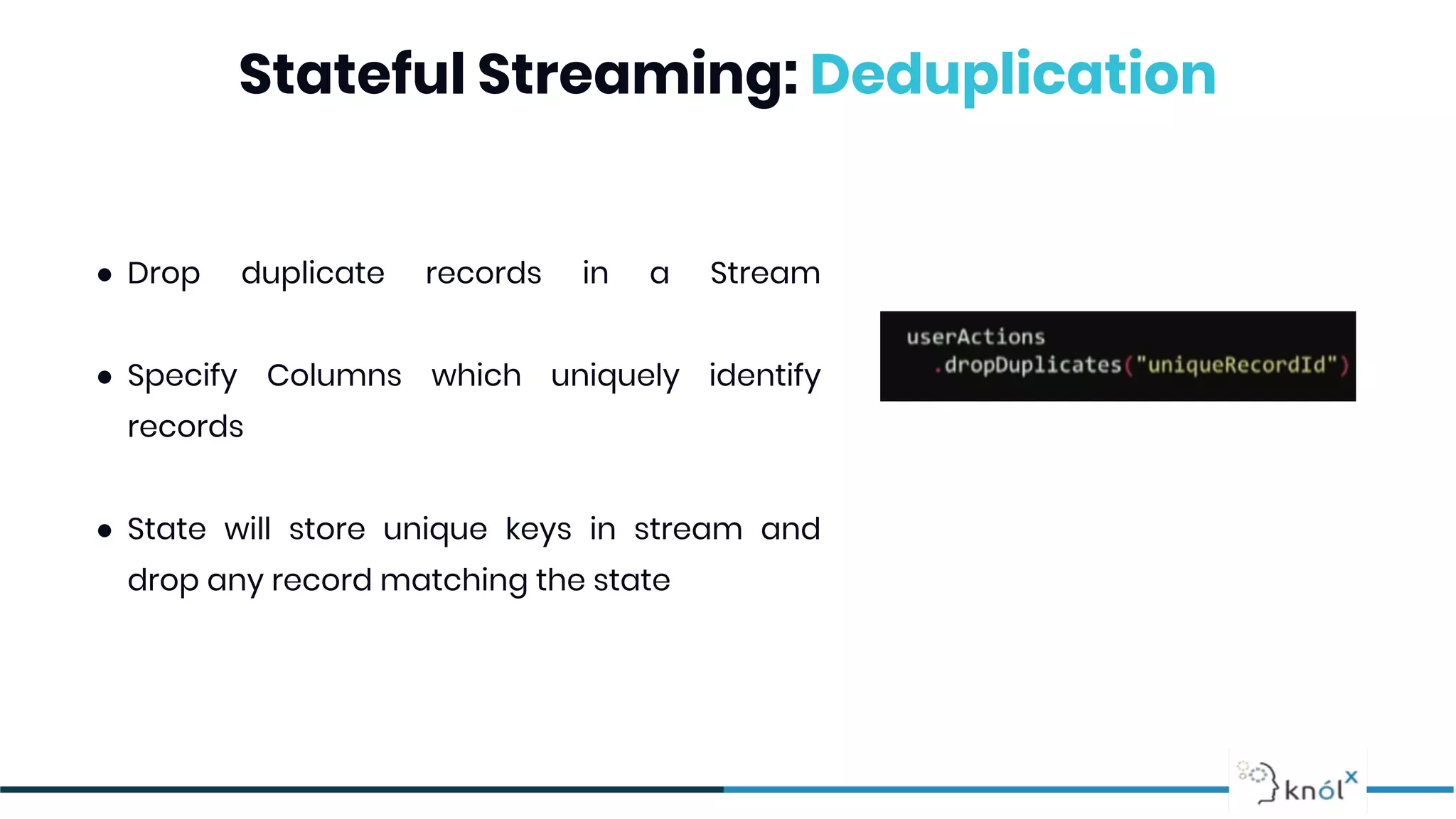
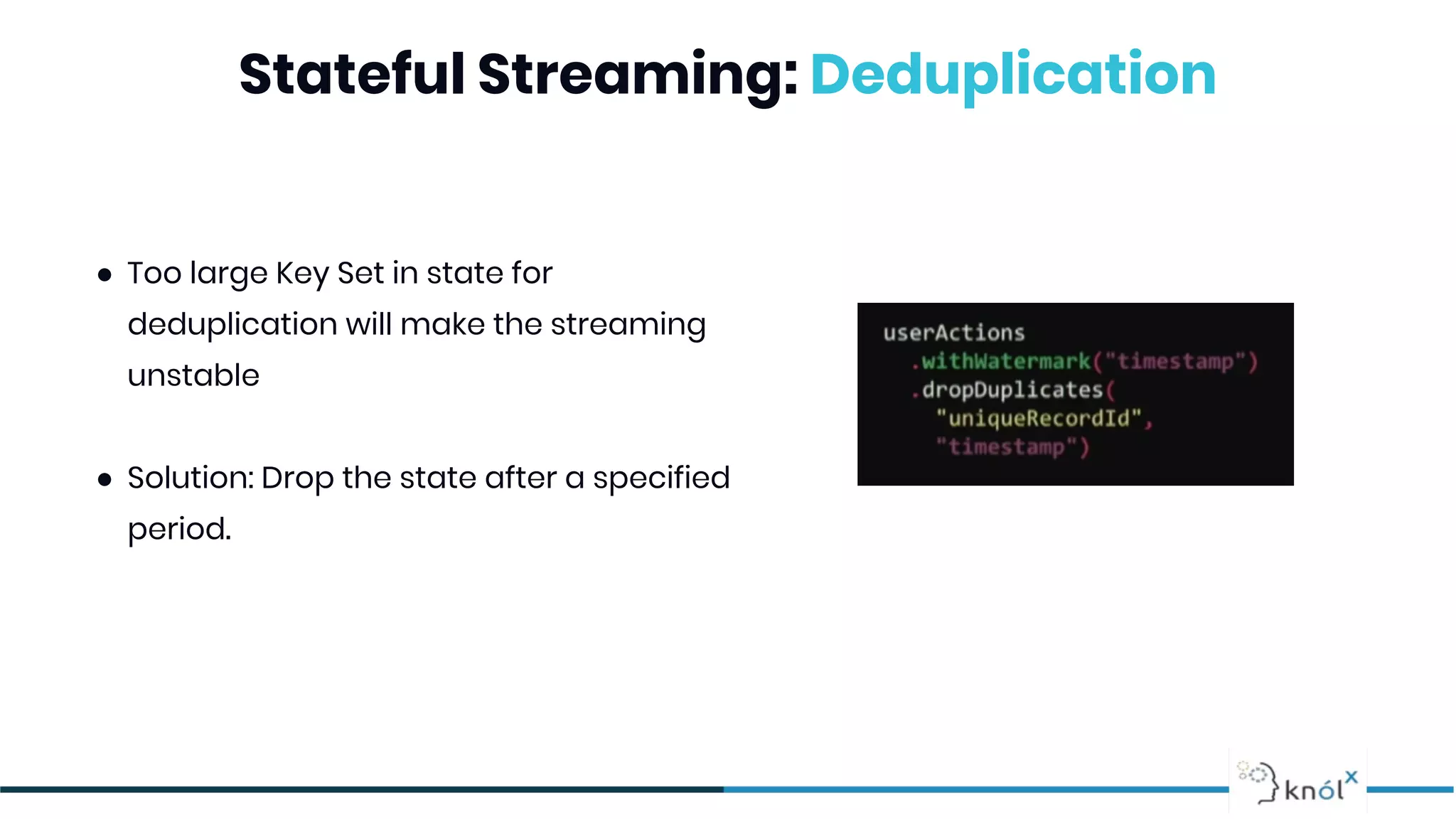
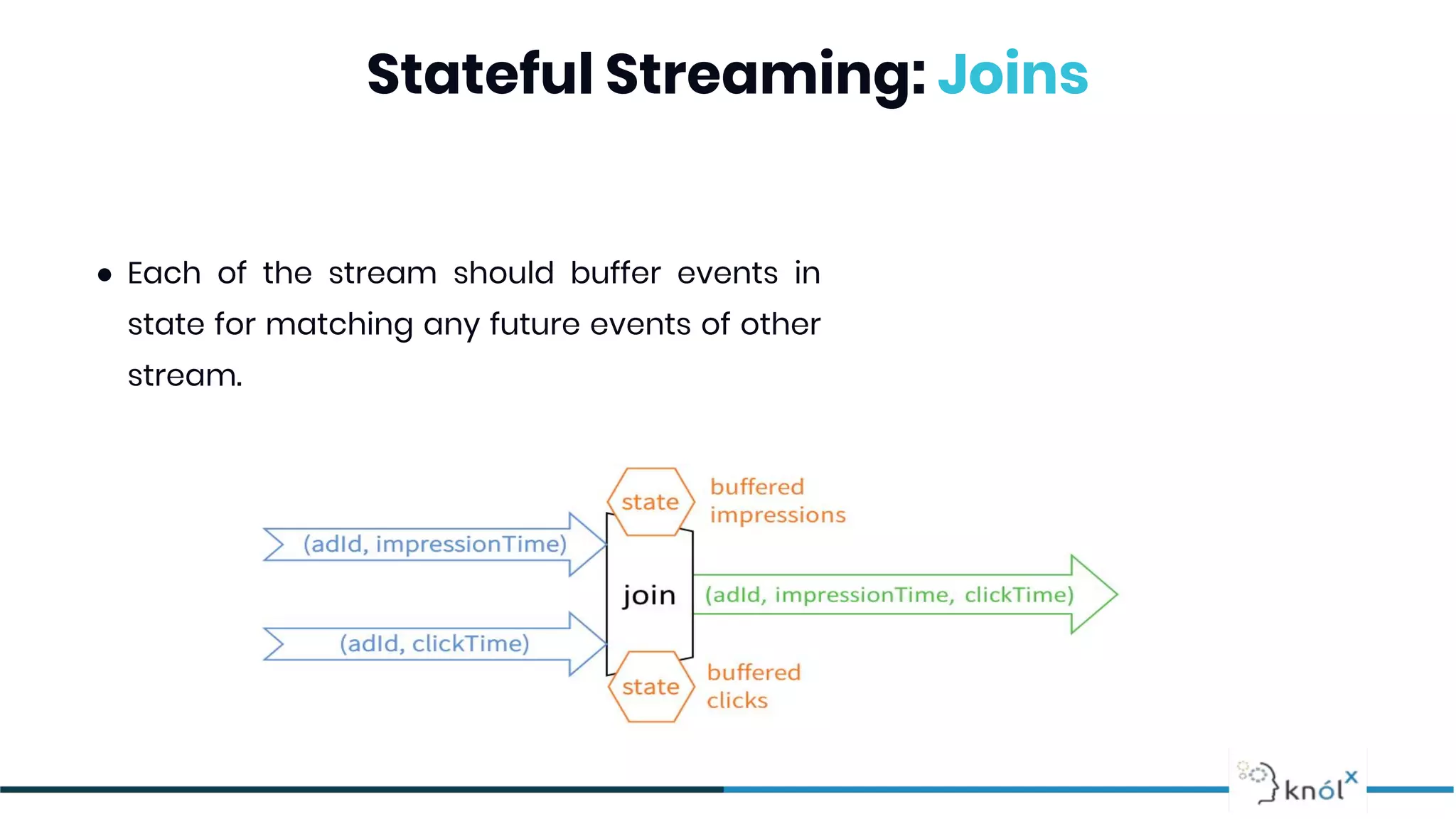
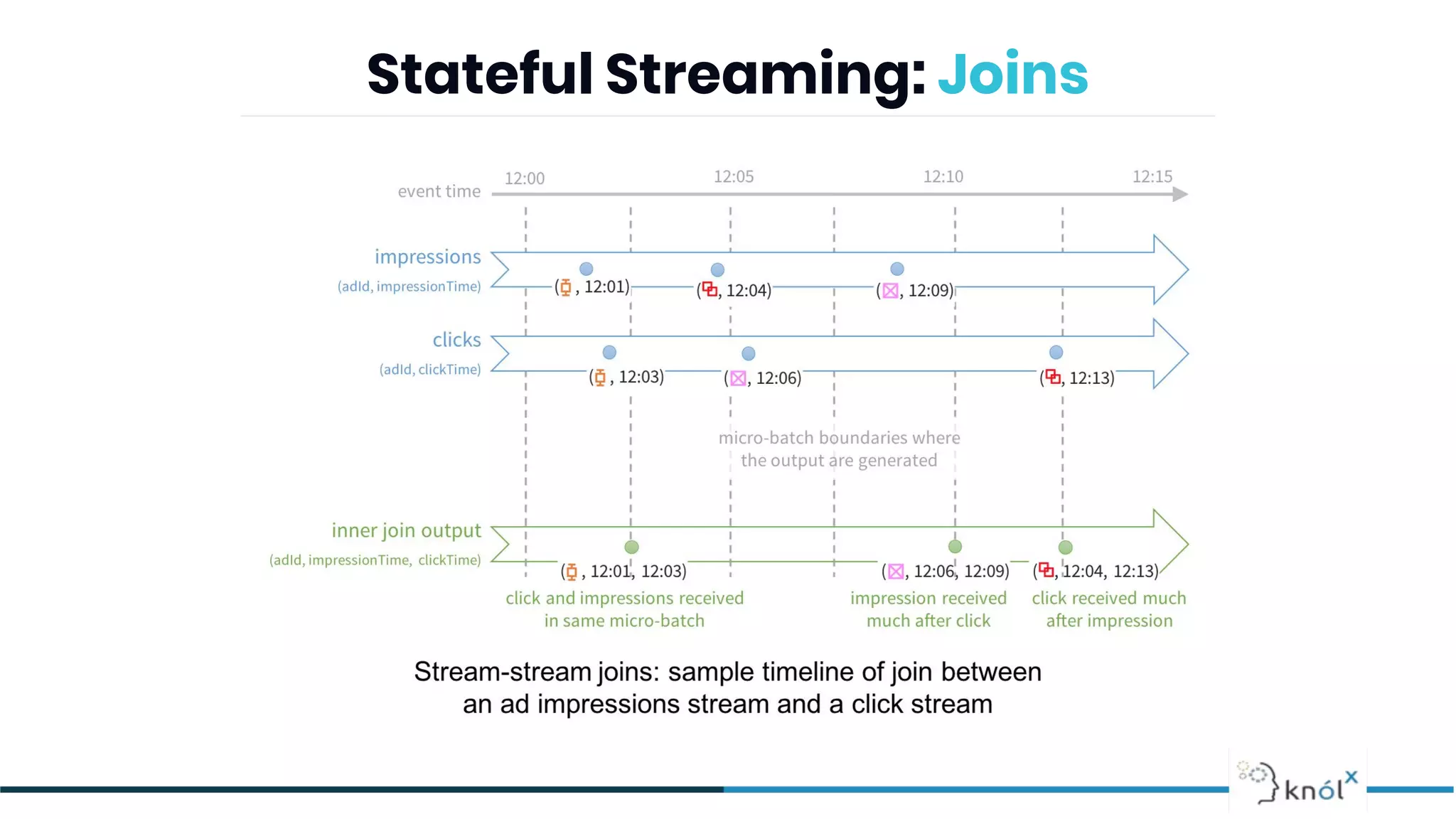
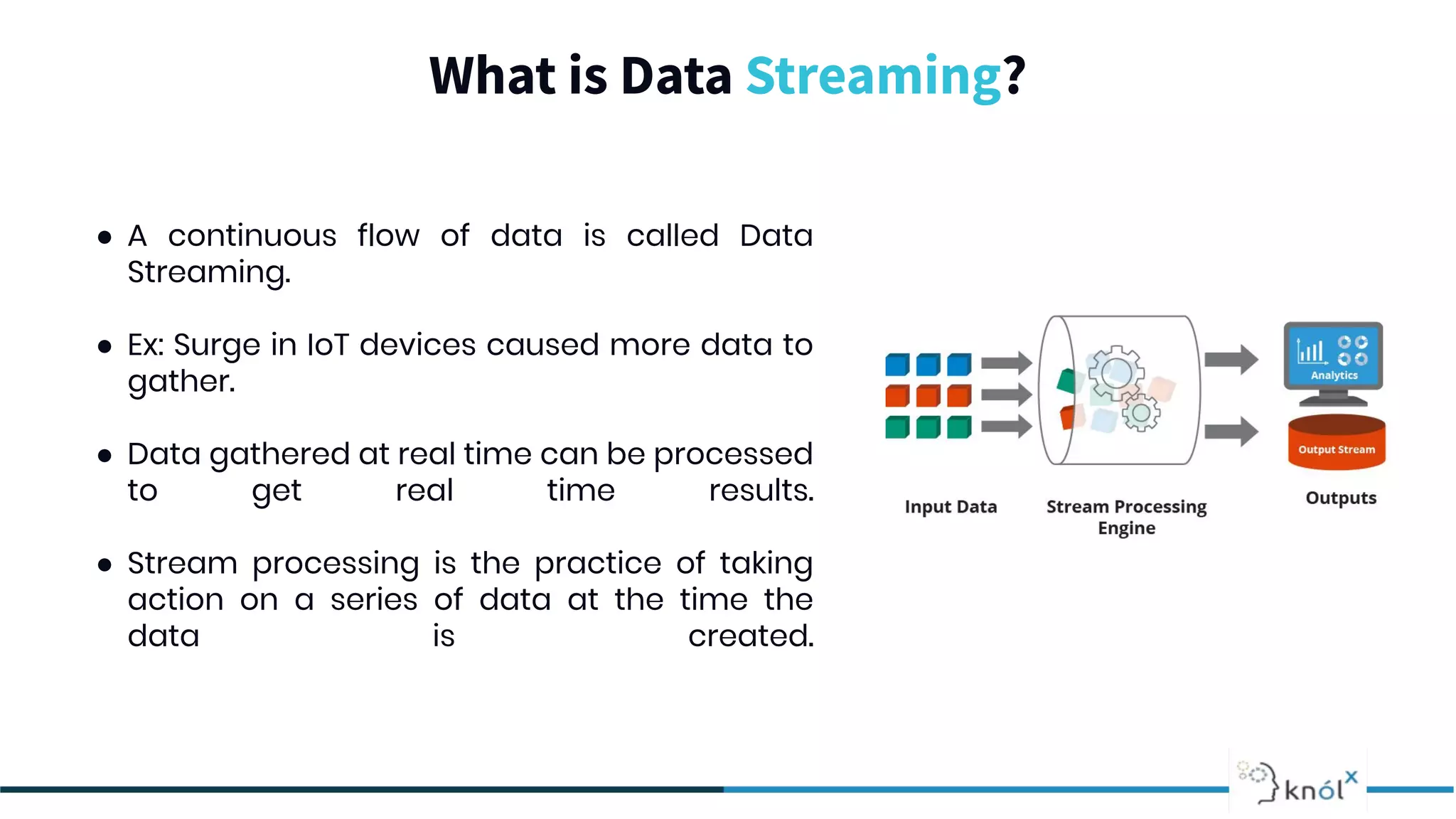
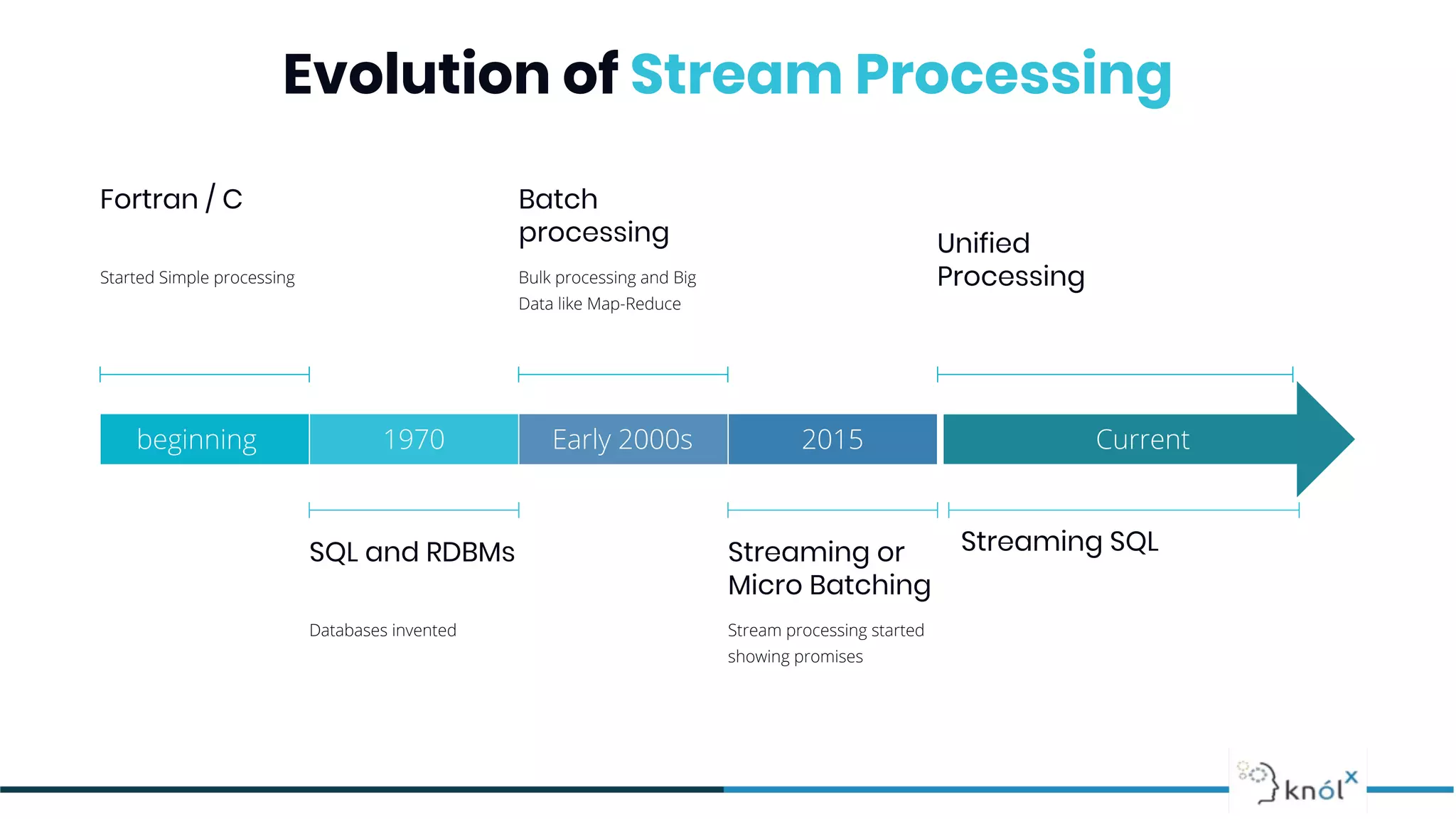
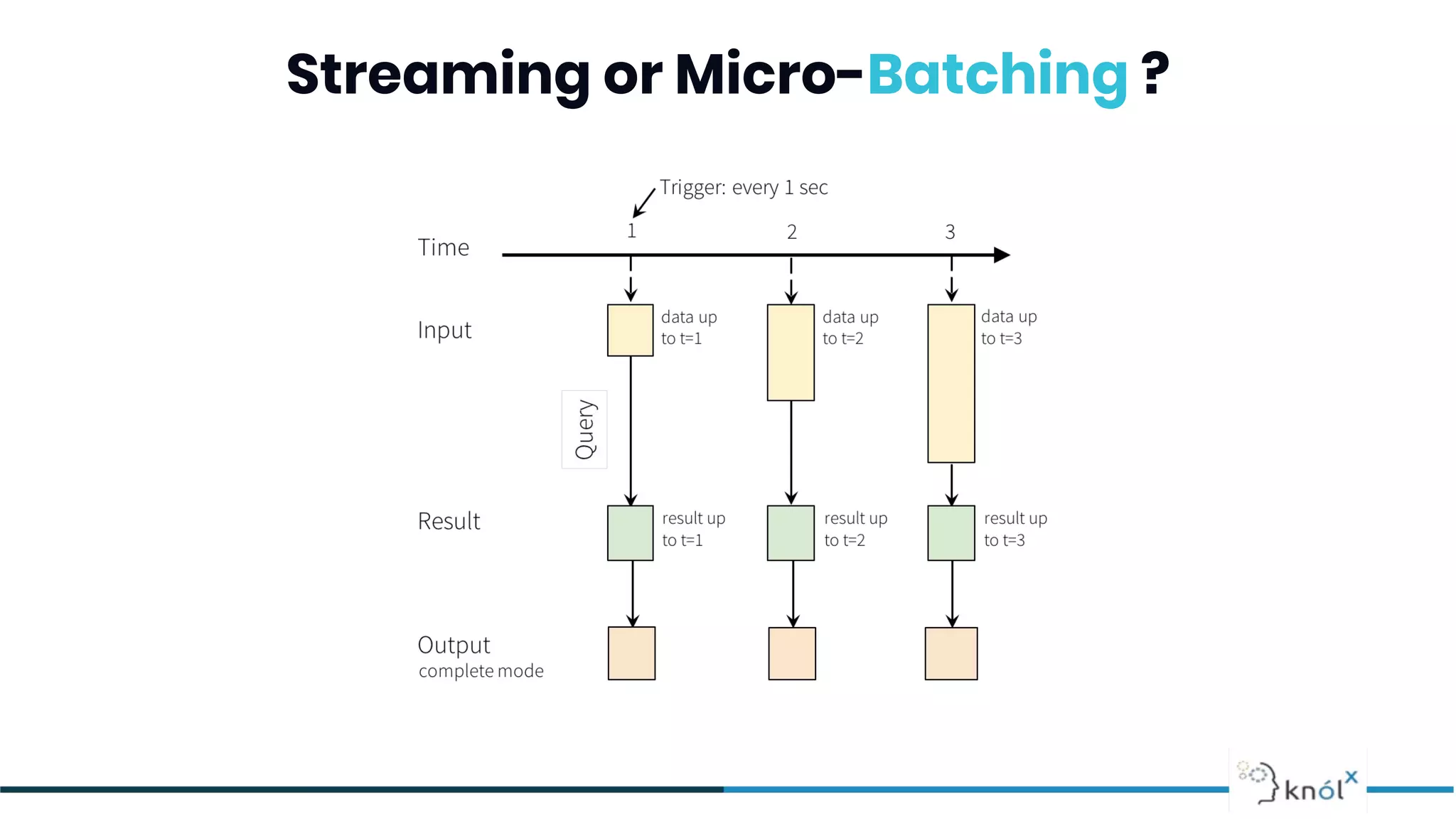
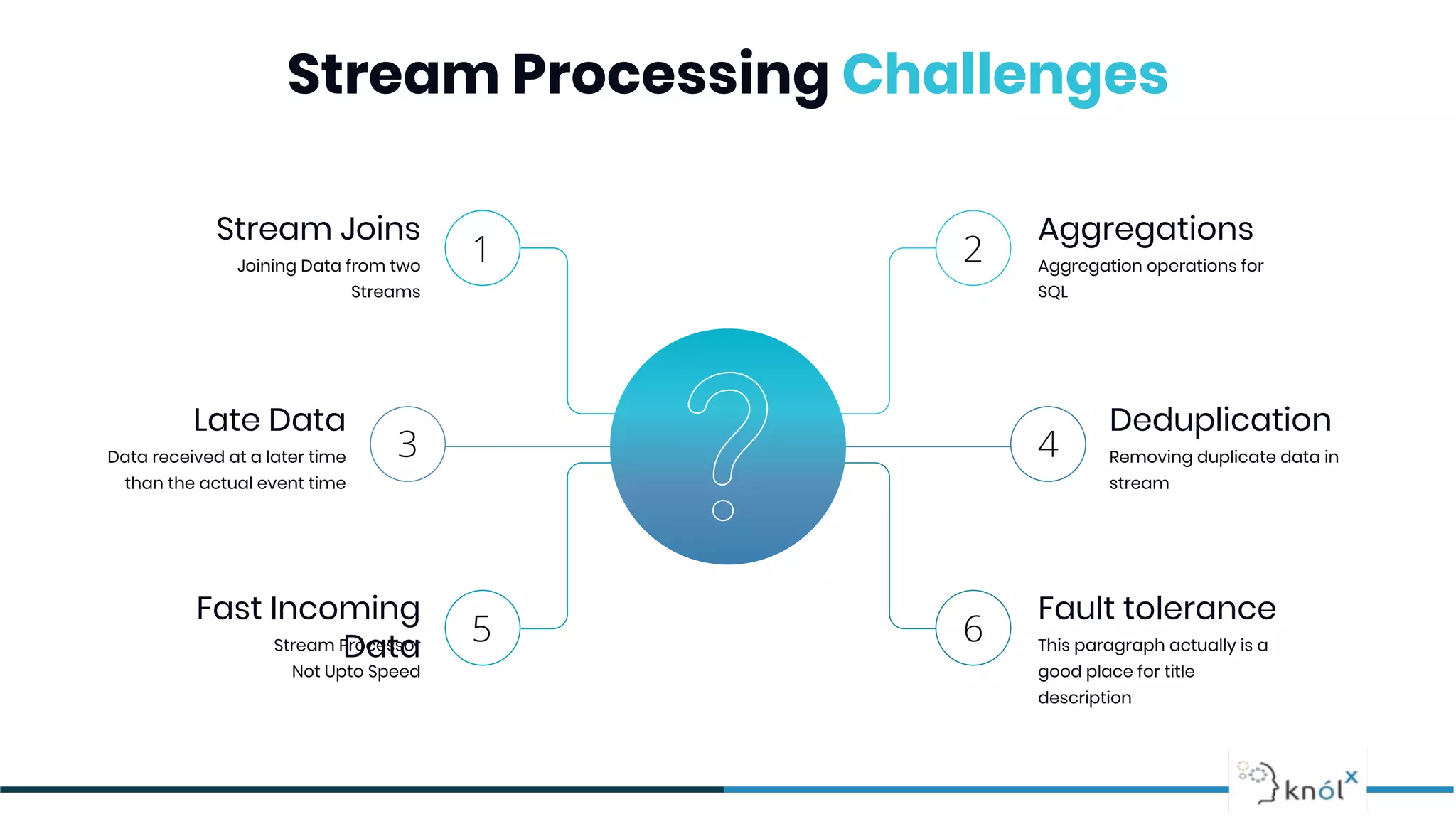
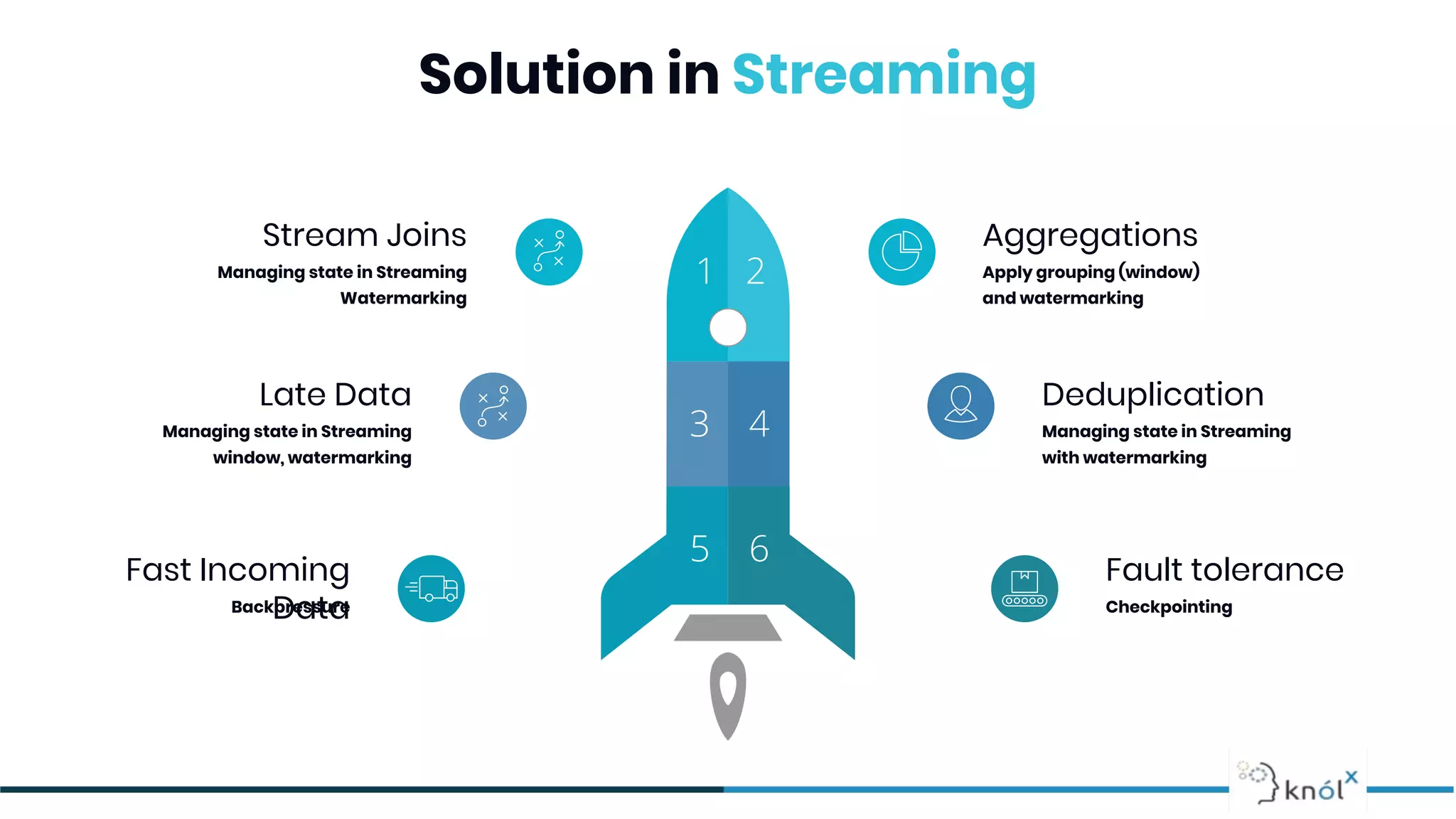
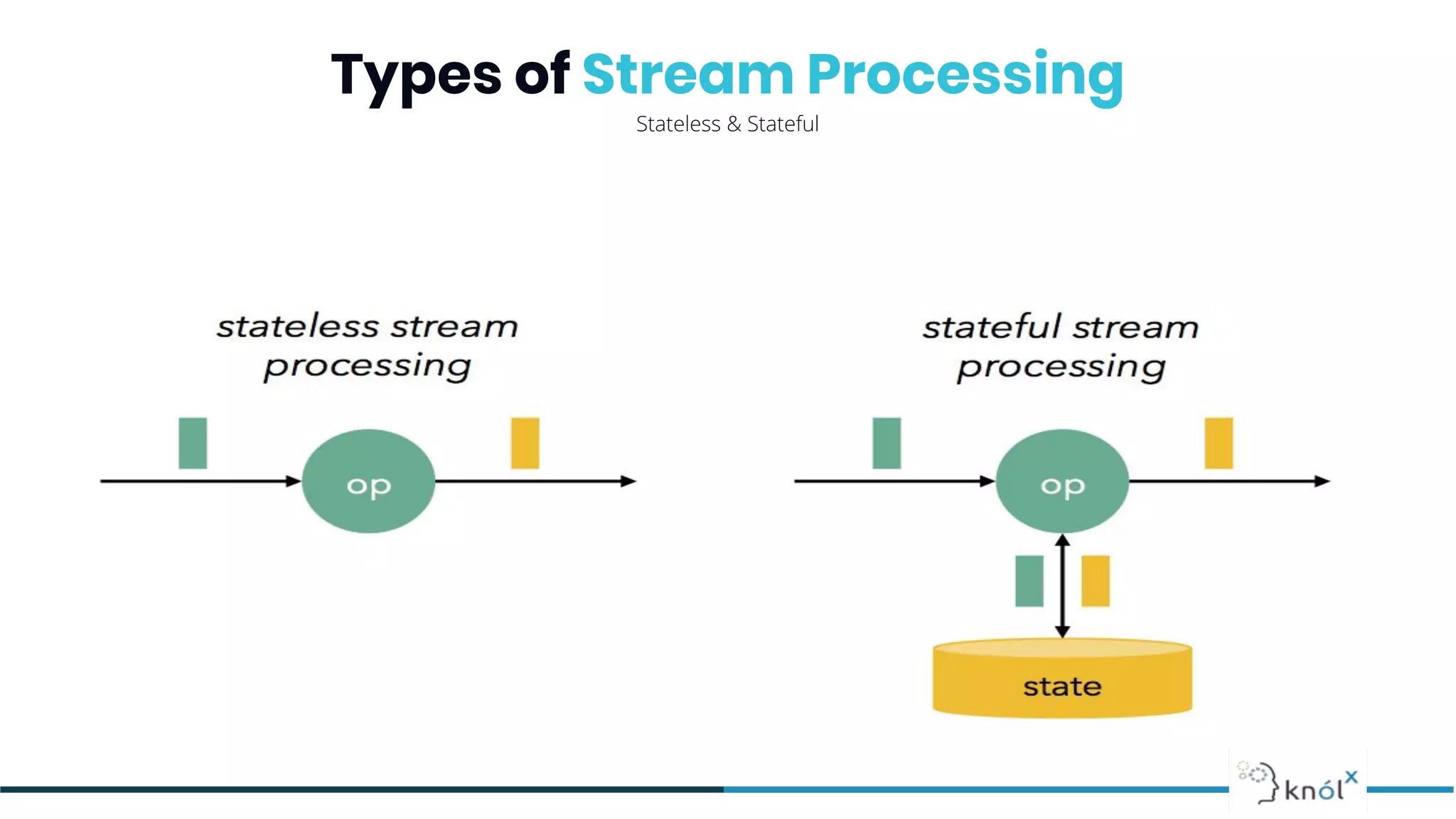
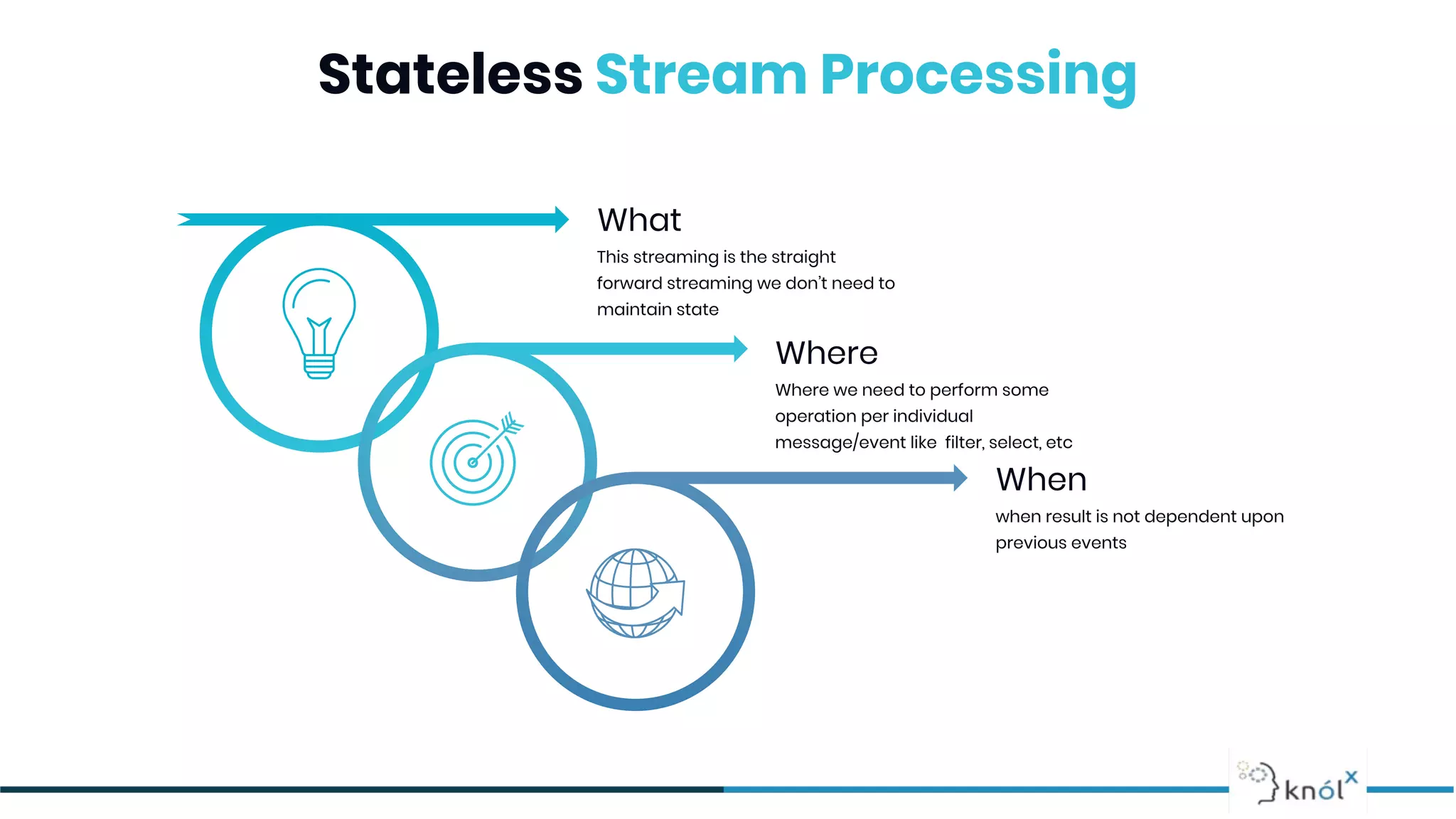
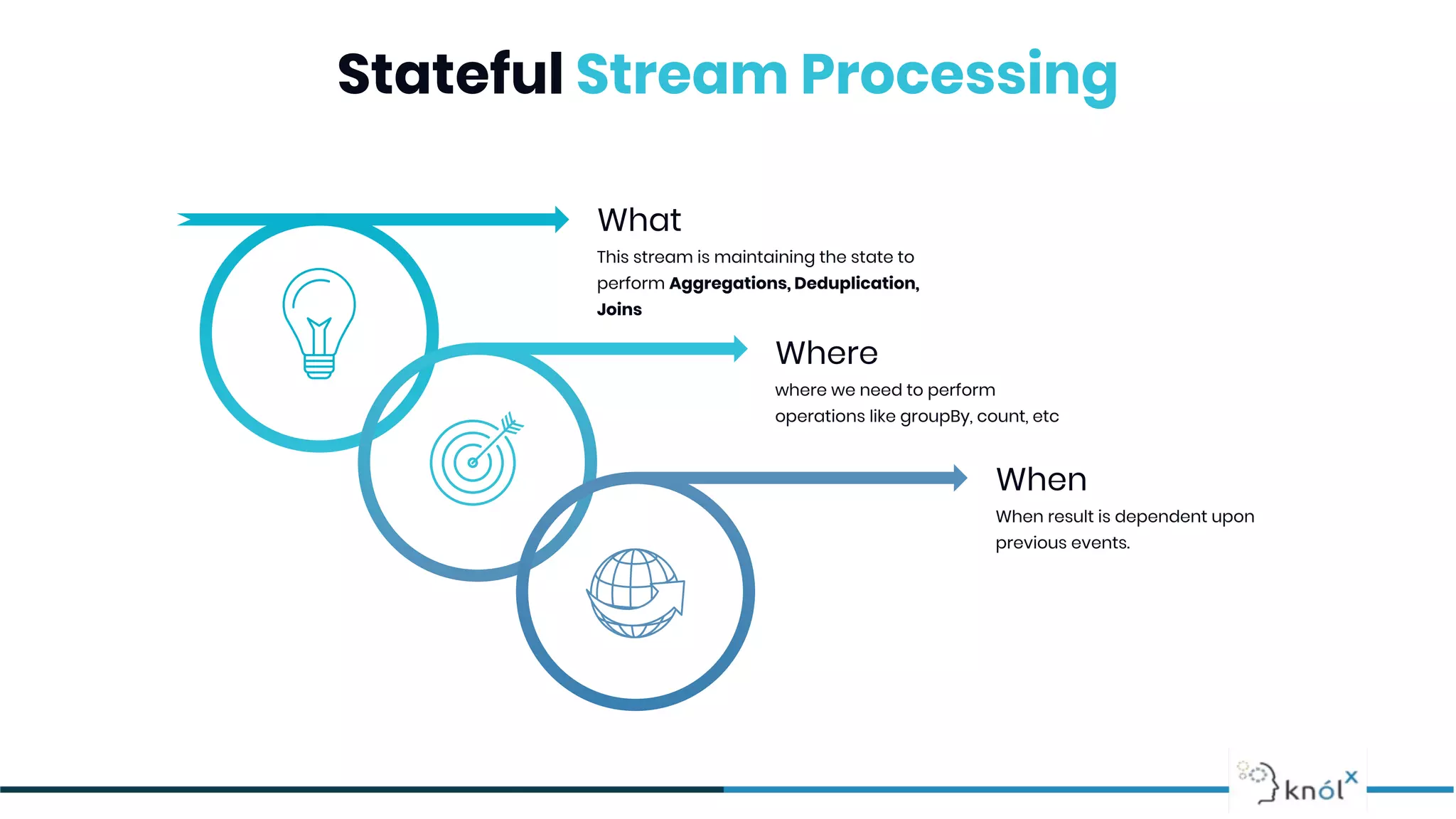
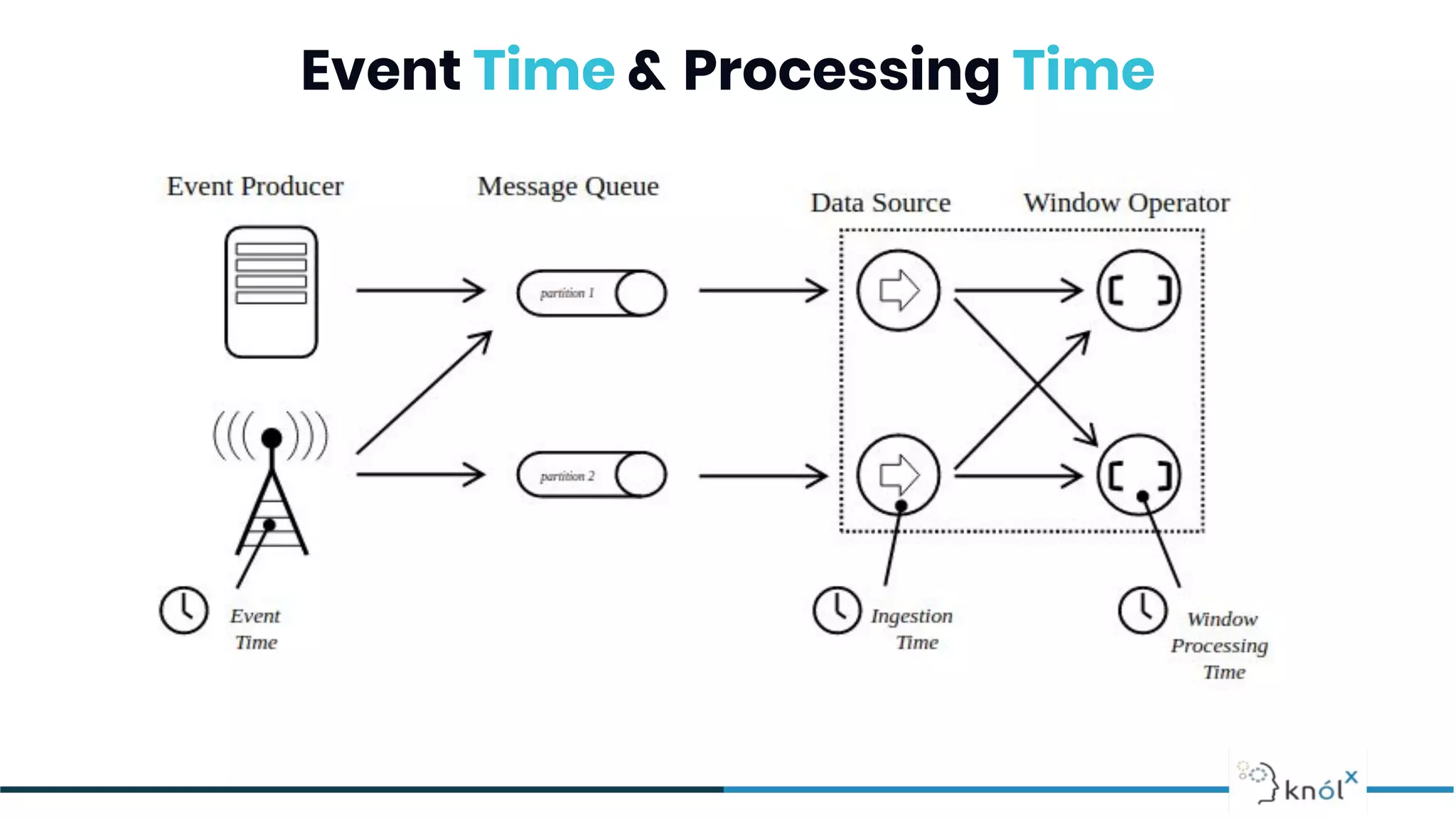
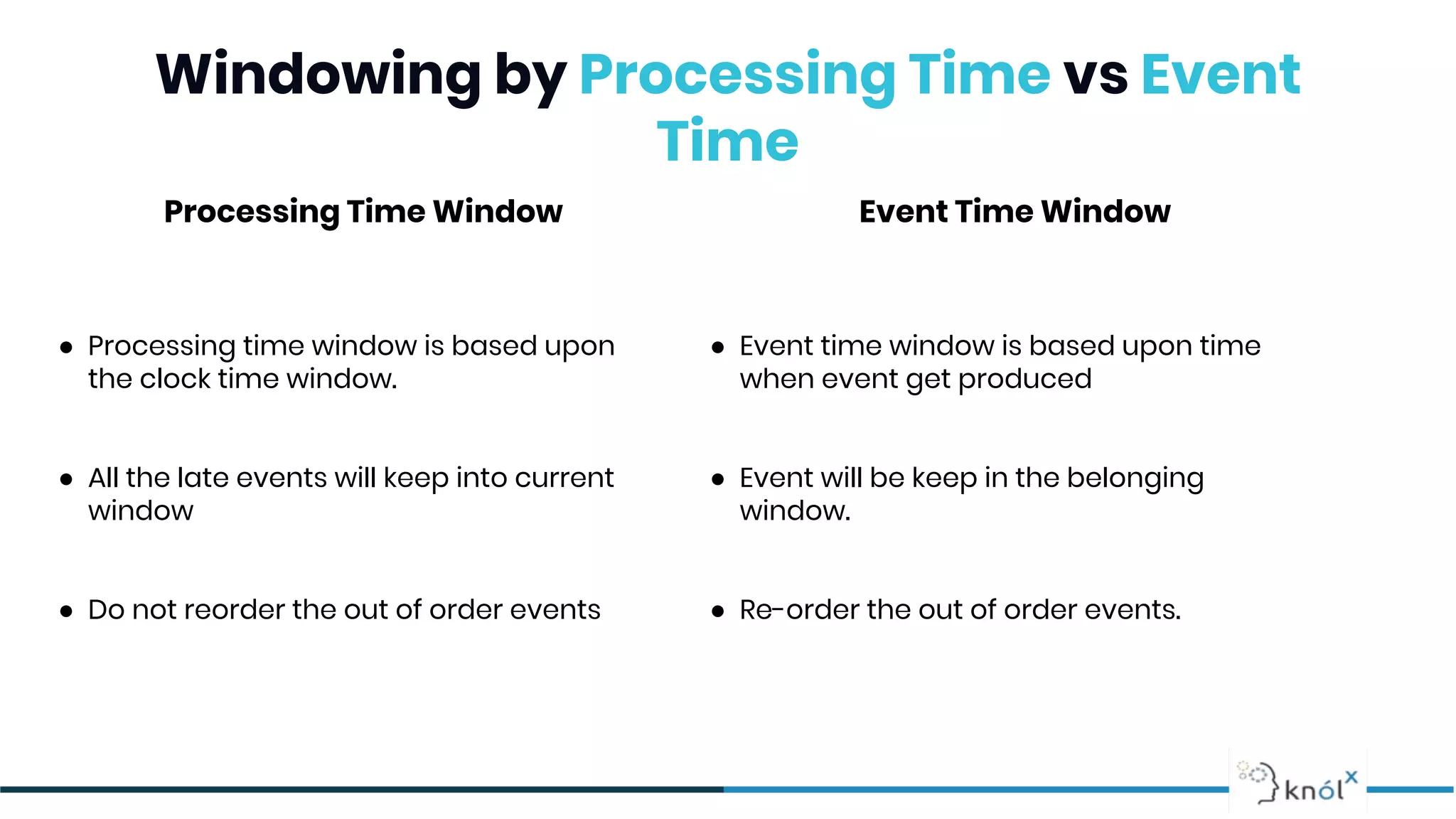
The document provides an overview of data streaming, its benefits, types, architectures, and challenges such as handling late data and deduplication. It details stateless and stateful stream processing methods, elaborating on aggregations, watermarking, and joins. Use cases are highlighted across various fields such as smart devices, trading, and analytics.




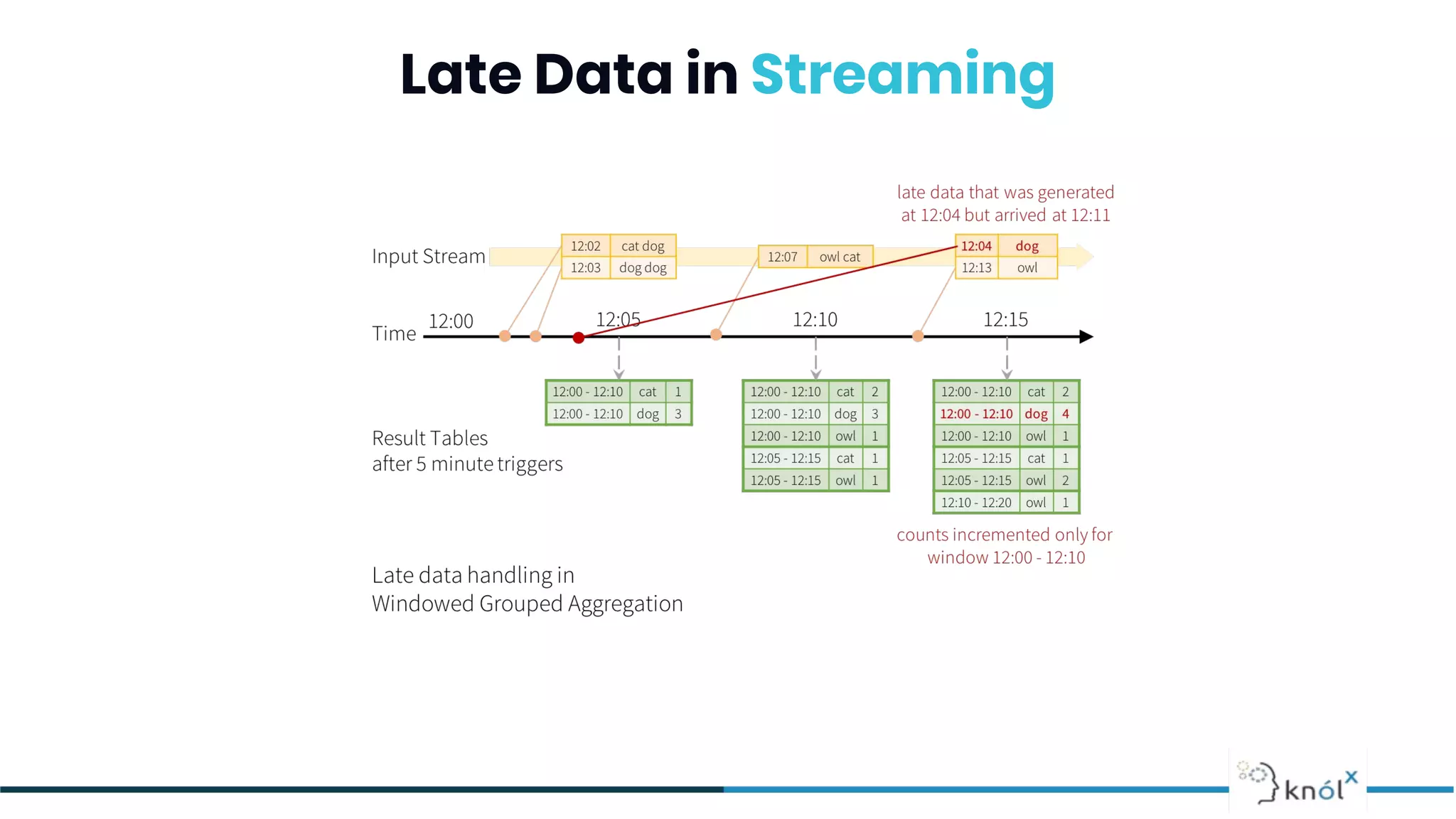


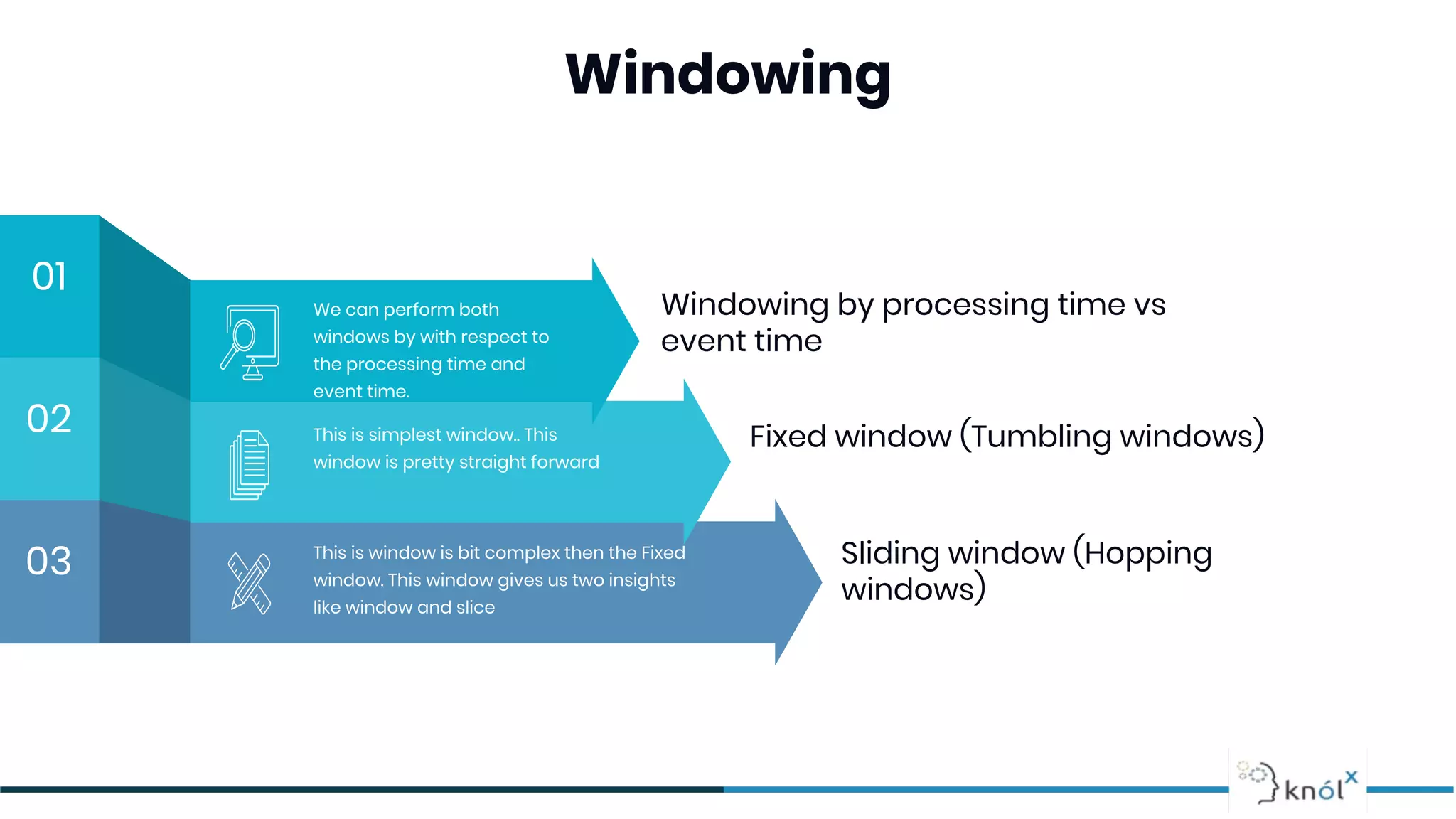
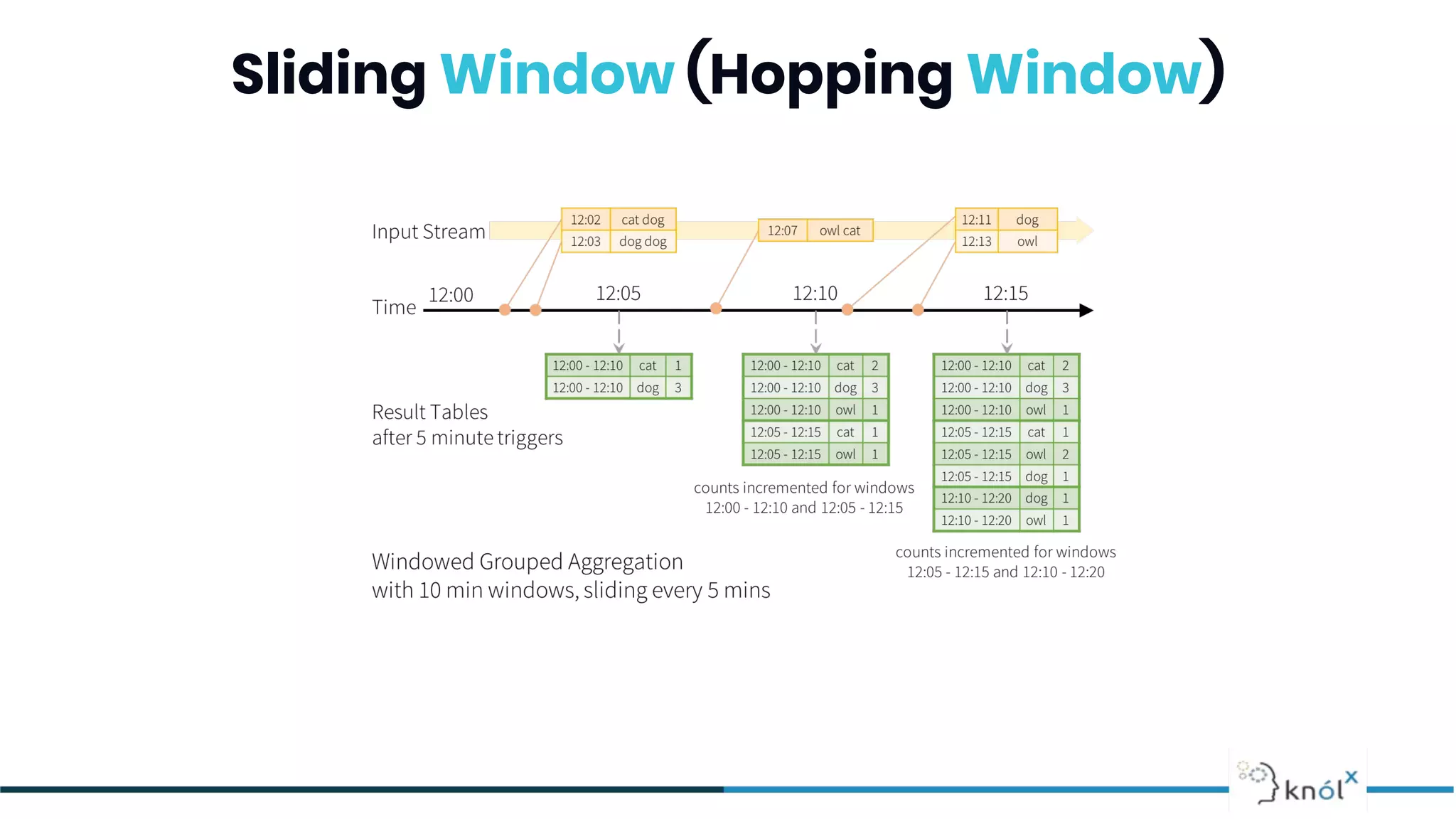
![Sliding Window (Hopping Window)
Sliding: windows have fixed length, but are separated by a time
interval (step) which can be smaller than the window length. Typically
the window interval is a multiplicity of the step. Each event belongs to
a number of windows ([window interval]/[window step]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letsgettoknowstreaming-200519072100/75/Let-s-get-to-know-the-Data-Streaming-27-2048.jpg)