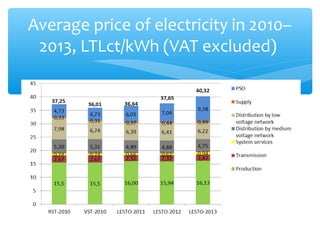
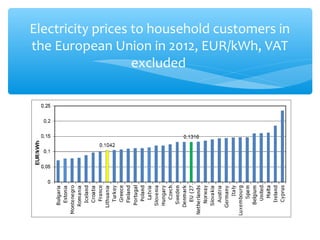
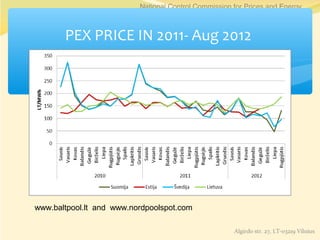
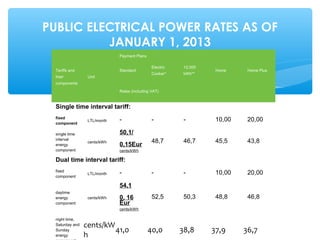
This document summarizes the key changes in Lithuania's electricity market since liberalization. It discusses how the market opened up to competition between electricity suppliers starting in 2010. Consumers now have a choice between fixed-price contracts and market-based variable prices. They receive separate invoices from their electricity supplier and the grid operator LESTO. The document addresses common consumer concerns, clarifying that suppliers are only responsible for electricity supply while LESTO remains responsible for grid infrastructure. Overall, liberalization has introduced competition that offers consumers more choice between suppliers and pricing options.