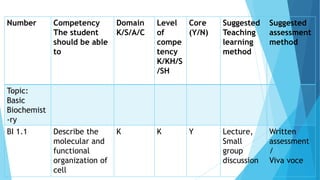
This document provides guidance on writing an effective lesson plan. It begins by defining a lesson plan and its importance in mapping out content, time management, and assessment. Key elements of an effective lesson plan are then outlined, including anticipatory sets, learning objectives, standards, the body of the lesson, checking for understanding, closure, and independent practice. An example lesson plan is also provided following this structure with objectives, content delivery methods, and durations for each section. In the end, participants are asked to work in groups to develop their own lesson plan based on a provided competency.