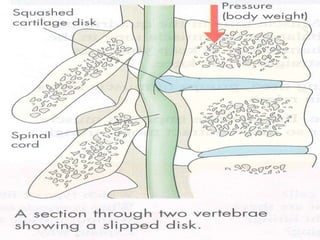
This document discusses the skeletal system, specifically the vertebral column and the effects of exercise. It defines the vertebral column as being made up of 33 bones that provide posture, movement, stability and protection. It identifies the different regions of the vertebral column (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx) and number of bones in each. Short term effects of exercise include increased synovial fluid and cartilage swelling, while long term effects involve increased bone density, strength and mineral storage.