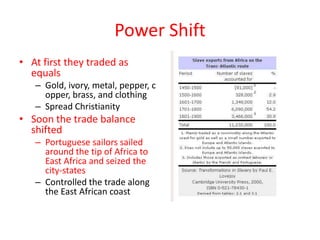
1) Europeans initially traded with West African kingdoms like Ghana and Mali for gold and other resources. However, the relationship shifted to one of enslavement as Europeans began capturing and forcibly transporting Africans across the Atlantic (known as the Middle Passage).
2) The Atlantic slave trade lasted from the 1500s to the 1800s. After it ended, European powers still sought to control Africa for its land and resources, dividing the continent among themselves through colonization.
3) The slave trade had devastating impacts on Africa, including depopulation as its healthiest people were taken, the halting of social and economic progress, and lasting effects from the division and rule of European colonial powers.