Embed presentation
Download to read offline


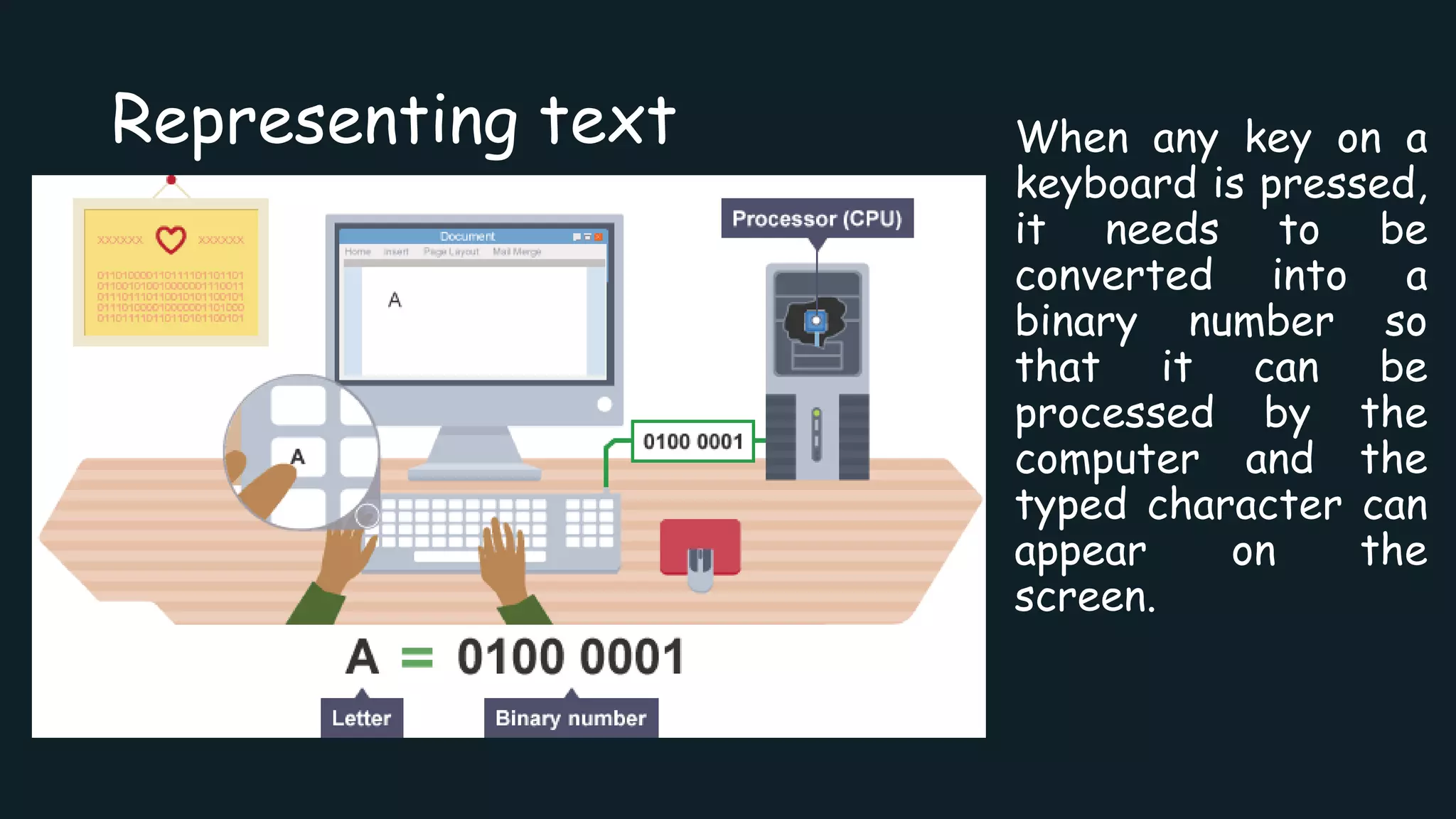
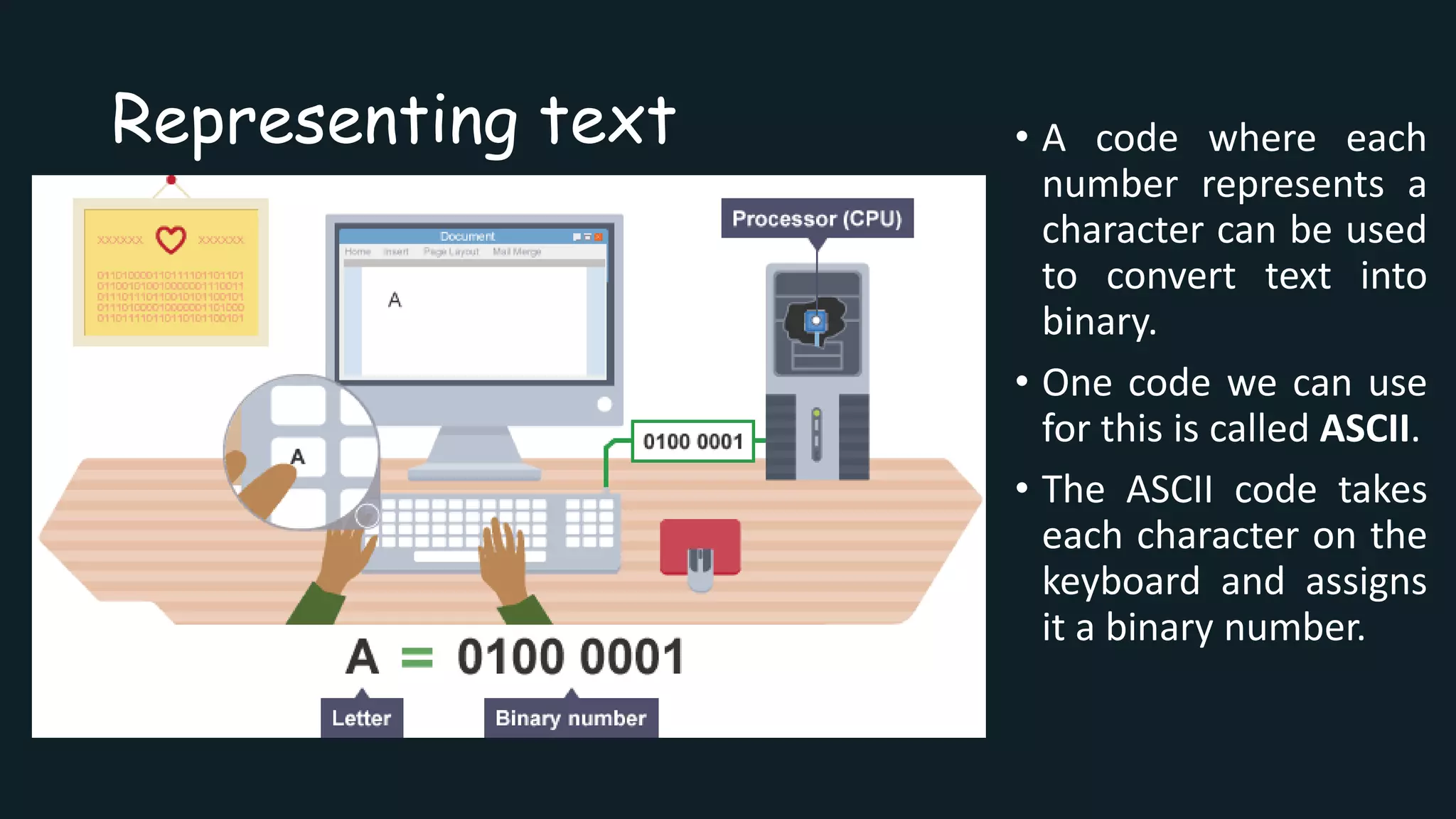



Text is represented in computers using character encoding schemes like ASCII and Unicode that assign a unique binary number to each character. When a key is pressed on a keyboard, the character is converted to its binary number using the encoding scheme so it can be processed and displayed by the computer. ASCII encodes the most common English characters using 7-bit binary numbers, but is limited to 128 characters total. Unicode was created to support encoding characters for more languages using 16-bit or 32-bit binary representations.





