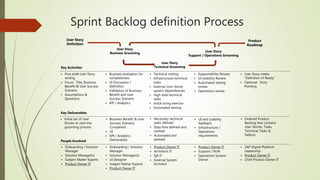
The document outlines a comprehensive approach for transitioning to an agile framework using LeSS (Large Scale Scrum), highlighting the necessary steps like team workshops, backlog management, and agile ceremonies. It discusses business and technical challenges encountered during the adoption process, emphasizing the importance of cross-functional teams and effective communication. Key deliverables include a structured product backlog, continuous improvement practices, and automation in deployment processes to enhance overall efficiency and quality.