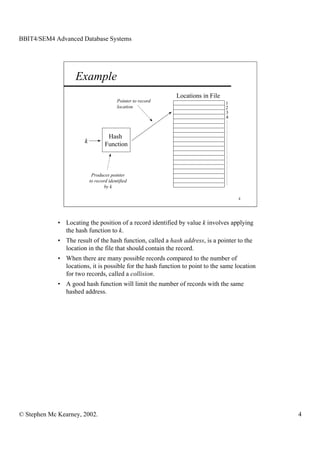
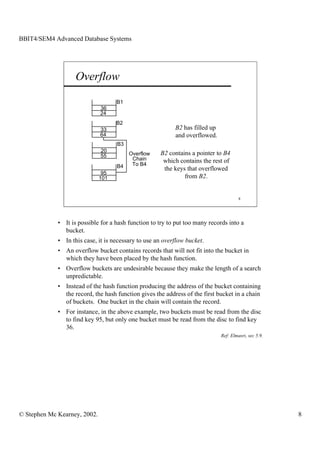
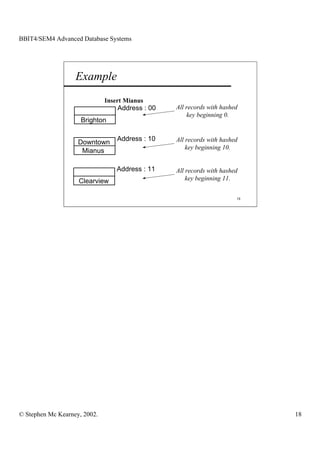
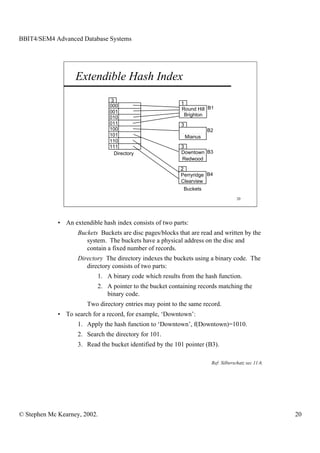
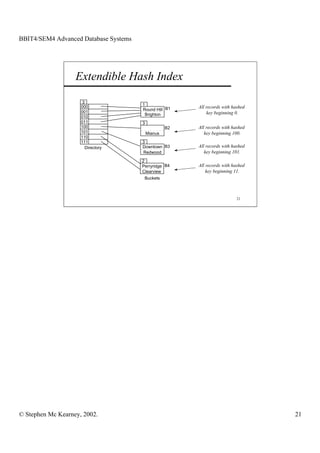
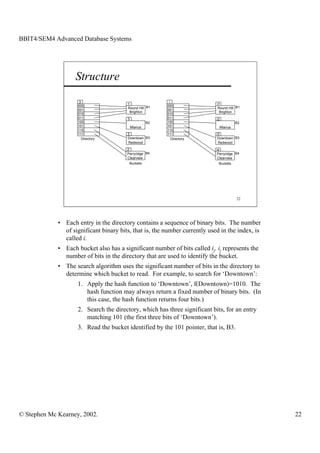
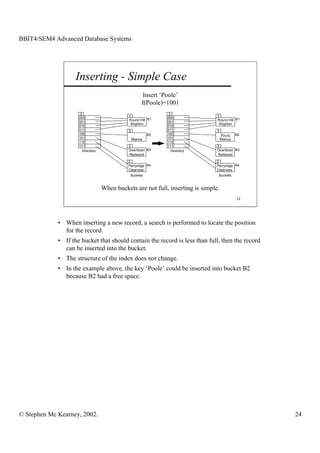
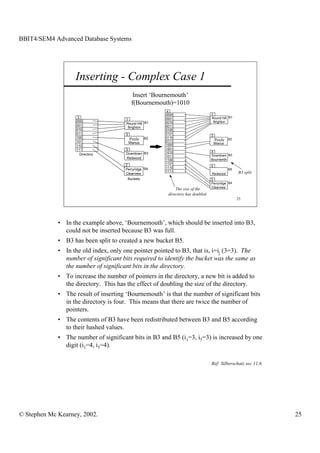
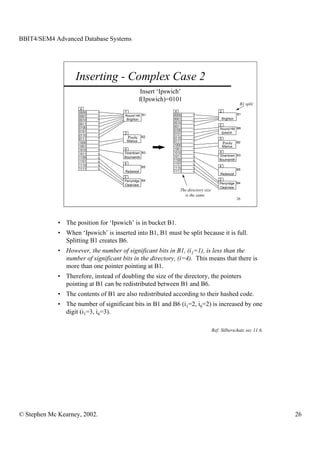
This document discusses extendible hashing and static hashing. Static hashing uses a single hash function to map records to fixed storage locations, which can cause collisions when the number of records exceeds locations. Extendible hashing solves this by allowing the number of locations to increase by splitting buckets as needed. It uses a binary hash function and binary addressing to map records across a hierarchical structure of buckets that can expand efficiently.