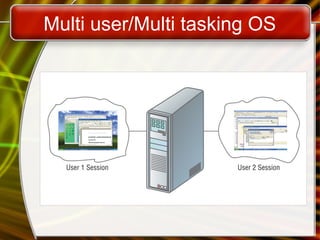
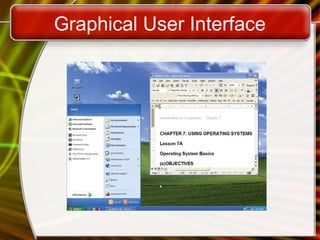
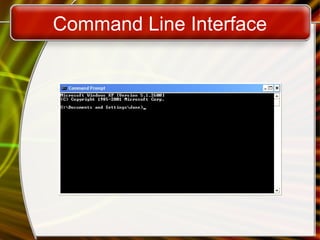
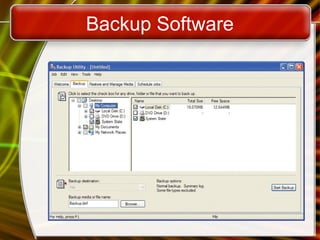
The document provides an overview of operating systems, detailing their functions such as user interfaces, program execution, hardware management, and organized file storage. It categorizes different types of operating systems, including real-time, single user/single tasking, and multi-user/multi-tasking systems, and explains user interfaces like graphical and command line interfaces. Additionally, it discusses utilities that enhance operating systems, including backup software, antivirus programs, and firewalls.