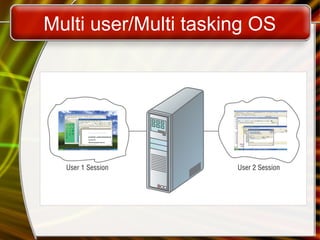
The document provides an overview of operating systems, detailing their functions, types, and user interfaces. It covers single-user and multi-user systems, hardware management, file organization, and utilities that enhance operating systems, such as antivirus software and firewalls. The text emphasizes the significance of consistent storage solutions and user interaction methods like graphical and command line interfaces.